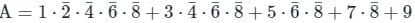Test: Priority Encoders - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Priority Encoders
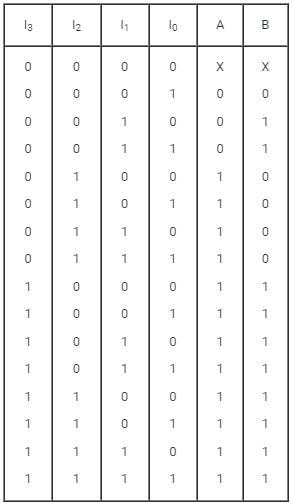
Consider the output A and B with I0, I1, I2 and I3 as input and ‘A’ and ‘B’ as output,
A = I2 + I3
B = I̅2 I1 + I3
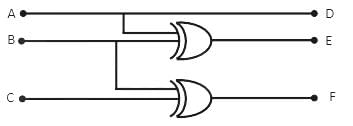
The above circuit is:
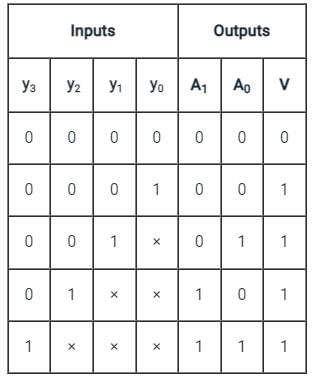
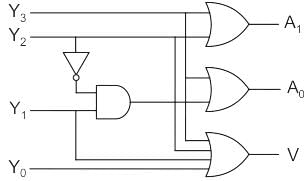
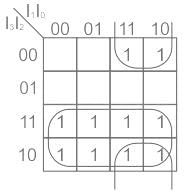
The truth table of logic function F is given below
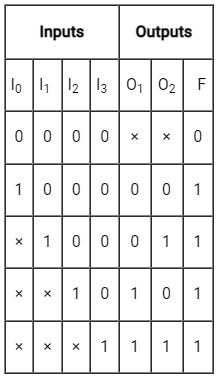
If in the truth table F = 1 if and only if the input is valid. What function does the truth table represent?
If two inputs are active on a priority encoder, which will be coded on the output?
What is a four-line to two-line priority encoder with active HIGH inputs and outputs, with priority assigned to the higher-order data input line?
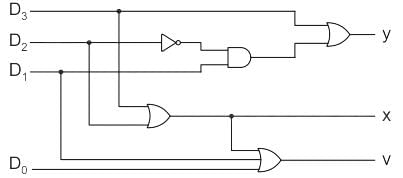
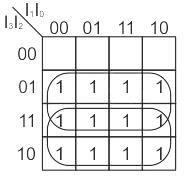
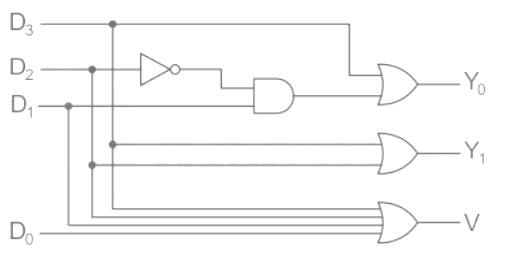
Determine the type of circuit shown in figure below consider y0 and y1 to be don’t care condition when all inputs are zero.
In a 8-bit ripple carry adder using identical full adders, each full adder takes 34 ns for computing sum. If the time taken for 8-bit addition is 90 ns, find time taken by each full adder to find carry