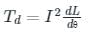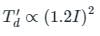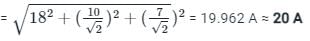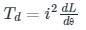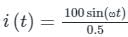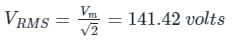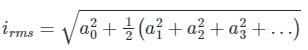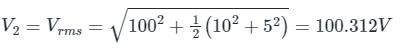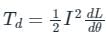Test: Moving Iron Instruments - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Moving Iron Instruments
Which of the below is an application of paper chromatography?
Which of the following is NOT a valid advantage of moving iron instruments?
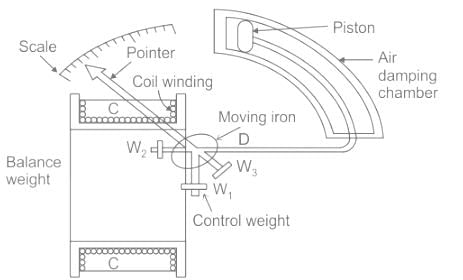
The deflecting torque of a moving iron instrument is
If the current through a moving iron instrument is increased by 20%, what is the percentage increase in the deflection torque?
Current flowing in a circuit is i = (18 + 10sinωt + 7sin2ωt). A moving iron ammeter is connected in the circuit to measure this current. The reading of the meter will be approximately
In a moving iron instrument, the deflecting torque is:
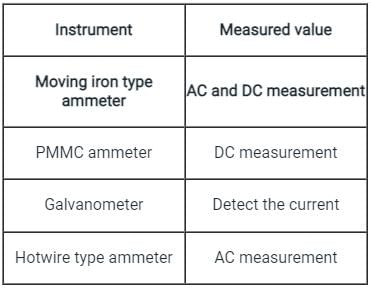
A moving iron type instrument is used for the measurement of:-
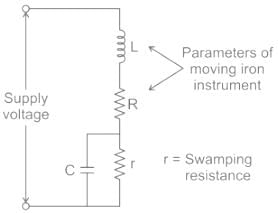
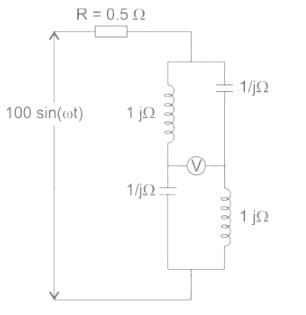
The reading of the voltmeter (rms) in volts, for the circuit shown in the figure is –
A dc voltage with ripple is given by V(t) = [100 + 10 sin (ωt) - 5 sin (3ωt)] volts. Measurements of this voltage v(t), made by moving-coil and moving-iron voltmeters, show, readings of V1 and V2 respectively. The value of V2 - V1, in volts, is _________.
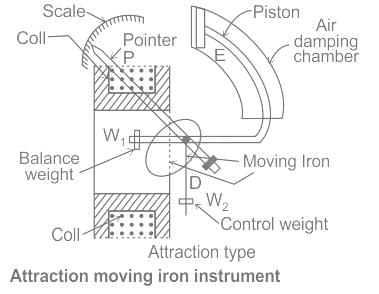
Which of the following types of instruments depends on the iron vane's attraction to the current-carrying coil to be measured for proper operation?
Error due to change in frequency in moving iron instruments may be reduced by using a/an: