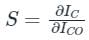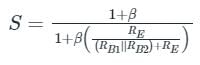Practice Questions: Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) - 2 - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Practice Questions: Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) - 2
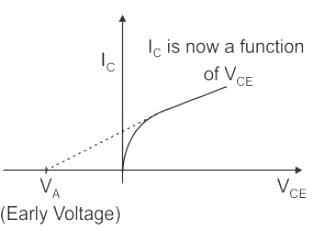
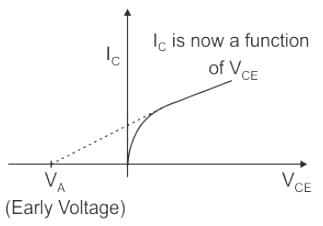
The early effect in a bipolar junction transistor is caused by
A transistor when connected in CE mode has:
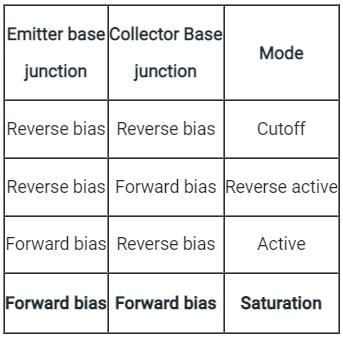
What is the region of operation of the bipolar junction transistor (BJT) where both the junctions are forward biased?
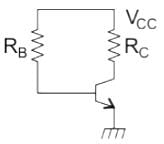
The effect of reduction in effective base width due to an increase in reverse voltage of BJT is
The ___________ region has the highest area in the transistor.
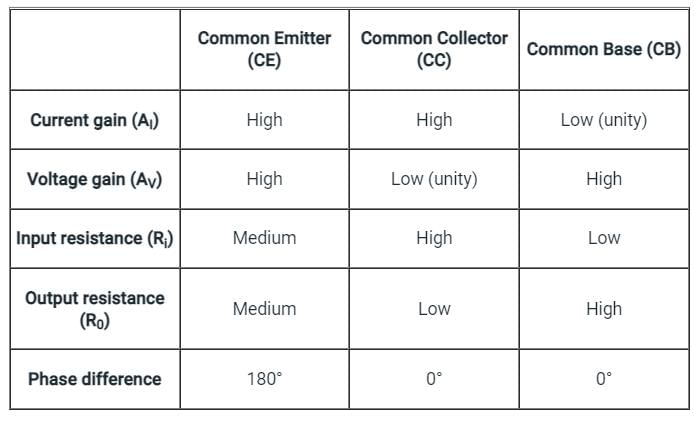
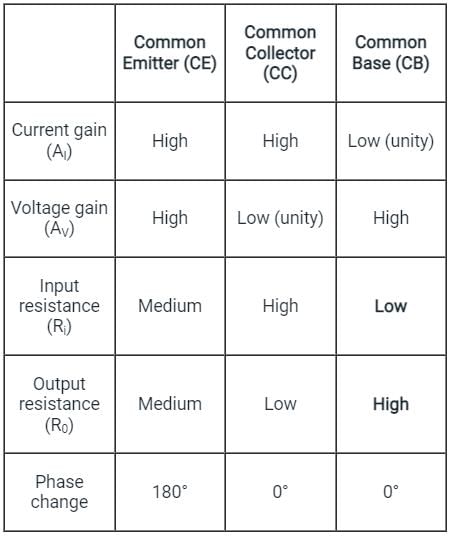
Which among the following configuration has High current and High voltage gain?
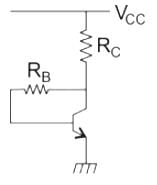
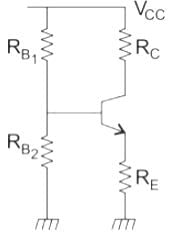
In which of the following bias circuit, the stability factor is dependent upon RC?
Which one is disadvantage of impedance matching?
A BJT with β = 50 has a base to collector leakage current ICBO of 2.5 μA. If the transistor is connected in CE configuration, the collector current for IB = 0 is
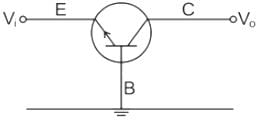
What is the input voltage and output current in the common base configuration of a transistor?