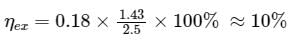Test: Laser - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Laser
The following is not a candidate material for Laser source in Fiber Optics
A Ruby Maser is preferred to Ammonia Maser for microwave amplification because it has:
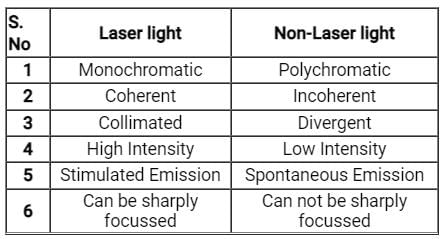
Which of the following are advantages of LASER over LED?
a) Higher bandwidth and higher data rate
b) Higher output power
c) Longer lifetime
d) Cheap
Select the correct answer:

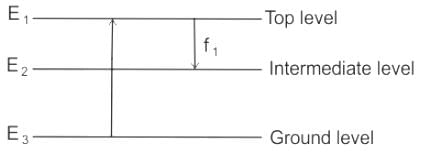
The figure represents, which of the following important property of LASER.
The total efficiency of an injection laser with a GaAs active region is 18%. The voltage applied to the device is 2.5 V and the bandgap energy for GaAs is 1.43 eV. The external power efficiency of the device is
Laser beam is highly intense, monochromatic and coherent, and can be used in monochromatic light and the experiments for the phenomenon of _________.
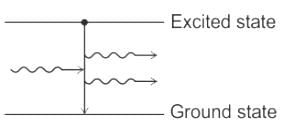
Which process gives the laser its special properties as an optical source?
A semiconductor laser crystal of length 5 cm, refractive index 1.8 is used as an optical source. Determine the frequency separation of the modes.