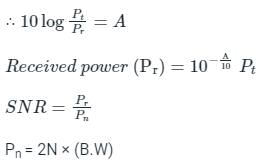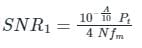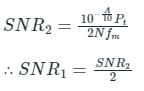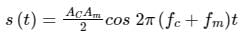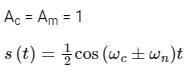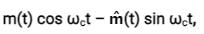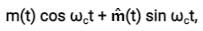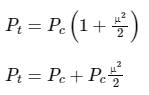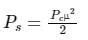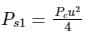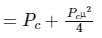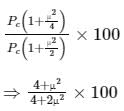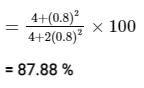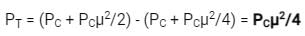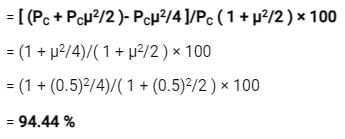Test: SSBSC (Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier) Transmission - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: SSBSC (Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier) Transmission
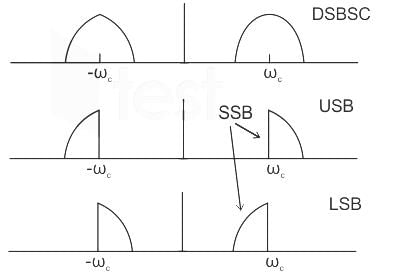
Which of the following modulation scheme is most bandwidth efficient?
Direction: Two statements are given. Based on the given information, choose the correct answer.
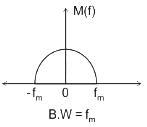
Statement-I: For the same message signal, the pre-detection SNR is double in the case of conventional practical AM modulation, than that in the case of SSB.
Statement-II: The AM signal bandwidth is double as compared to SSB signal bandwidth.
Statement-II: The AM signal bandwidth is double as compared to SSB signal bandwidth.
The signal m(t) = cos(ωmt) is SSB (single side-band) modulated with a carrier cos(ωct) to get s(t). The signal obtained by passing s(t) through an ideal envelope detector is
Which of the following analog modulation scheme requires the minimum transmitted power and minimum channel bandwidth?
What should be the bandwidth figure of signal to noise ratio for SSB?
What is the percentage of power saved when an 80% modulated wave is transmitted over SSB-SC which was initially transmitted over AM?
The modulation technique that takes the lowest bandwidth among the given
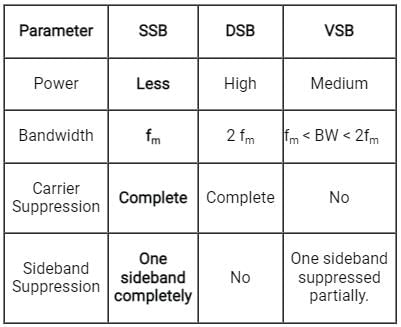
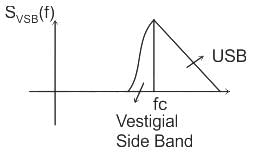
Which of the following is NOT one of the types of amplitude modulation?
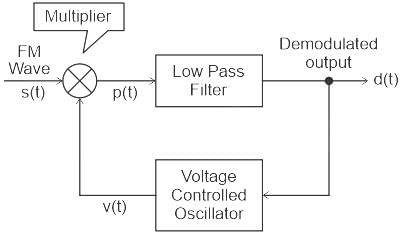
Which of the following circuits could NOT be used as demodulator of SSB?
How much percentage power will be saved when the carrier and one of the sidebands are suppressed in an AM wave modulated to a depth of 50% ?