Chemistry Exam > Chemistry Tests > Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes - Chemistry MCQ
Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes - Chemistry MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes
Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes for Chemistry 2025 is part of Chemistry preparation. The Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Chemistry exam syllabus.The Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes MCQs are made for Chemistry 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes below.
Solutions of Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes questions in English are available as part of our course for Chemistry & Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes solutions in
Hindi for Chemistry course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Chemistry Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes | 10 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for Chemistry preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Chemistry Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes - Question 1
For the central metal atom in a complex, coordination number is
Detailed Solution for Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes - Question 1
Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes - Question 2
The square planar geometry is based on
Detailed Solution for Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes - Question 2
Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes - Question 3
The minimum number of monodentate ligand required for the formation of square planar and tetrahedral complex is
Detailed Solution for Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes - Question 3
Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes - Question 4
The zero magnetic moment of octahedral K2NiF6 is due to
Detailed Solution for Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes - Question 4
Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes - Question 5
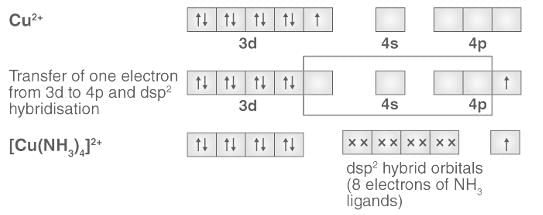
Cuprammonium ion has ___________ shape.
Detailed Solution for Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes - Question 5
Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes - Question 6
Which orbital would form a more stronger bond if both of them have identical stability?
Detailed Solution for Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes - Question 6
Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes - Question 7
The p-orbital is in the shape of a _____________
Detailed Solution for Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes - Question 7
Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes - Question 8
According to VBT, the formation of a stable bond requires _____________
Detailed Solution for Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes - Question 8
Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes - Question 9
Valence Bond Theory was developed in the year?
Detailed Solution for Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes - Question 9
Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes - Question 10
The s-orbital does not show preference to any direction because _____________
Detailed Solution for Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes - Question 10
Information about Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Valence Bond Approach: structure, color & magnetic properties of CN Complexes , EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF