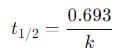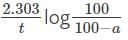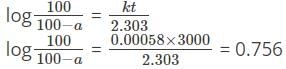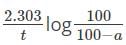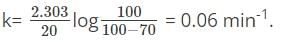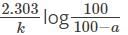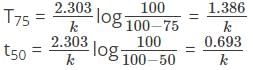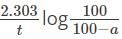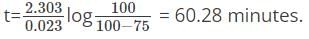Test: Zero, First, Second and Third Order reactions - Chemistry MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Zero, First, Second and Third Order reactions
A first-order reaction is 50 percent complete in 30 minutes. Calculate the time taken for completion of 87.5 percent of the reaction.
For the reaction X → Y + Z, the rate constant is 0.00058 s-1. What percentage of X will be decomposed in 50 minutes?
first-order reaction was 70 percent complete in 20 minutes. What is the rate constant of the reaction?
What is the formula to calculate the time taken for the completion of a zero-order reaction?
For a certain reaction the values of Arrhenius factor and Activation energy are 4 x 1013 collision/sec and 98.6KJ/mol at 303K. Calculate the rate constant if reaction is 1st order?( R=8.341mol-1K-1)
A zero-order reaction is 25% complete in 30seconds. What time does it take for 50% completion?
The rate constant of a reaction is 0.01s-1, how much time does it take for 2.4 mol L-1 concentration of reactant reduced to 0.3 mol L-1?
What is the time required for 75 percent completion of a first-order reaction?
What is the time taken to complete 75 percent of the reaction if the rate of the first-order reaction is 0.023 min-1?
The half-life of a given reaction is doubled if the initial concentration of the reactant is doubled. What is the order of the reaction?
The decomposition of N2O5 in CCl4 solution was studied. N2O5 → 2NO2 + 1/2O2. The rate constant of the reaction is 6.2 x 10-4 sec-1. Calculate the rate when the concentration of N2O5 is 1.25 molar.
What is the integrated rate equation for a first order reaction?
What time does it take for reactants to reduce to 3/4 of initial concentration if the rate constant is 7.5 x 10-3 s-1?
The unit of the rate constant of a zero-order reaction and second-order reaction is same.
The unit of rate constant of a first-order reaction is s-1.


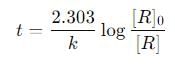
 using the relation:
using the relation: