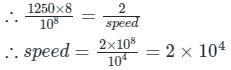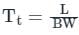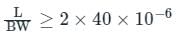Test: Access Control Protocols - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Access Control Protocols
For increasing the battery life in mobile system which type of access technology are used?
Which of the following is, "A device used to connect two separate Ethernet networks into one extended Ethernet."?
A slotted ALOHA network transmits 200-bit frames using a shared channel with a 200 Kbps bandwidth. Find the throughput of the system, if the system (all stations put together) produces 250 frames per second:
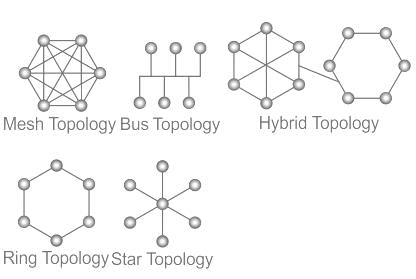
Which of the following is not a topology in computer field?
Devices on one network can communicate with devices on another network via a-
Consider a CSMA/CD network that transmits data at a rate of 100 Mbps (108 bits per second) over a 1 km (kilometer) cable with no repeaters. If the minimum frame size required for this network is 1250 bytes, what is the signal speed (km/sec) in the cable?
The third-generation mobile phone are digital and based on
A network has a data transmission bandwidth of 20 × 106 bits per second. It uses CSMA/CD in the MAC layer. The maximum signal propagation time from one node to another node is 40 microseconds. The minimum size of a frame in the network is ______bytes.
For increasing the battery life in mobile system which type of access technology are used?