Test: Data Analysis - 1 - SAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Data Analysis - 1
If data has been recorded using technical media, which among the following is a necessary step on the way to its interpretation?
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: In order to ensure authenticity, a researcher has to indicate original sources from which data are called.
Statement II: In data analysis and interpretation the researcher has to evince the necessary rigour and appropriateness of procedures.
In the light of the above statements, Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
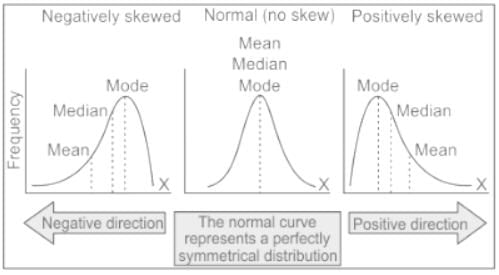
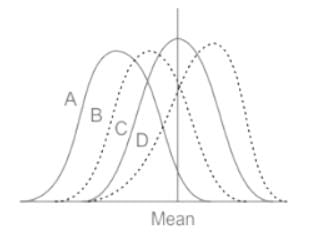
Which one of the following frequency distribution is negatively skewed?

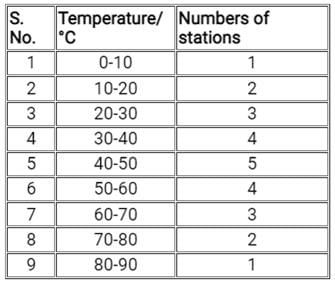
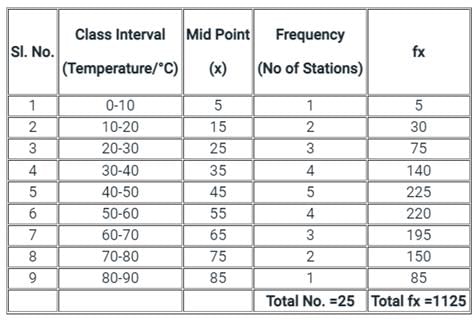
Answer the following question on the basis of above table
The average temperature in the region is
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: Use of multivariate statistics in social research has increased due to the availability of statistical software.
Statement II: Multivariate statistics are easier to comprehend as compared to the bi‐variate statistics.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
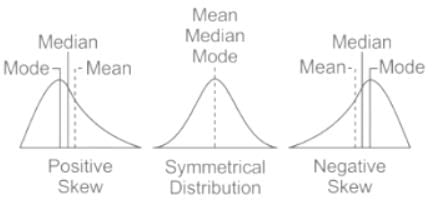
A university teacher administers a self-made test for the summative evaluation of his/her students. The distribution of scores of students is found to be positively skewed.
What inference he/she should make about the difficulty level of this test?
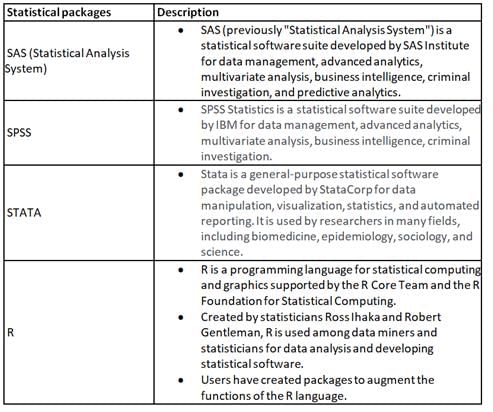
Which among the following are statistical packages?
A. SPSS
B. SAS
C. ANOVA
D. STATA
E. R
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Given below are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R
Assertion A: The value of correlation coefficient is in the range of ‐1 to +1.
Reason R: Correlation between two variables doesn't help in predicting the value of a variable even if we know the value of another variable.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
When the researcher does not know the identity of the experimental and placebo groups, the study is termed as
At the stage of data analysis in which quantitative techniques have been used by a researcher, the evidence warrants the rejection of Null Hypothesis (H0). Which of the following decisions of the researcher will be deemed appropriate?