Test: Arrays - 2 - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Arrays - 2
What is the output for the given program?
int sum(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
return sum;
}
main()
{
int arr[] = {12, 30, 40, 15};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << sum(arr, n);
return 0;
}
int sum(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
return sum;
}
main()
{
int arr[] = {12, 30, 40, 15};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << sum(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Find the output of the following program
int main()
{
int i; int arr[6]={1};
for(i=0;i<6;i++)
{
printf("%d",arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}
A two-dimensional array named Arr is with the range Arr[10........20, 25......45]. The base address of the array is 10 and the size of each element is 2 bytes. What will be the location of Arr[15][30] using column major order?
If integer requires two bytes space, then what will be the size of the following 'C’ array?
int array[3][4]=(0);
What is the output of the following Java code?
public class array
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int []arr = {1,2,3,4,5};
System.out.println(arr[2]);
System.out.println(arr[4]);
}
}
Consider the following ANSI C program.
#include
int main()
{
int arr[4][5];
int i, j;
for(i =0; i<4; i++)
{
for (j =0; j<5; j++)
{
arr [i][j] = 10 * i + j;
}
}
print("%d", *(arr[1] + 9));
return 0;
}
Q. What is the output of the above program?
The correct syntax for initialization of a one-dimensional array is _________.
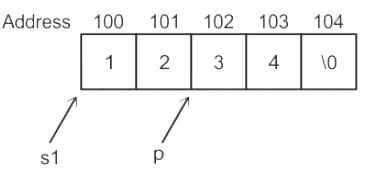
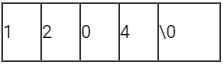
Consider the following C program segment.
#include
int main()
{
char s1[7] = "1234", *p;
p = s1 + 2; *p = ‘0’;
printf("%s", s1);
}
Q. What will be printed by the program?
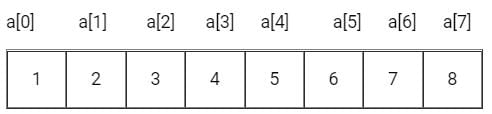
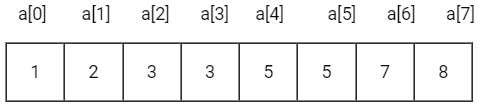
Consider the following program of ‘C’
main ( )
{
static int a [ ] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 } ;
int i;
for(i = 2; I < 6; ++i)
a [a [i] ] = a [i];
for (I = 0; I < 8 ; ++i)
printf (“%d”, a[i]);
}
Q. The output of the program is :