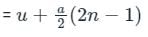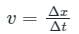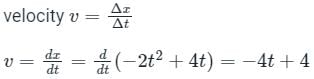Test: Instantaneous Velocity and Speed - ACT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Instantaneous Velocity and Speed
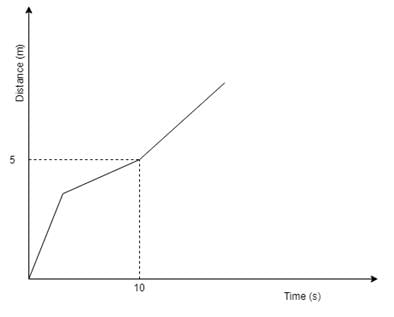
What is the velocity for a body following the graph below at 10s?

A car is moving in a spiral starting from the origin with uniform angular velocity. What can be said about the instantaneous velocity?
The trajectory of an object is defined as x = (t - 4)2, what is the velocity at t = 5?
Which of the following can be used to describe how fast an object is moving along with the direction of motion at a given instant of time?
What happen to the instantaneous velocity in a non-uniformly accelerated motion?
A ball is thrown up in the sky, at what position will the instantaneous speed be minimum?
Which of the following is the correct formula for instantaneous velocity?
A point is moving with uniform acceleration, in the eleventh and fifteenth seconds from the commencement it moves through 640 and 840 cms respectively, find its initial velocity, and the acceleration with which it moves?
In which of the following motion the net force on the body will be zero?
The position of a particle is given by x = -2t2 + 4t. How much time the particle will take to come in rest?