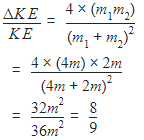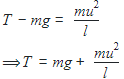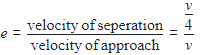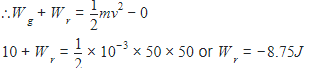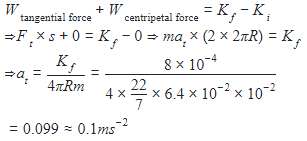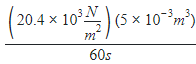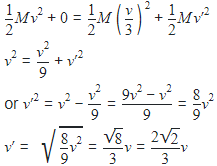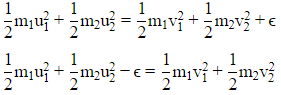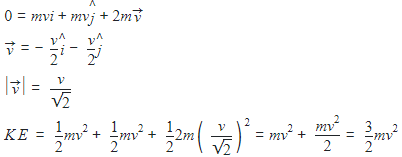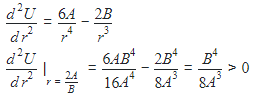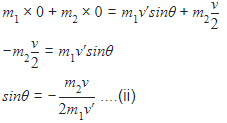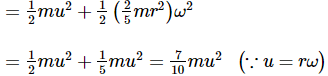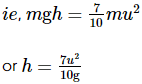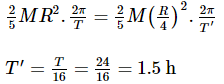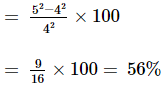NEET Minor Test - 2 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - NEET Minor Test - 2
An electric lift with a maximum load of 2000kg (lift + passengers) is moving up with a constant speed of 1.5ms−1. The frictional force opposing the motion is 3000N. The minimum power delivered by the motor to the lift in watts is : (g=10ms−2)
The distance covered by a body of mass 5g having linear momentum 0.3kgm∕s in 5s is:
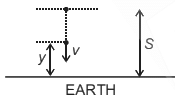
A particle is released from height S from the surface of the Earth. At a certain height its kinetic energy is three times its potential energy. The height from the surface of earth and the speed of the particle at that instant are respectively
Body A of mass 4m moving with speed u collides with another body B of mass 2m, at rest. The collision is head on and elastic in nature. After the collision the fraction of energy lost by the colliding body A is
A mass m is attached to a thin wire and whirled in a vertical circle. The wire is most likely to break when
A moving block having mass m, collides with another stationary block having mass 4m. The lighter block comes to rest after collision. When the initial velocity of the lighter block is v, then the value of coefficient of restitution (e) will be
Consider a drop of rain water having mass 1 g falling from a height of 1 km. It hits the ground with a speed of 50ms−1. Take 'g' constant with a value 10ms−2. The work done by the
(i) gravitational force and the
(ii) resistive force of air is
Two identical balls A and B having velocities of 0.5ms−1 and 0.3ms−1 respectively collide elastically in one dimension. The velocities of B and A after the collision respectively will be
A particle of mass 10 g moves along a circle of radius 6.4 cm with a constant tangential acceleration. What is the magnitude of this acceleration if the kinetic energy of the particle becomes equal to 8×10−4J by the end of the second revolution after the beginning of the motion?
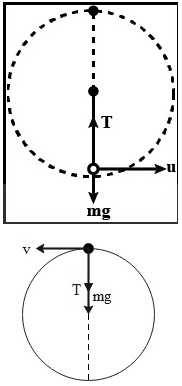
What is the minimum velocity with which a body of mass m must enter a vertical loop of radius R so that can complete the loop?
The heart of a man pump s 5 litres of blood through the arteries per minute at a pressure of 150 mm of mercury. If the density of mercury be 13. × 103kg/m3 and g=10m/s2 then the power of heart in watt is
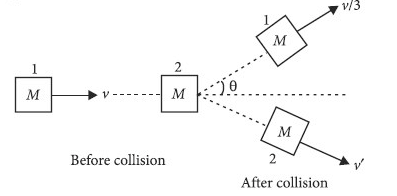
On a frictionless surface, a block of mass M moving at speed v collides elastically with another block of same mass M which is initially at rest. After collision the first block moves at an angle 0 to its initial direction and has a speed v/3. The second block's speed after the collision
Two particles of masses m1,m2 move with initial velocities u1 and u2.On collision, one of the particles get excited to higher level, after absorbing energy e. If final velocities of particles be v1 and v2 then we must have
A body of mass (4m) is lying in x-y plane at rest. It suddenly explodes into three pieces. Two pieces, each of mass (m) move perpendicular to each other with equal speeds (v). The total kinetic energy generated due to explosion is
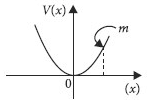
A particle with total energy E is moving in a potential energy region U(x). Motion of the particle is restricted to the region when
The potential energy of a particle in a force field is
![]()
where A and B are positive constants and r is the distance of particle from the center of the field. For stable equilibrium, the distance of the particle is
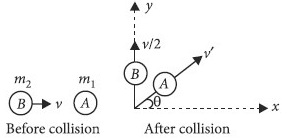
Two spheres A and B of masses m1 and m2 respectively collide. A is at rest initially and B is moving with velocity v and along x-axis. After collision B has a velocity v/2 in a direction perpendicular to the original direction. The mass A moves after collision in the direction
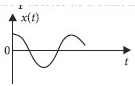
A particle of mass m is released from rest and follows a parabolic path as shown. Assuming that the displacement of the mass from the origin is small, which graph correctly depicts the position of the particle as a function of time?
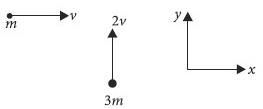
A mass m moving horizontally (along the x-axis) with velocity v collides and sticks to a mass of 3m moving vertically upward (along the y-axis) with velocity 2v. The final velocity of the combination is
A circular disc A of radius r is made from an iron plate of thickness t, and another circular disc B of radius 4r is made from an iron plate of thickness t/4. The relation between the moments of inertia IA and IB is
A solid homogeneous sphere is moving on a rough horizontal surface, partly rolling and partly sliding. During this kind of motion of the sphere
A sphere of mass m and radius r rolls on a horizontal plane without slipping with the speed u. Now, if it rolls up vertically, the maximum height it would attain will be
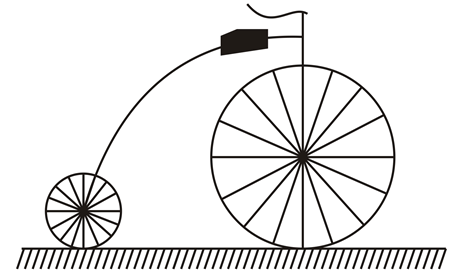
The wheels on the old-time bicycle shown in the diagram have radii of 60.0 cm. and 10.0 cm. If the larger wheel is rotating at 12.0 rad s-1, what is the angular speed of the smaller wheel?
If the earth shrinks such that its mass does not change but radius decreases to one-quarter of its original value then one complete day will take
A solid sphere rolls down two different inclined planes of same height, but of different inclinations. In both cases,
The angular speed of rotating rigid body is increased from 4ω to 5ω keeping moment of inertia constant. The percentage increase in its K.E is -
The radius of a solid sphere is R and its density D. When it is made to rotate about an axis passing through any diameter of sphere, expression for its moment of inertia is