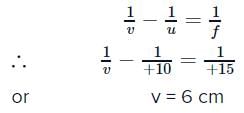JEE Advanced 2010 Paper - 2 with Solutions - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advanced 2010 Paper - 2 with Solutions
SECTION – I (Single Correct Choice Type)
This Section contains 6 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices A), B), C) and D) out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q. A block of mass 2 kg is free to move along the x-axis. It is at rest and from t = 0 onwards it is subjected to a time-dependent force F(t) in the x direction. The force F(t) varies with t as shown in the figure. The kinetic
energy of the block after 4.5 seconds is
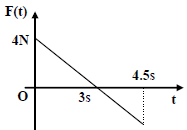
energy of the block after 4.5 seconds is
A uniformly charged thin spherical shell of radius R carries uniform surface charge density of σ per unit
area. It is made of two hemispherical shells, held together by pressing them with force F (see figure). F is
proportional to
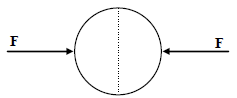
area. It is made of two hemispherical shells, held together by pressing them with force F (see figure). F is
proportional to
A tiny spherical oil drop carrying a net charge q is balanced in still air with a vertical uniform electric field
of strength 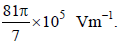 When the field is switched off, the drop is observed to fall with terminal
When the field is switched off, the drop is observed to fall with terminal
velocity 2 × 10−3 ms−1. Given g = 9.8 ms−2, viscosity of the air = 1.8 × 10−5 Ns m−2 and the density of oil =
900 kg m−3, the magnitude of q is
of strength
velocity 2 × 10−3 ms−1. Given g = 9.8 ms−2, viscosity of the air = 1.8 × 10−5 Ns m−2 and the density of oil =
900 kg m−3, the magnitude of q is
A Vernier calipers has 1 mm marks on the main scale. It has 20 equal divisions on the Vernier scale which
match with 16 main scale divisions. For this Vernier calipers, the least count is
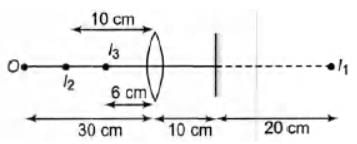
A biconvex lens of focal length 15 cm is in front of a plane mirror. The distance between the lens and the mirror is 10 cm. A small object is kept at a distance of 30 cm from the lens. The final image is
A hollow pipe of length 0.8 m is closed at one end. At its open end a 0.5 m long uniform string is vibrating
in its second harmonic and it resonates with the fundamental frequency of the pipe. If the tension in the
wire is 50 N and the speed of sound is 320 ms−1, the mass of the string is
SECTION –II (Integer Type)
This Section contains 5 questions. The answer to each question is a single-digit integer, ranging from 0 to 9.
Q. A large glass slab (μ = 5/3) of thickness 8 cm is placed over a point source of light on a plane surface. It is
seen that light emerges out of the top surface of the slab from a circular area of radius R cm. What is the
value of R?
Image of an object approaching a convex mirror of radius of curvature 20 m along its optical axis is
observed to move from m in 30 seconds. What is the speed of the object in km per hour ?
To determine the half life of a radioactive element, a student plots a graph of is the rate of radioactive decay at time t. If the number of radioactive nuclei of this element decreases by a factor of p after 4.16 years, the value of p is
A diatomic ideal gas is compressed adiabatically to of its initial volume. If the initial temperature of
the gas is Ti (in Kelvin) and the final temperature is aTi, the value of a is
At time t = 0, a battery of 10 V is connected across points A and B in the given circuit. If the capacitors have no charge initially, at what time (in seconds) does the voltage across them becomes 4 volt?
[take ln 5 = 1.6, ln 3 = 1.1]
SECTION –III (Paragraph Type)
This Section contains 2 paragraphs. Based upon each of the paragraphs 3 multiple choice questions have to be answered. Each of these questions has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Paragraphs for Question 12 To 14
When liquid medicine of density ρ is to be put in the eye, it is done with the help of a dropper. As the bulb on the top of the dropper is pressed, a drop forms at the opening of the dropper. We wish to estimate the size of the drop.
We first assume that the drop formed at the opening is spherical because that requires a minimum increase in its surface energy. To determine the size, we calculate the net vertical force due to the surface tension T when the radius of the drop is R. When the force becomes smaller than the weight of the drop, the drop gets detached from the dropper.
Q. If the radius of the opening of the dropper is r, the vertical force due to the surface tension on the drop of
radius R (assuming r << R) is
Paragraphs for Question 12 To 14
When liquid medicine of density ρ is to be put in the eye, it is done with the help of a dropper. As the bulb on the top of the dropper is pressed, a drop forms at the opening of the dropper. We wish to estimate the size of the drop.
We first assume that the drop formed at the opening is spherical because that requires a minimum increase in its surface energy. To determine the size, we calculate the net vertical force due to the surface tension T when the radius of the drop is R. When the force becomes smaller than the weight of the drop, the drop gets detached from the dropper.
Q. If r = 5 × 10−4 m, ρ = 103 kg m−3, g = 10 m/s2, T = 0.11 Nm−1, the radius of the drop when it detaches from the dropper is approximately
Paragraphs for Question 12 To 14
When liquid medicine of density ρ is to be put in the eye, it is done with the help of a dropper. As the bulb on the top of the dropper is pressed, a drop forms at the opening of the dropper. We wish to estimate the size of the drop.
We first assume that the drop formed at the opening is spherical because that requires a minimum increase in its surface energy. To determine the size, we calculate the net vertical force due to the surface tension T when the radius of the drop is R. When the force becomes smaller than the weight of the drop, the drop gets detached from the dropper.
Q. After the drop detaches, its surface energy is
Paragraph for questions 15 to 17.
The key feature of Bohr’s theory of spectrum of hydrogen atom is the quantization of angular momentum when an electron is revolving around a proton. We will extend this to a general rotational motion to find quantized rotational energy of a diatomic molecule assuming it to be rigid. The rule to be applied is Bohr’s quantization condition.
Q. A diatomic molecule has moment of inertia I. By Bohr’s quantization condition its rotational energy in the
nth level (n = 0 is not allowed) is
Paragraph for questions 15 to 17.
The key feature of Bohr’s theory of spectrum of hydrogen atom is the quantization of angular momentum when an electron is revolving around a proton. We will extend this to a general rotational motion to find quantized rotational energy of a diatomic molecule assuming it to be rigid. The rule to be applied is Bohr’s quantization condition.
Q. It is found that the excitation frequency from ground to the first excited state of rotation for the CO
molecule is close to . Then the moment of inertia of CO molecule about its centre of mass is
close to
Paragraph for questions 15 to 17.
The key feature of Bohr’s theory of spectrum of hydrogen atom is the quantization of angular momentum when an electron is revolving around a proton. We will extend this to a general rotational motion to find quantized rotational energy of a diatomic molecule assuming it to be rigid. The rule to be applied is Bohr’s quantization condition.
Q. In a CO molecule, the distance between C (mass = 12 a.m.u) and O (mass = 16 a.m.u.),
where 1 a.m.u. is close to
SECTION – IV (Matrix Type)
This Section contains 2 questions. Each question has four statements (A, B, C and D) given in Column I and five statements (p, q, r, s and t) in Column II. Any given statement in Column I can have correct matching with one or more statement(s) given in Column II.
Q. Two transparent media of refractive indices μ1 and μ3 have a solid lens shaped transparent material of
refractive index μ2 between them as shown in figures in Column II. A ray traversing these media is also
shown in the figures. In Column I different relationships between μ1, μ2 and μ3 are given. Match them to
the ray diagram shown in Column II.
You are given many resistances, capacitors and inductors. These are connected to a variable DC voltage
source (the first two circuits) or an AC voltage source of 50 Hz frequency (the next three circuits) in
different ways as shown in Column II. When a current I (steady state for DC or rms for AC) flows through
the circuit, the corresponding voltage V1 and V2. (indicated in circuits) are related as shown in Column I.
Match the two
SECTION – I (Single Correct Choice Type)
This Section contains 6 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices A), B), C) and D) out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q. The compounds P, Q and S
were separately subjected to nitration using HNO3/H2SO4 mixture. The major product formed in each case
respectively, is
Assuming that Hund’s rule is violated, the bond order and magnetic nature of the diatomic molecule B2 is
The packing efficiency of the two-dimensional square unit cell shown below is
The complex showing a spin-only magnetic moment of 2.82 B.M. is
SECTION-II (Integer Type)
This Section contains 5 questions. The answer to each question is a single-digit integer, ranging from 0 to 9.
Enter only the numerical value in the space provided below.
Q. Silver (atomic weight = 108 g mol−1) has a density of 10.5 g cm−3. The number of silver atoms on a surface of area 10−12 m2 can be expressed in scientific notation as y × 10x. The value of x is
Among the following , the number of elements showing only one non-zero oxidation state is
O, Cl, F, N, P, Sn, Tl, Na, Ti
One mole of an ideal gas is taken from a to b along two paths denoted by the solid and the dashed lines as
shown in the graph below. If the work done along the solid line path is ws and that along the dotted line
path is wd, then the integer closest to the ratio wd/ws is
The total number of dirpotic acids among the following is
Total number of geometrical isomers for the complex [RhCl(CO)(PPh3)(NH3)] is