JEE Advanced 2012 Paper -2 with Solutions - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advanced 2012 Paper -2 with Solutions
SECTION I : Single Correct Answer Type
This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of
which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q. Two identical discs of same radius R are rotating about their axes in opposite directions with the same constant angular speed ω. The discs are in the same horizontal plane. At time t = 0, the points P and Q are facing each other as shown in the figure. The relative speed between the two points P and Q is vr. In one time period (T) of rotation of the discs, vr as a function of time is best represented by
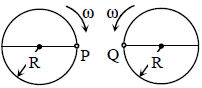
which ONLY ONE is correct.
A loop carrying current I lies in the x-y plane as shown in the figure. The unit vector  is coming
is coming
out of the plane of the paper. The magnetic moment of the current loop is
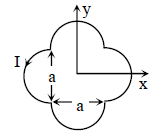
out of the plane of the paper. The magnetic moment of the current loop is
An infinitely long hollow conducting cylinder with inner radius R/2 and outer radius R carries a uniform current density along its length. The magnitude of the magnetic field,  as a function of the radial distance r from the axis is best represented by
as a function of the radial distance r from the axis is best represented by
A thin uniform cylindrical shell, closed at both ends, is partially filled with water. It is floating vertically in water in half-submerged state. If ρc is the relative density of the material of the shell with respect to water, then the correct statement is that the shell is
In the given circuit, a charge of +80 μC is given to the upper plate of the 4 μF capacitor. Then in the steady state, the charge on the upper plate of the 3 μF capacitor is
Two moles of ideal helium gas are in a rubber balloon at 30°C. The balloon is fully expandable and can be assumed to require no energy in its expansion. The temperature of the gas in the balloon is slowly changed to 35°C. The amount of heat required in raising the temperature is nearly (take R = 8.31 J/mol.K)
Consider a disc rotating in the horizontal plane with a constant angular speed w about its centre O. The disc has a shaded region on one side of the diameter and an unshaded region on the other side as shown in the figure. When the disc is in the orientation as shown, two pebbles P and Q are simultaneously projected at an angle towards R. The velocity of projection is in the y-z plane and is same for both pebbles with respect to the disc. Assume that
(i) they land back on the disc before the disc has 1/8 completed rotation,
(ii) their range is less than half the disc radius, and
(iii) ω remains constant throughout. Then
A student is performing the experiment of resonance Column. The diameter of the column tube is 4 cm. The frequency of the tuning fork is 512 Hz. The air temperature is 38°C in which the speed of sound is 336 m/s. The zero of the meter scale coincides with the top end of the Resonance Column tube. When the first resonance occurs, the reading of the water level in the column is
SECTION II : Paragraph Type
This section contains 6 multiple choice questions relating to three paragraphs with two questions on each
paragraph. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Paragraph for Questions 9 and 10
The general motion of a rigid body can be considered to be a combination of (i) a motion of its centre of
mass about an axis, and (ii) its motion about an instantaneous axis passing through the centre of mass.
These axes need not be stationary. Consider, for example, a thin uniform disc welded (rigidly fixed)
horizontally at its rim to a massless stick, as shown in the figure. When the disc-stick system is rotated
about the origin on a horizontal frictionless plane with angular speed ω, the motion at any instant can be
taken as a combination of (i) a rotation of the centre of mass of the disc about the z-axis, and (ii) a rotation
of the disc through an instantaneous vertical axis passing through its centre of mass (as is seen from the
changed orientation of points P and Q). Both these motions have the same angular speed ω in this case
Now consider two similar systems as shown in the figure: Case(a) the disc with its face vertical and
parallel to x-z plane; Case (b) the disc with its face making an angle of 45° with x-y plane and its
horizontal diameter parallel to x-axis. In both the cases, the disc is welded at point P, and the systems are
rotated with constant angular speed ω about the z-axis.
Q. Which of the following statements about the instantaneous axis (passing through the centre of mass) is correct?
Paragraph for Questions 9 and 10
The general motion of a rigid body can be considered to be a combination of (i) a motion of its centre of
mass about an axis, and (ii) its motion about an instantaneous axis passing through the centre of mass.
These axes need not be stationary. Consider, for example, a thin uniform disc welded (rigidly fixed)
horizontally at its rim to a massless stick, as shown in the figure. When the disc-stick system is rotated
about the origin on a horizontal frictionless plane with angular speed ω, the motion at any instant can be
taken as a combination of (i) a rotation of the centre of mass of the disc about the z-axis, and (ii) a rotation
of the disc through an instantaneous vertical axis passing through its centre of mass (as is seen from the
changed orientation of points P and Q). Both these motions have the same angular speed ω in this case
Now consider two similar systems as shown in the figure: Case(a) the disc with its face vertical and
parallel to x-z plane; Case (b) the disc with its face making an angle of 45° with x-y plane and its
horizontal diameter parallel to x-axis. In both the cases, the disc is welded at point P, and the systems are
rotated with constant angular speed ω about the z-axis.
Q. Which of the following statements regarding the angular speed about the instantaneous axis (passing through the centre of mass) is correct?
Paragraph for Questions 11 and 12
The β-decay process, discovered around 1900, is basically the decay of a neutron (n). In the laboratory, a proton (p) and an electron (e–) are observed as the decay products of the neutron. Therefore, considering the decay of a neutron as a two-body decay process, it was predicted theoretically that the kinetic energy of the electron should be a constant. But experimentally, it was observed that the electron kinetic energy has continuous spectrum. Considering a three-body decay process, i.e.
around 1930, Pauli explained the observed electron energy spectrum. Assuming the anti-neutrino to be massless and possessing negligible energy, and the neutron to be at rest, momentum and energy conservation principles are applied. From this calculation, the maximum kinetic energy of the electron is 0.8 × 106 eV. The kinetic energy carried by the proton is only the recoil energy.
Q. If the anti-neutrino had a mass of 3eV/c2 (where c is the speed of light) instead of zero mass, what
should be the range of the kinetic energy, K, of the electron?
Paragraph for Questions 11 and 12
The β-decay process, discovered around 1900, is basically the decay of a neutron (n). In the laboratory, a proton (p) and an electron (e–) are observed as the decay products of the neutron. Therefore, considering the decay of a neutron as a two-body decay process, it was predicted theoretically that the kinetic energy of the electron should be a constant. But experimentally, it was observed that the electron kinetic energy has continuous spectrum. Considering a three-body decay process, i.e.
around 1930, Pauli explained the observed electron energy spectrum. Assuming the anti-neutrino to be massless and possessing negligible energy, and the neutron to be at rest, momentum and energy conservation principles are applied. From this calculation, the maximum kinetic energy of the electron is 0.8 × 106 eV. The kinetic energy carried by the proton is only the recoil energy.
Q. What is the maximum energy of the anti-neutrino?
Paragraph for Questions 13 and 14
Most materials have the refractive index, n > 1. So, when a light ray from air enters a naturally occurring
material, then by Snell’s law, it is understood that the refracted ray bends towards the normal.
But it never emerges on the same side of the normal as the incident ray. According to electromagnetism,
the refractive index of the medium is given by the relation, where c is the speed of
electromagnetic waves in vacuum, v its speed in the medium, εr and μr are the relative permittivity and
permeability of the medium respectively.
In normal materials, both εr and μr, are positive, implying positive n for the medium. When both εr and μr are negative, one must choose the negative root of n. Such negative refractive index materials can now
be artificially prepared and are called meta-materials. They exhibit significantly different optical behavior,
without violating any physical laws. Since n is negative, it results in a change in the direction of
propagation of the refracted light. However, similar to normal materials, the frequency of light remains
unchanged upon refraction even in meta-materials.
Q. For light incident from air on a meta-material, the appropriate ray diagram is
Paragraph for Questions 13 and 14
Most materials have the refractive index, n > 1. So, when a light ray from air enters a naturally occurring
material, then by Snell’s law, it is understood that the refracted ray bends towards the normal.
But it never emerges on the same side of the normal as the incident ray. According to electromagnetism,
the refractive index of the medium is given by the relation, where c is the speed of
electromagnetic waves in vacuum, v its speed in the medium, εr and μr are the relative permittivity and
permeability of the medium respectively.
In normal materials, both εr and μr, are positive, implying positive n for the medium. When both εr and μr are negative, one must choose the negative root of n. Such negative refractive index materials can now
be artificially prepared and are called meta-materials. They exhibit significantly different optical behavior,
without violating any physical laws. Since n is negative, it results in a change in the direction of
propagation of the refracted light. However, similar to normal materials, the frequency of light remains
unchanged upon refraction even in meta-materials.
Q. Choose the correct statement.
SECTION III : Multiple Correct Answer(s) Type
This section contains 6 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of
which ONE or MORE are correct.
15. In the given circuit, the AC source has ω = 100 rad/s. Considering the inductor and capacitor to be ideal, the correct choice(s) is (are)
Six point charges are kept at the vertices of a regular hexagon of side L and centre O, as shown
in the figure. Given that , which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
Two spherical planets P and Q have the same uniform density r, masses Mp and MQ and surface
areas A and 4A respectively. A spherical planet R also has uniform density ρ and its mass is (MP
+ MQ). The escape velocities from the planets P, Q and R are VP, VQ and VR, respectively. Then
The figure shows a system consisting of (i) a ring of outer radius 3R rolling clockwise without slipping on a horizontal surface with angular speed ω and (ii) an inner disc of radius 2R rotating anti-clockwise with angular speed ω/2. The ring and disc are separated by frictionless ball bearings. The point P on the inner disc is at a distance R from the origin, where OP makes an angle of 300 with the horizontal. Then with respect to the horizontal surface,
Two solid cylinders P and Q of same mass and same radius start rolling down a fixed inclined plane from the same height at the same time. Cylinder P has most of its mass concentrated near its surface, while Q has most of its mass concentrated near the axis. Which statement(s) is(are) correct?
A current carrying infinitely long wire is kept along the diameter of a circular wire loop, without
touching it, the correct statement(s) is(are)
SECTION I : Single Correct Answer Type
This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of
which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q. The major product H of the given reaction sequence is
NiCl2{P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2 exhibits temperature dependent magnetic behaviour (paramagnetic/diamagnetic).
The coordination geometries of Ni2+ in the paramagnetic and diamagnetic states are respectively
In the cyanide extraction process of silver from argentite ore, the oxidising and reducing agents used are
The reaction of white phosphorous with aqueous NaOH gives phosphine along with another phosphorous
containing compound. The reaction type; the oxidation states of phosphorus in phosphine and the other
product are respectively
For a dilute solution containing 2.5 g of a non–volatile non–electrolyte solute in 100 g of water, the elevation in boiling point at 1 atm pressure is 2°C. Assuming concentration of solute is much lower than the concentration of solvent, the vapour pressure (mm of Hg) of the solution is (take Kb = 0.76 K kg mol-1)
The compound that undergoes decarboxylation most readily under mild condition is
Using the data provided, calculate the multiple bond energy (kJ mol-1) of a CºC bond in C2H2. That energy
is (take the bond energy of a C–H bond as 350 kJ mol-1)
SECTION II : Paragraph Type
This section contains 6 multiple choice questions relating to three paragraphs with two questions on each
paragraph. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Paragraph for Questions 29 and 30
In the following reaction sequence, the compound J is an intermediate.
Q. The compound I is
SECTION II : Paragraph Type
This section contains 6 multiple choice questions relating to three paragraphs with two questions on each
paragraph. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Paragraph for Questions 29 and 30
In the following reaction sequence, the compound J is an intermediate.
Q. The compound K is














