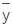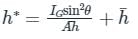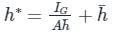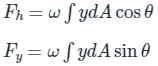Test: Hydrostatic Force on Plane Area - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Hydrostatic Force on Plane Area
A cuboidal beaker is half filled with water. By what percent will the hydrostatic force on one of the vertical sides of the beaker increase if it is completely filled?
Equal volume of two liquids of densities ρ1 and ρ2 are poured into two identical cuboidal beakers. The hydrostatic forces on the respective vertical face of the beakers are F1 and F2 respectively. If ρ1 > ρ2, which one will be the correct relation between F1 and F2?
A beaker contains water up to a height of h. What will be the location of the centre of pressure?
A rectangular lamina of width b and depth d is submerged vertically in water, such that the upper edge of the lamina is at a depth h from the free surface. What will be the expression for the depth of the centroid (G)?
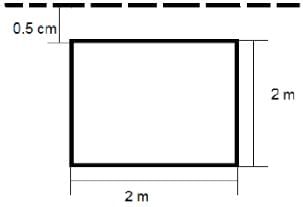
A square lamina (each side equal to 2m) is submerged vertically in water such that the upper edge of the lamina is at a depth of 0.5 m from the free surface. What will be the total water pressure (in kN) on the lamina?
By what factor will the hydrostatic force on one of the vertical sides of a beaker decrease if the height of the liquid column is halved?
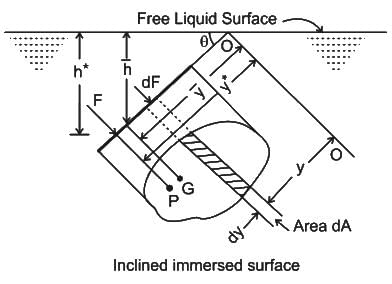
Which of the following is the correct relation between centroid (G) and the centre of pressure (P) of a plane submerged in a liquid?
A cubic tank is completely filled with water. What will be the ratio of the hydrostatic force exerted on the base and on any one of the vertical sides?
What is the direction of total liquid pressure on submerged surface?
In a fluid system, the point of intersection of the line of action of the resultant hydrostatic force and the corresponding surface is known as:


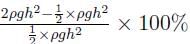

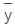 and the centre of pressure yCP are related by:
and the centre of pressure yCP are related by: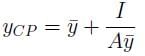
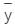 = h ⁄ 2; I = bh3/12 ;A = bh, then
= h ⁄ 2; I = bh3/12 ;A = bh, then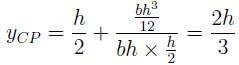
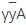 ,
,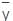 = depth of centroid of the lamina from the free surface,
= depth of centroid of the lamina from the free surface,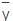
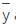 and the centre of pressure yCP are related by:
and the centre of pressure yCP are related by: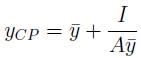
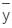 can be negative. Thus, YCP >
can be negative. Thus, YCP > 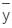 . For horizontal planes, I = 0, hence YCP =
. For horizontal planes, I = 0, hence YCP =