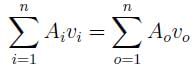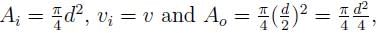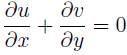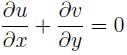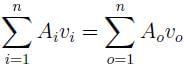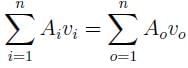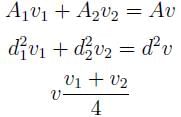Test: Continuity Equation - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Continuity Equation
If a liquid enters a pipe of diameter d with a velocity v, what will it’s velocity at the exit if the diameter reduces to 0.5d?
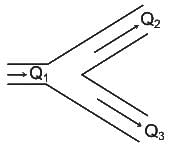
Two pipes, each of diameter d, converge to form a pipe of diameter D. What should be the relation between d and D such that the flow velocity in the third pipe becomes double of that in each of the two pipes?
In a two dimensional flow, the component of the velocity along the X-axis and the Y-axis are u = ax2 + bxy + cy2 and v = cxy. What should be the condition for the flow field to be continuous?
In a two dimensional flow, the component of the velocity along the X-axis and the Y-axis are u = ax2 + bxy and v = bxy + ay2. The condition for the flow field to be continuous is
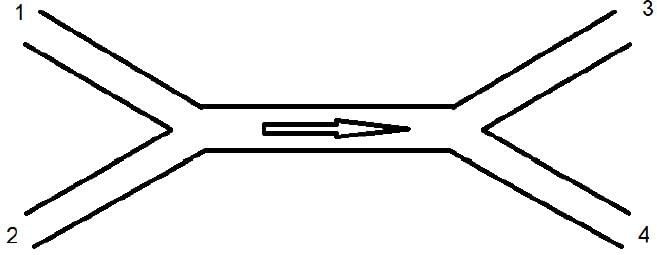
In a water supply system, water flows in from pipes 1 and 2 and goes out from pipes 3 and 4 as shown. If all the pipes have the same diameter, which of the following must be correct?
Two pipes of diameters d1 and d2 converge to form a pipe of diameter 2d. If the liquid flows with a velocity of v1 and v2 in the two pipes, what will be the flow velocity in the third pipe?
A fluid flowing through a pipe of diameter 450 mm with velocity 3 m/s is divided into two pipes of diameters 300 mm and 200 mm. The velocity of flow in 300 mm diameter pipe is 2.5 m/s, then the velocity of flow through 200 mm diameter pipe will be
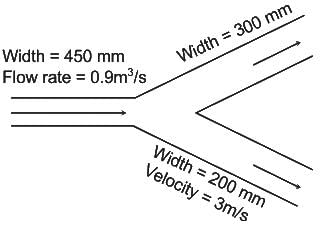
A channel of width 450 mm branches into two sub-channels having width 300 mm and 200 mm as shown in figure. If the volumetric flow rate (taking unit depth) of an incompressible flow through the main channel is 0.9 m3/s and the velocity in the sub-channel of width 200 mm is 3 m/s, the velocity in the sub-channel of width 300 mm is ______m/s
Assume both inlet and otlet to be at the same elevation.