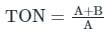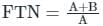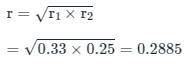Test: Quality of Water - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Quality of Water
The odour of the water or the waste-water can be measured by a term called:
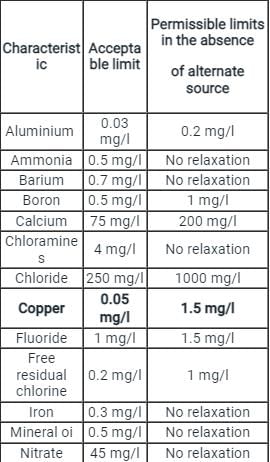
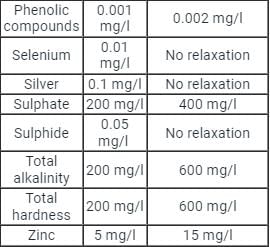
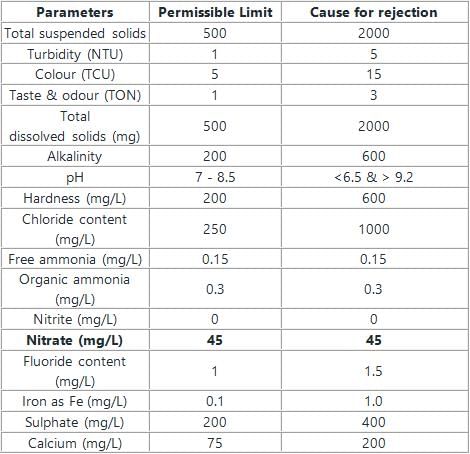
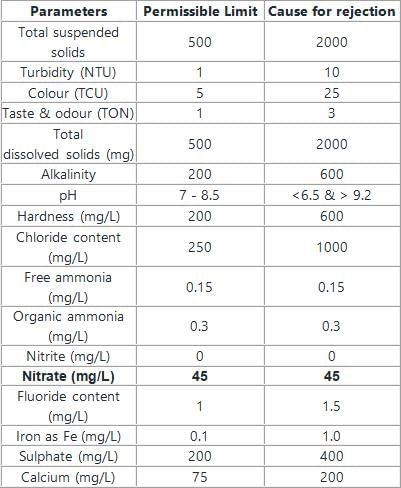
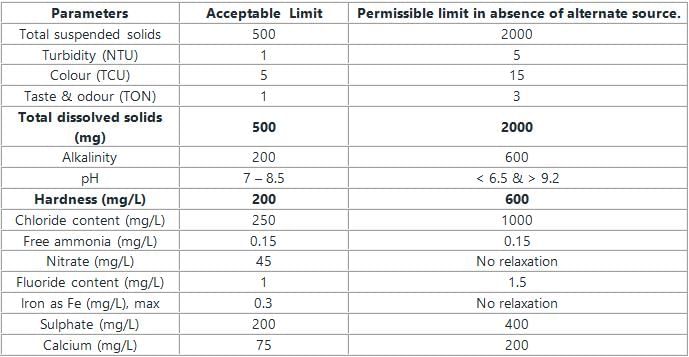
The permissible limit of nitrate content in potable water is:
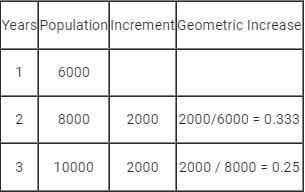
The population of a city in the first three continuous years is given as 6000, 8000 and 10000 respectively. What is the population of the city in the fourth continuous year, according to the geometric increase method?
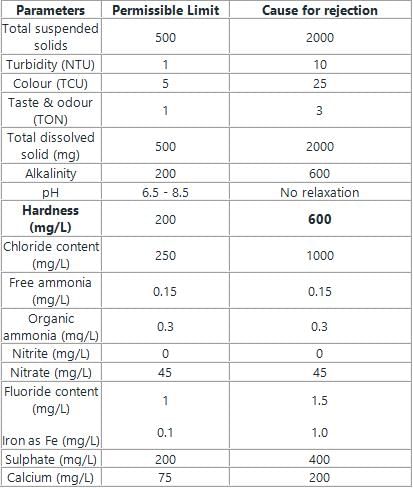
The tolerance limit of hardness in water as per IS drinking water standard is specified as
Which of the following method is used to forecast the population of old and very large city?
Blue baby disease found in infants is due to excessive _____ in drinking water.
The spacing between two bars in medium size screen ranges from
As per IS 10500:2012, the permissible limit of total dissolved solids (TDS), (in mg/l), in drinking water in the absence of an alternate source is: