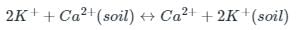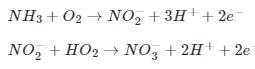Test: Solid Waste Management - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Solid Waste Management
Which of the below is not an idea behind solid waste management?
How many major sources of solid waste are there based on their origin?
The number of functional components of solid waste management is:
Under which rule of Government, guidelines for solid waste management are followed today?
A reversible reaction in which a charged ion in solution is exchanged for a similarly charged ion electrostatically attached to an immobile solid particle is termed as:
Decomposition of domestic wastes under natural processes is known as :
Consider the following regarding the incineration process of solid waste.
A. It is an oxidation process.
B. The two major combustible chemical elements are carbon and hydrogen.
C. Cellulose in the biowaste is transformed into organic acids.
D. Excess source of air is not necessary.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
Which of the following sources of solid waste has the highest chance of causing infections like Hepatitis B and C through skin route if not handled properly?