Test: Geography - 1 - UPSC MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Geography - 1
Which of the following statements best describe “Virgin Vegetation”?
With reference to the ‘break in monsoon’, consider the following statements:
1. It happens due to the northward shift of the ITCZ over the foothills of Himalayas.
2. It occurs over the west coast due to wind blowing parallel to the coast.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
India is said to experience comparatively milder winters as compared to Central Asia.
Which of the following statements could be the reason(s) for this?
1. The continentality of North India.
2. The Himalayas in the north.
3. A vast coastline.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
1. Eastern Ghats are broken and uneven whereas Western Ghats form a continuous ridge.
2.The Eastern coastal plains are narrower as compared to the Western coastal plains.
3. Rivers Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna and Vaigai all drain into the Bay of Bengal.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
This river is mainly known for its badland topography. It originates on the south slope of Vindhyachal range in Madhya Pradesh and is a tributary of river Yamuna. This river is known as?
Consider the following statements with respect to “Inter Tropical Convergence Zone”:
1. It is a broad trough of low pressure in equatorial latitudes.
2. It is in this zone, that the northeast and southeast trade winds converge.
3. It does not extend beyond the tropics.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Which of the following pairs are correctly matched?
Hot weather phenomena Region
1. Loo West Bengal
2. Kal Baisakhi Odisha
3. Mango showers Karnataka
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Which of the following states in India have made rooftop rainwater harvesting structure compulsory for all the houses across the state?
In the context of rainfall in India, consider the following statements:
1. There is an increase in rainfall generally from east to west in the Northern Plains.
2. The Coromandel coast receives most of its rain during October and November.
Which of the statements given above is/are incorrect?
The character and extent of vegetation of a region is mainly determined by which of the
following factors?
1. Temperature
2. Photoperiod
3. Relief
4. Precipitation
5. Soil
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
With reference to Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) , consider the following statements:
1. It helps to make the diesel generator less dependent on surface air.
2. It offers the possibility of increasing underwater endurance .
3. It has a force multiplier effect on the lethality of a diesel electric submarine .
Which of the statements given above are correct?
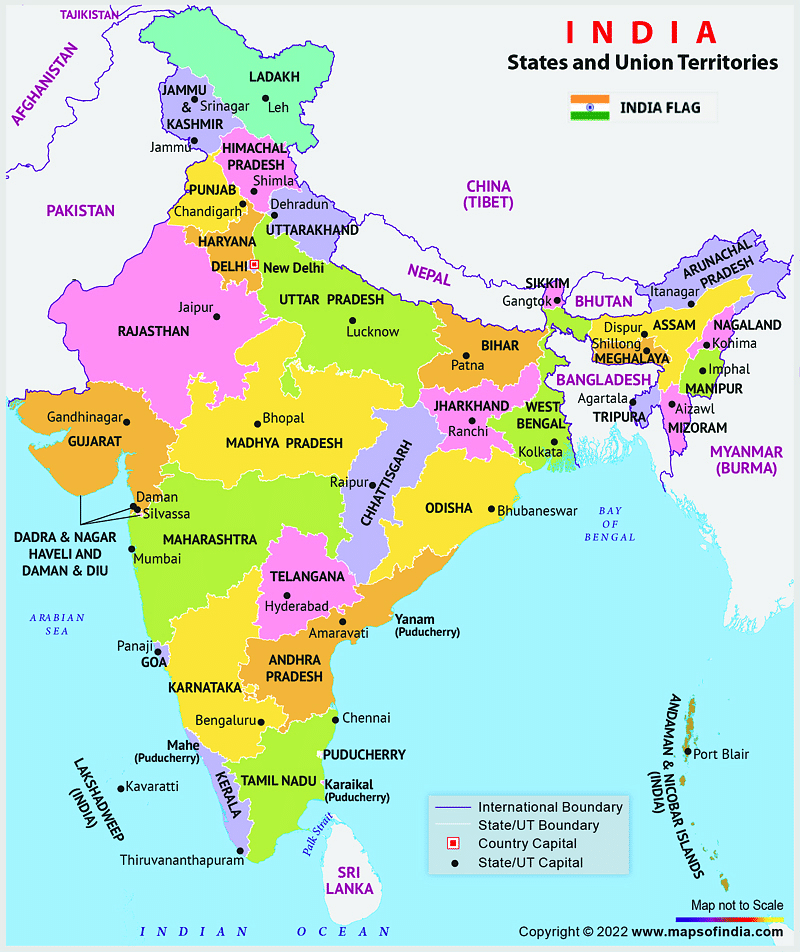
If you travel from Jammu and kashmir to Mizoram, what is the minimum number of states within India through which you can travel, excluding the origin and destination?
Consider the following statements regarding Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC)
1. It has functional autonomy within UNESCO.
2. It organises IOWave18 exercise in the Indian Ocean.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding “Jet Streams”:
1. Jet Streams are a narrow belt of high altitude (above 12,000 m) winds in the troposphere.
2. The western cyclonic disturbances experienced in the north and north-western parts of India are brought in by westerly flow of Jet Streams.
3. An easterly jet stream blows over peninsular India during the winter months.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
With reference to International Commission on Irrigation and Drainage (ICID), consider the following statements:
1. It is a non-governmental organization.
2. It maintains a register of Heritage Irrigation Structures
3. Punjab in the first state having a Heritage Irrigation Structure in the ICID register.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
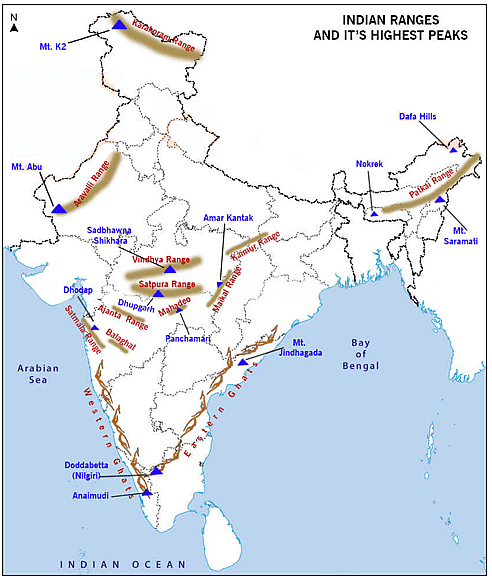
Arrange the following mountain ranges from North to south:
1. Satpura
2. Himalayan
3. Aravali
4. Vindhya
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Consider the following statements:
1. The Tea plant grows well in the subtropical and temperate climates.
2. The Tea plant requires heavy seasonal rainfall for its optimum growth.
3. India is the largest producer of Tea in the world.
Which of the statements given above is/are not correct?
Consider the following statements regarding the Geographical Indication (GI) Tag:
1. It is established under the Patents Act, 1970.
2. They are covered under the WTO Agreement of TRIPS (Trade Related aspects of Intellectual Property Rights)
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statement regarding ‘Weather’ and ‘climate’.
1. Climate refers to the sum total of weather conditions and variations over a large area for a
long period of time, while Weather refers to the state of the atmosphere over an area at any point of time.
2. The elements of weather and climate differs according to latitudinal shift.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
With reference to Jog Falls , consider the following statements:
1. It is created by the Sharavathi River.
2. It is the second-highest plunge waterfall in India.
3. It is situated in Kerala.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding United Nations Sustainable Development Framework (UNSDF)
1. It supports India in achieving its key national development priorities.
2. It puts a special focus on the North-East and the aspirational districts.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
1. Cultivation of wheat requires high humidity with annual rainfall above 100cm.
2. Cultivation of rice requires annual rainfall of 50cm to 75cm.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
1. Seifs are crescent shaped sand dunes.
2. Barchans are longitudinal sand ridges.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
With reference to Ayushman Bharat- Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana, consider the following statements:
1. The on-going centrally sponsored schemes Rashtriya Swasthya Bima Yojana and the Senior Citizen Health Insurance Scheme are subsumed in Ayushman Bharat Mission.
2. It has a defined benefit cover of Rs. 5 lakh per family per year.
3. Beneficiaries covered under the scheme are allowed to take cashless benefits from any of
the public/private empanelled hospitals across the country.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statement regarding National Mission on Government eMarketplace (GeM):
1. It aims to enhance transparency, efficiency and speed in public procurement of agricultural produce only.
2. It also offers offline, end-to-end solution for procurement of commonly used goods and services.
3. It can be used only by Central Public Sector Undertakings (CPSU).
Which of the statements given above is/are incorrect?
Which of the following statements is not correct regarding Planet Venus?
Consider the following statements about retreating monsoon:
1. It begins when the low-pressure trough over the northern plains starts moving southwards.
2. It is associated with wet weather in North India and rains in eastern part of Peninsula.
3. It is characterized by wind blowing from Northeast to Southwest.
Which of the statements given above is/are not correct?
Consider the following statements:
1. Forest area is the area notified and recorded as the forest land irrespective of the existence of trees.
2. Forest cover is the area occupied by forests with canopy.
3. Both the forest area and forest cover are based on the records of State Revenue Department.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
With reference to National Digital Communications Policy, 2018, consider the following statements:
1. It aims to provide universal broadband connectivity to every citizen.
2. It aims to establish Common Service Ducts and utility corridors in all new city and highway road projects.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
1. In most of the tribal areas of the north-east India, minerals are owned by individuals or communities
2. Mining of coal in Meghalaya is done by digging long narrow tunnels.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?