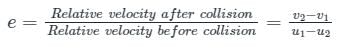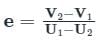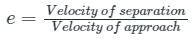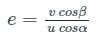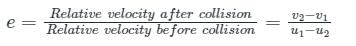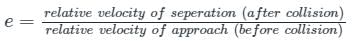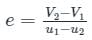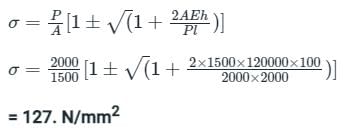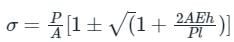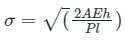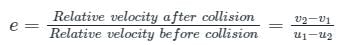Test: Types of Impact - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
8 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Types of Impact
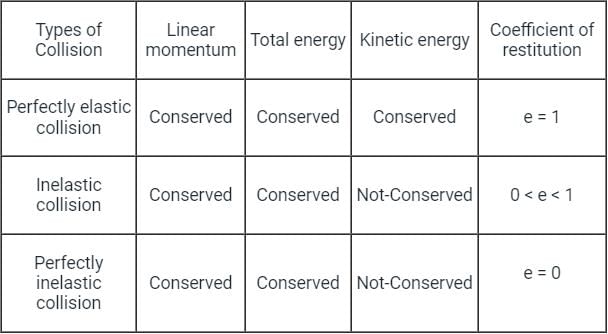
The impact is said to be inelastic or plastic when the coefficient of restitution is ________.
Identify correct statement(s) about the coefficient of restitution 'e' -
A ball 'A' of mass 'm' falls under gravity from a height 'h' and strikes another ball 'B' of mass 'm' which supported at rest on a spring of stiffness 'k' . Assume perfectly elastic impact . Immediately after the impact,
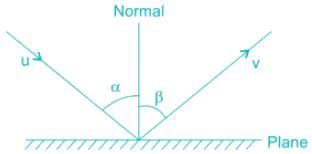
Collision of Elastic Bodies in case of indirect impact of a body with a fixed plane is
During inelastic collision of two particles, which one of the following is conserved ?
If u1 and u2 are the velocities of two moving bodies in the same direction before impact and V1 and V2 are their velocities after impact, then coefficient of restitution is given by
A 2 m long alloy bar of 1500 mm2 cross-sectional area hangs vertically and has a collar securely fixed at its lower end. What is the stress-induced in the bar when a weight of 2 kN falls from a height of 100 mm on the collar? (Take E = 120 GPa)
The impact is said to be inelastic or plastic when the coefficient of restitution is ________.