IBPS RRB Clerk Prelims Mock Test - 6 - Bank Exams MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - IBPS RRB Clerk Prelims Mock Test - 6
Answer the following questions after studying the information given below:
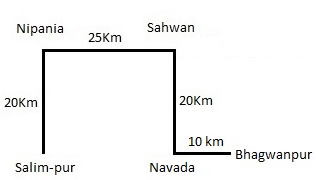
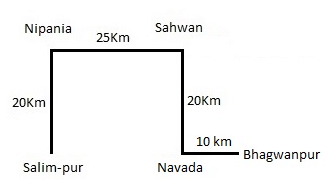
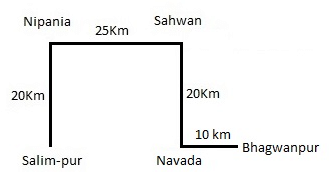
The village Sahwan is 20 km from the village Navada in North. The village Salimpur is 20 km from Nipania in South. Navada is 10 km from Bhagwanpur in West. Sahwan is 25 km from Nipania in East. Salimpur is in West of Bhagwanpur and these both villages are in a straight line.
Q. Suresh goes to Salimpur from Nipania and then comes back. After some time he goes to Bhagwanpur via Sahwan and Navada and then returns to Navada. How much total distance does he cover in the total journey?
Answer the following questions after studying the information given below:
The village Sahwan is 20 km from the village Navada in North. The village Salimpur is 20 km from Nipania in South. Navada is 10 km from Bhagwanpur in West. Sahwan is 25 km from Nipania in East. Salimpur is in West of Bhagwanpur and these both villages are in a straight line.
Q. If karim goes from Navada to Nipania via Salimpur and then returns to Salimpur, how much total distance he should travel?
Answer the following questions after studying the information given below:
The village Sahwan is 20 km from the village Navada in North. The village Salimpur is 20 km from Nipania in South. Navada is 10 km from Bhagwanpur in West. Sahwan is 25 km from Nipania in East. Salimpur is in West of Bhagwanpur and these both villages are in a straight line.
Q. Which of the following villages is just next to Salimpur in East?
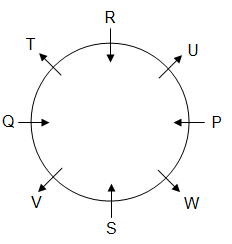
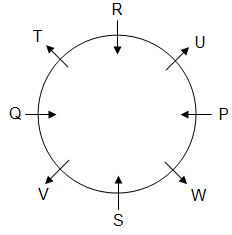
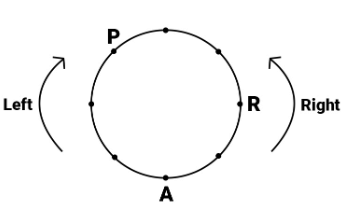
Directions: Study the following information and answer the given question.
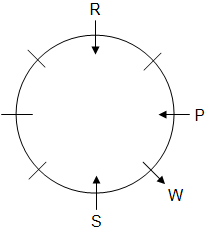
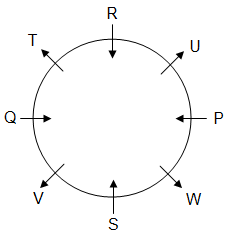
Eight persons P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W are sitting around a circular table, but not necessarily in the same order. Some of them are facing towards the centre and some are facing outwards. No two persons facing the same direction are sitting together.
Q is on the immediate left of T, who is sitting second to the left of U. P is sitting second to the left of R. R is sitting fourth to S and both are facing the centre. W is the immediate neighbour of P and S. Only two persons are sitting between Q and W.
Note: Here, direction means inwards (facing the centre) or outwards (having back towards the centre).
Q. Who among the following are immediate neighbours of 'R'?
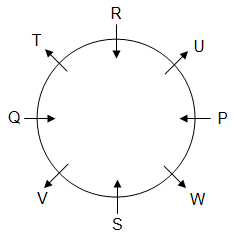
Directions: Study the following information and answer the given question.
Eight persons P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W are sitting around a circular table, but not necessarily in the same order. Some of them are facing towards the centre and some are facing outwards. No two persons facing the same direction are sitting together.
Q is on the immediate left of T, who is sitting second to the left of U. P is sitting second to the left of R. R is sitting fourth to S and both are facing the centre. W is the immediate neighbour of P and S. Only two persons are sitting between Q and W.
Note: Here, direction means inwards (facing the centre) or outwards (having back towards the centre).
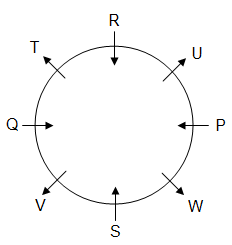
Q. Who is sitting second to the left of T?
Directions: Study the following information and answer the given question.
Eight persons P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W are sitting around a circular table, but not necessarily in the same order. Some of them are facing towards the centre and some are facing outwards. No two persons facing the same direction are sitting together.
Q is on the immediate left of T, who is sitting second to the left of U. P is sitting second to the left of R. R is sitting fourth to S and both are facing the centre. W is the immediate neighbour of P and S. Only two persons are sitting between Q and W.
Note: Here, direction means inwards (facing the centre) or outwards (having back towards the centre).
Q. Which of the following combinations of persons represents those facing outwards?
Directions: Study the following information and answer the given question.
Eight persons P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W are sitting around a circular table, but not necessarily in the same order. Some of them are facing towards the centre and some are facing outwards. No two persons facing the same direction are sitting together.
Q is on the immediate left of T, who is sitting second to the left of U. P is sitting second to the left of R. R is sitting fourth to S and both are facing the centre. W is the immediate neighbour of P and S. Only two persons are sitting between Q and W.
Note: Here, direction means inwards (facing the centre) or outwards (having back towards the centre).
Q. How many persons are sitting between W and Q when counted from the left of W?
Directions: Study the following information and answer the given question.
Eight persons P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W are sitting around a circular table, but not necessarily in the same order. Some of them are facing towards the centre and some are facing outwards. No two persons facing the same direction are sitting together.
Q is on the immediate left of T, who is sitting second to the left of U. P is sitting second to the left of R. R is sitting fourth to S and both are facing the centre. W is the immediate neighbour of P and S. Only two persons are sitting between Q and W.
Note: Here, direction means inwards (facing the centre) or outwards (having back towards the centre).
Q. Who is sitting on the immediate left of V?
These questions are based on the given five three-letter words.
ACT SHY EON ACE WEB
Q. If the first and the third letters of each of the given words is changed to the next letter in the English alphabetical series, how many of them will have at least two vowels?
These questions are based on the given five three-letter words.
ACT SHY EON ACE WEB
Q. If the first and the second letters of each of the given words are interchanged, then which of the following will become a meaningful English word?
These questions are based on the given five three-letter words.
ACT SHY EON ACE WEB
Q. If the letter F is added before each of the given words, how many of them form meaningful English words?
Directions: Study the following number sequence and answer the question that follows.
2 5 3 4 7 8 9 6 3 5 4 2 3 6 5 3 6 9 8 3 6 9 4 5 6 7 8 9 7 8 9
Q. How many odd digits are there which are immediately preceded by an odd digit and immediately followed by an even digit or immediately preceded by an even digit and immediately followed by an odd digit?
Directions: Study the following number sequence and answer the question that follows.
2 5 3 4 7 8 9 6 3 5 4 2 3 6 5 3 6 9 8 3 6 9 4 5 6 7 8 9 7 8 9
Q. If all the 9s are replaced by 2s, then how many even digits will be immediately followed by an even digit?
Directions: Study the following number sequence and answer the question following it.
2 5 3 4 7 8 9 6 3 5 4 2 3 6 5 3 6 9 8 3 6 9 4 5 6 7 8 9 7 8 9
Q. What is the difference between the sum of the digits placed at even and odd places from left in the given number sequence?
Directions: Study the following number sequence and answer the question that follows.
2 5 3 4 7 8 9 6 3 5 4 2 3 6 5 3 6 9 8 3 6 9 4 5 6 7 8 9 7 8 9
Q. How many multiples of 3 are there in the given number sequence which are immediately preceded by an odd digit?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
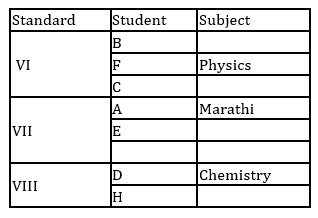
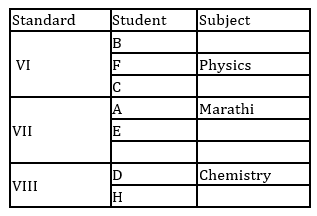
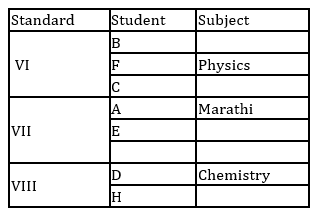
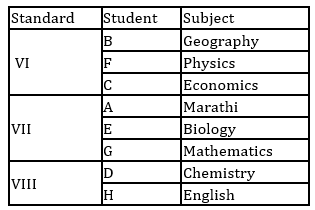
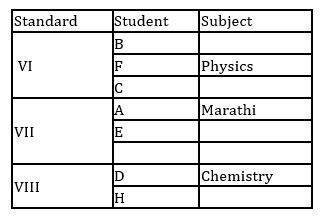
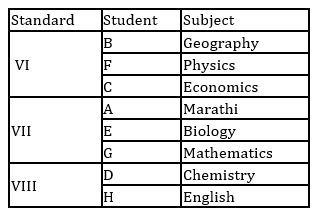
A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are eight students of a school. They study in VI, VII and VIII standard with not more than three in any standard. Each of them has a favourite subject from Physics, Geography, English, Marathi, Mathematics, Chemistry, Biology and Economics not necessarily in the same order. D likes Chemistry and studies in VIII standard with only H. B does not study in VII standard. E and A study in the same standard but not with B. C and F study in the same standard. Those who study in VI standard do not like Mathematics or Biology. F likes Physics. The one who studies in VIII standard likes English. C does not like Geography. A's favourite subject is Marathi and G does not like Biology.
Q. Which of the following group of student's study in VII Std.?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are eight students of a school. They study in VI, VII and VIII standard with not more than three in any standard. Each of them has a favourite subject from Physics, Geography, English, Marathi, Mathematics, Chemistry, Biology and Economics not necessarily in the same order. D likes Chemistry and studies in VIII standard with only H. B does not study in VII standard. E and A study in the same standard but not with B. C and F study in the same standard. Those who study in VI standard do not like Mathematics or Biology. F likes Physics. The one who studies in VIII standard likes English. C does not like Geography. A's favourite subject is Marathi and G does not like Biology.
Q. Which of the following combinations of Student - Standard - Subject is correct?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are eight students of a school. They study in VI, VII and VIII standard with not more than three in any standard. Each of them has a favourite subject from Physics, Geography, English, Marathi, Mathematics, Chemistry, Biology and Economics not necessarily in the same order. D likes Chemistry and studies in VIII standard with only H. B does not study in VII standard. E and A study in the same standard but not with B. C and F study in the same standard. Those who study in VI standard do not like Mathematics or Biology. F likes Physics. The one who studies in VIII standard likes English. C does not like Geography. A's favourite subject is Marathi and G does not like Biology.
Q. What is G's favourite subject?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are eight students of a school. They study in VI, VII and VIII standard with not more than three in any standard. Each of them has a favourite subject from Physics, Geography, English, Marathi, Mathematics, Chemistry, Biology and Economics not necessarily in the same order. D likes Chemistry and studies in VIII standard with only H. B does not study in VII standard. E and A study in the same standard but not with B. C and F study in the same standard. Those who study in VI standard do not like Mathematics or Biology. F likes Physics. The one who studies in VIII standard likes English. C does not like Geography. A's favourite subject is Marathi and G does not like Biology.
Q. Which subject does H like?
Directions: Study the following information and answer the question.
There are six persons - L, M, N, O, P, Q. O is heavier than Q. There are only 2 persons lighter than Q. There are only 2 persons heavier than O. M is lighter than O. L is lighter than M. P is not the heaviest person.
Q. If the weight of O is 42 kg and that of M is 30 kg, then what could be the weight of Q?
Directions: Study the following information and answer the question.
There are six persons - L, M, N, O, P, Q. O is heavier than Q. There are only 2 persons lighter than Q. There are only 2 persons heavier than O. M is lighter than O. L is lighter than M. P is not the heaviest person.
Q. If all of them are arranged in decreasing order of their rank in the English alphabet dictionary, how many persons will remain at their earlier position?
Directions: Study the following information and answer the question.
There are six persons - L, M, N, O, P, Q. O is heavier than Q. There are only 2 persons lighter than Q. There are only 2 persons heavier than O. M is lighter than O. L is lighter than M. P is not the heaviest person.
Q. If the weight of P is 47 kg, then what could be the possible weight of N?
In these questions, relationship between different elements is shown in the statements. These statements are followed by four conclusions. Analyse the statements and give answer.
Statements: A ≤ T = S, M ≥ R > F ≤ T = S ≥ A
Conclusions:
I. S > F
II. M < S
III. R < A
IV. T ≤ M
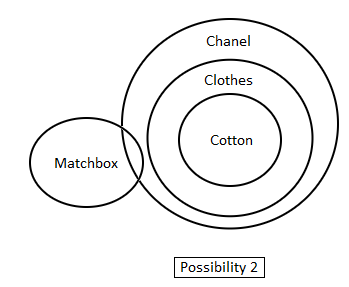
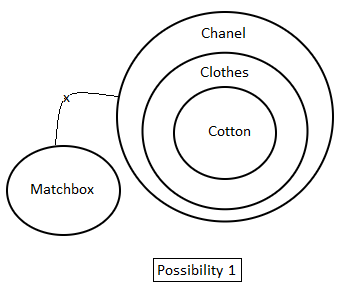
Directions: In the question below are given three statements followed by two conclusions. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follow(s) from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
1. All cotton is clothes.
2. No clothes are matchboxes.
3. All clothes are Chanel.
Conclusions:
I. Some Chanel is matchbox.
II. No matchbox is Chanel.
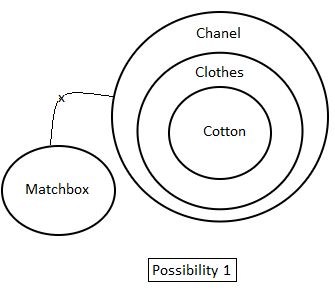
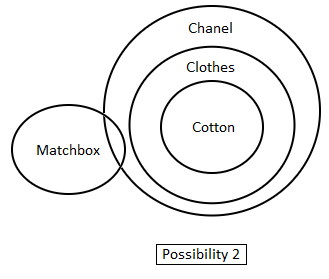
Directions: In the question below are given three statements followed by two conclusions. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follow(s) from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
1. All cotton is clothes.
2. No clothes are matchboxes.
3. All clothes are Chanel.
Conclusions:
I. No cotton is matchbox.
II. Some matchboxes are Chanel.
In these questions, relationship between different elements is shown in the statements. These statements are followed by four conclusions. Analyse the statements and give answer.
Statements: A ≥ B, D > B, F < D, G < F
Conclusions:
I. D > G
II. D ≤ A
III. B > F
IV. A < D
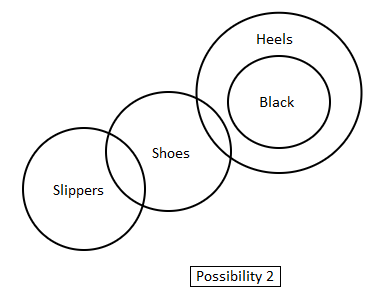
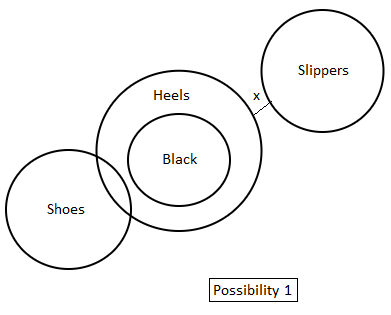
Directions: In the question below are given three statements followed by two conclusions. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follow(s) from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
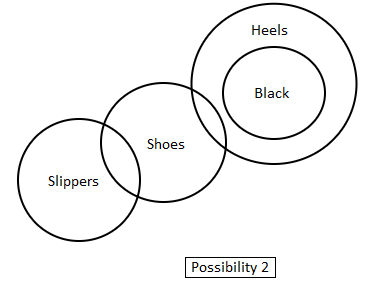
Statements:
1. All black are heels.
2. Some shoes are heels.
3. No heels are slippers.
Conclusions:
I. All shoes are slippers.
II. Some slippers are heels
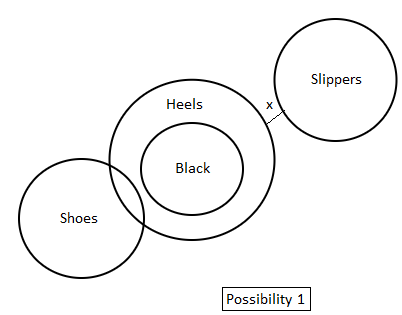
Directions: In the question below are given three statements followed by two conclusions. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follow(s) from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
1. All black are heels.
2. Some shoes are heels.
3. No heels are slippers.
Conclusions:
I. No slippers are shoes.
II. Some heels are black.
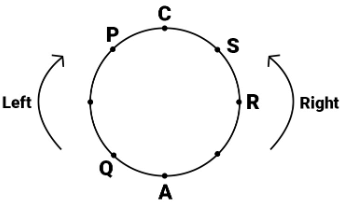
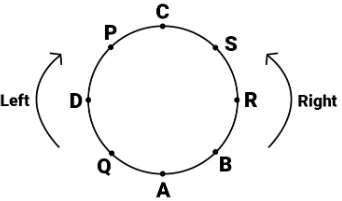
Study the following information carefully and answer the question given below.
A, B, C, D, P, Q, R and S are sitting around a circle facing the centre. P is third to the left of A and R is second to the right of A. Q is not an immediate neighbour of either P or R. C sits third to the right of B and S sits exactly between C and R.
Q. What is S's position with respect to D?
Study the following information carefully and answer the question given below.
A, B, C, D, P, Q, R and S are sitting around a circle facing the centre. P is third to the left of A and R is second to the right of A. Q is not an immediate neighbour of either P or R. C sits third to the right of B and S sits exactly between C and R.
Q. Four of the following five are similar in a certain way based on their positions in the seating arrangement and so form a group. Which of the following does not belong to that group?