IBPS RRB Clerk Mains Mock Test - 9 - Bank Exams MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - IBPS RRB Clerk Mains Mock Test - 9
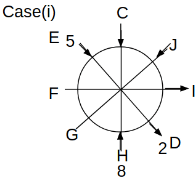
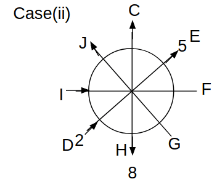
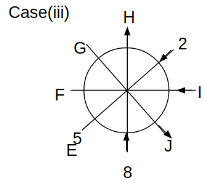
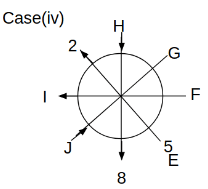
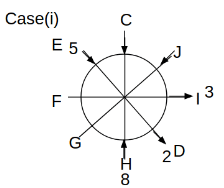
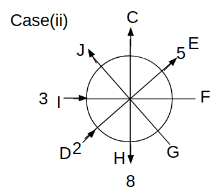
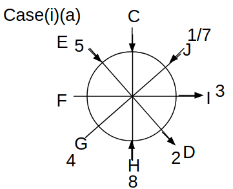
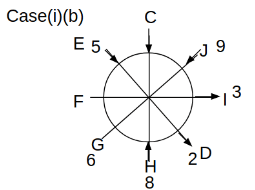
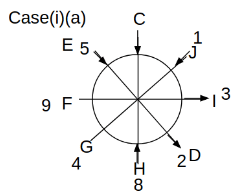
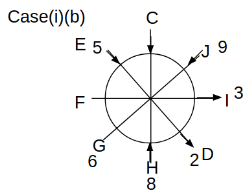
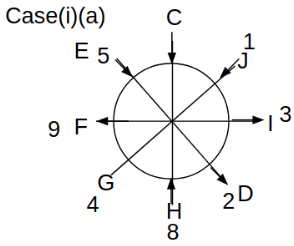
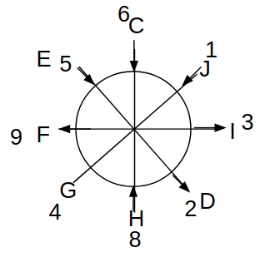
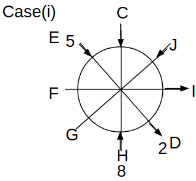
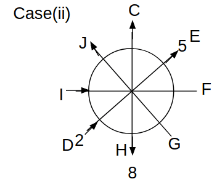
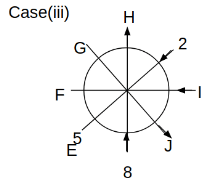
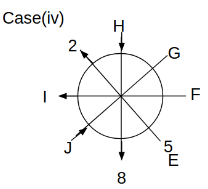
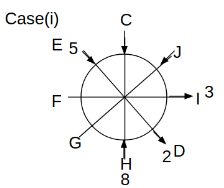
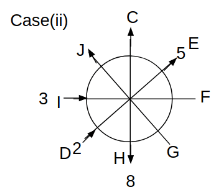
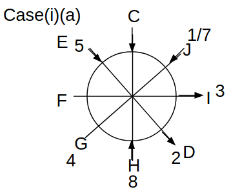
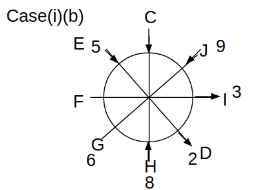
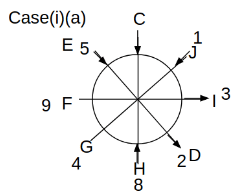
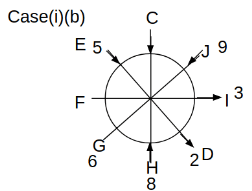
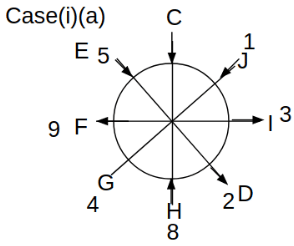
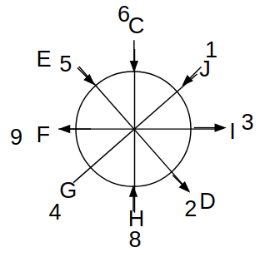
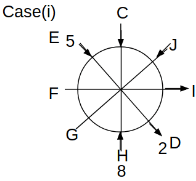
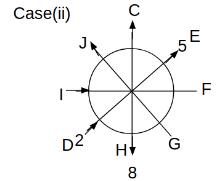
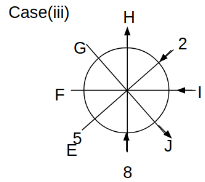
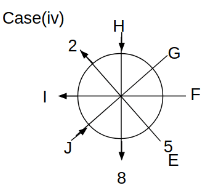
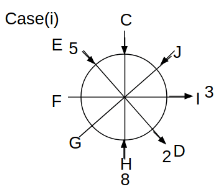
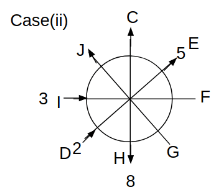
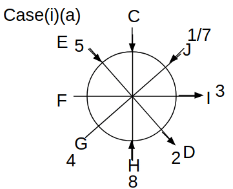
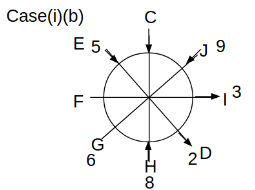
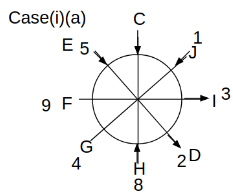
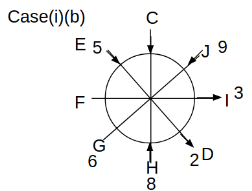
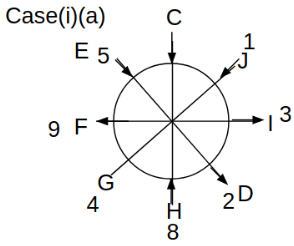
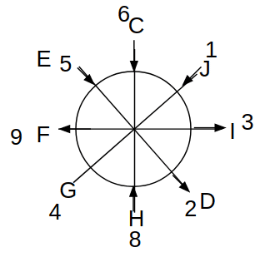
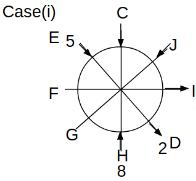
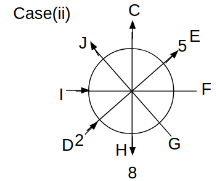
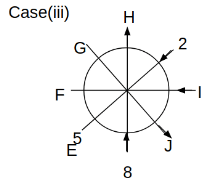
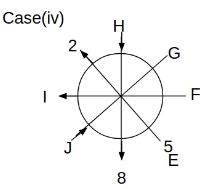
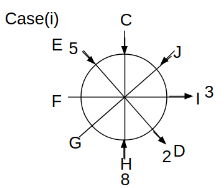
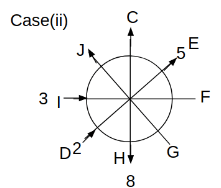
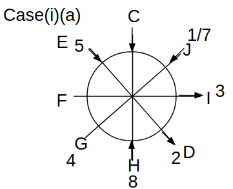
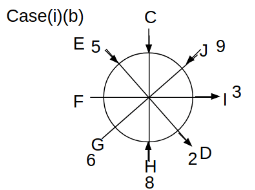
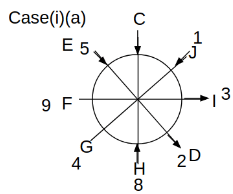
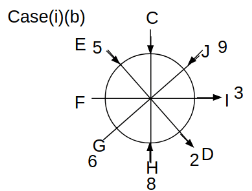
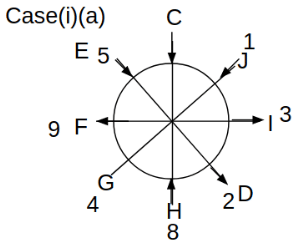
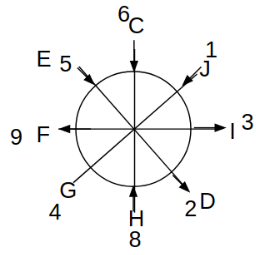
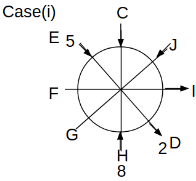
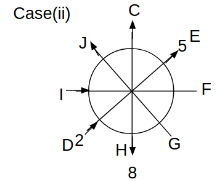
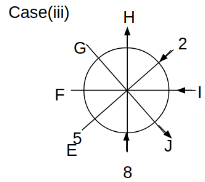
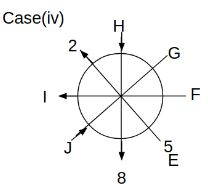
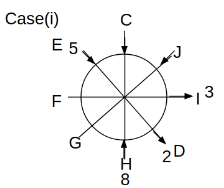
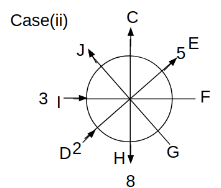
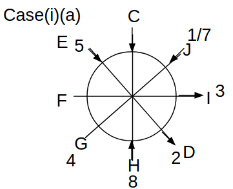
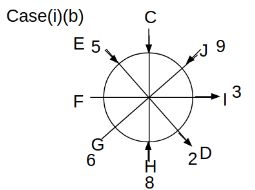
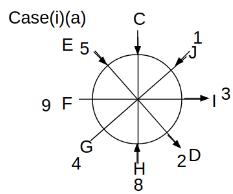
Eight people C, D, E, F, G, H, I and J are sitting around a circular table. Some of them are facing the center of the circle. While some of them are facing opposite to the center of the circle. Each person has a different lucky number from 1 to 9.
The direction of E is opposite to D. The person whose lucky number is 3 is second to the left of C. The difference between the lucky numbers of G and J is three. H is immediately right of the one whose lucky number is an even prime number who is not an immediate neighbour of F. The sum of the lucky number is J and H is equal to the lucky number of F. The immediate neighbours of the person whose lucky number is 4 face opposite directions to each other. The person whose lucky number is the multiple of 5 is third to the left of I whose immediate neighbours face opposite directions to each other. F is second to the left of one whose lucky number is the cubic number but not 1. The difference between the lucky numbers of E and G is one. The lucky numbers of J and C are not a prime number. The lucky number of E is not an even number. G sits exactly between F and H. The person whose lucky number is 3 does not face the center of the table. E is immediately right of C and both of them face the same direction. Two people are sitting between F and J who is third to the right of H. One person is sitting between the person whose lucky number is 5 and G.
Q. Which of the following statements are true?
(i) The person whose lucky number is 9 is fourth to the left of the person whose lucky number is 3.
(ii) No one has 7 as a lucky number.
(iii) One person is sitting between D and I.
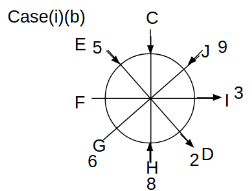
Eight people C, D, E, F, G, H, I and J are sitting around a circular table. Some of them are facing the center of the circle. While some of them are facing opposite to the center of the circle. Each person has a different lucky number from 1 to 9.
The direction of E is opposite to D. The person whose lucky number is 3 is second to the left of C. The difference between the lucky numbers of G and J is three. H is immediately right of the one whose lucky number is an even prime number who is not an immediate neighbour of F. The sum of the lucky number is J and H is equal to the lucky number of F. The immediate neighbours of the person whose lucky number is 4 face opposite directions to each other. The person whose lucky number is the multiple of 5 is third to the left of I whose immediate neighbours face opposite directions to each other. F is second to the left of one whose lucky number is the cubic number but not 1. The difference between the lucky numbers of E and G is one. The lucky numbers of J and C are not a prime number. The lucky number of E is not an even number. G sits exactly between F and H. The person whose lucky number is 3 does not face the center of the table. E is immediately right of C and both of them face the same direction. Two people are sitting between F and J who is third to the right of H. One person is sitting between the person whose lucky number is 5 and G.
Q. Which of the following people has the largest lucky number?
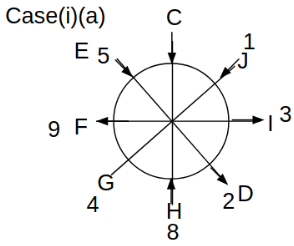
Eight people C, D, E, F, G, H, I and J are sitting around a circular table. Some of them are facing the center of the circle. While some of them are facing opposite to the center of the circle. Each person has a different lucky number from 1 to 9.
The direction of E is opposite to D. The person whose lucky number is 3 is second to the left of C. The difference between the lucky numbers of G and J is three. H is immediately right of the one whose lucky number is an even prime number who is not an immediate neighbour of F. The sum of the lucky number is J and H is equal to the lucky number of F. The immediate neighbours of the person whose lucky number is 4 face opposite directions to each other. The person whose lucky number is the multiple of 5 is third to the left of I whose immediate neighbours face opposite directions to each other. F is second to the left of one whose lucky number is the cubic number but not 1. The difference between the lucky numbers of E and G is one. The lucky numbers of J and C are not a prime number. The lucky number of E is not an even number. G sits exactly between F and H. The person whose lucky number is 3 does not face the center of the table. E is immediately right of C and both of them face the same direction. Two people are sitting between F and J who is third to the right of H. One person is sitting between the person whose lucky number is 5 and G.
Q. If all the people are arranged in alphabetical order around the circular table starting from C in the anticlockwise direction, then the position of how many people remain unchanged (except C).
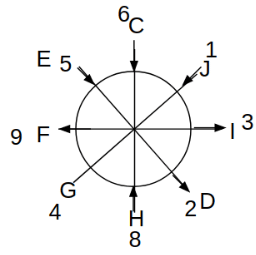
Eight people C, D, E, F, G, H, I and J are sitting around a circular table. Some of them are facing the center of the circle. While some of them are facing opposite to the center of the circle. Each person has a different lucky number from 1 to 9.
The direction of E is opposite to D. The person whose lucky number is 3 is second to the left of C. The difference between the lucky numbers of G and J is three. H is immediately right of the one whose lucky number is an even prime number who is not an immediate neighbour of F. The sum of the lucky number is J and H is equal to the lucky number of F. The immediate neighbours of the person whose lucky number is 4 face opposite directions to each other. The person whose lucky number is the multiple of 5 is third to the left of I whose immediate neighbours face opposite directions to each other. F is second to the left of one whose lucky number is the cubic number but not 1. The difference between the lucky numbers of E and G is one. The lucky numbers of J and C are not a prime number. The lucky number of E is not an even number. G sits exactly between F and H. The person whose lucky number is 3 does not face the center of the table. E is immediately right of C and both of them face the same direction. Two people are sitting between F and J who is third to the right of H. One person is sitting between the person whose lucky number is 5 and G.
Q. What is the lucky number of C?
Eight people C, D, E, F, G, H, I and J are sitting around a circular table. Some of them are facing the center of the circle. While some of them are facing opposite to the center of the circle. Each person has a different lucky number from 1 to 9.
The direction of E is opposite to D. The person whose lucky number is 3 is second to the left of C. The difference between the lucky numbers of G and J is three. H is immediately right of the one whose lucky number is an even prime number who is not an immediate neighbour of F. The sum of the lucky number is J and H is equal to the lucky number of F. The immediate neighbours of the person whose lucky number is 4 face opposite directions to each other. The person whose lucky number is the multiple of 5 is third to the left of I whose immediate neighbours face opposite directions to each other. F is second to the left of one whose lucky number is the cubic number but not 1. The difference between the lucky numbers of E and G is one. The lucky numbers of J and C are not a prime number. The lucky number of E is not an even number. G sits exactly between F and H. The person whose lucky number is 3 does not face the center of the table. E is immediately right of C and both of them face the same direction. Two people are sitting between F and J who is third to the right of H. One person is sitting between the person whose lucky number is 5 and G.
Q. The direction of how many people cannot be determined definitely.
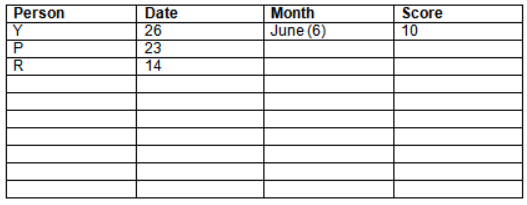
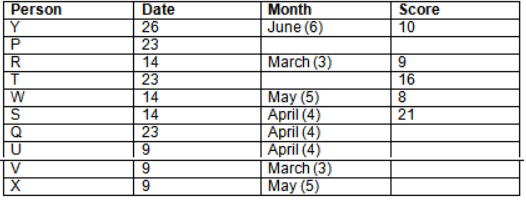
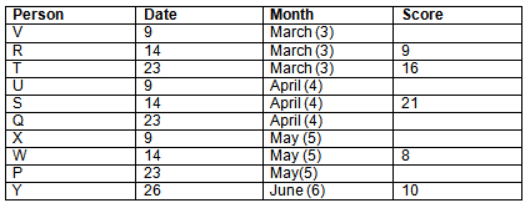
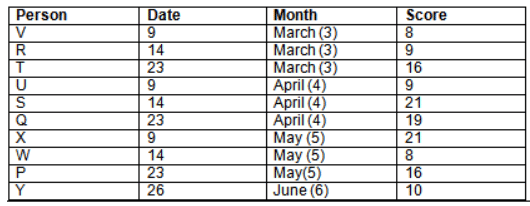
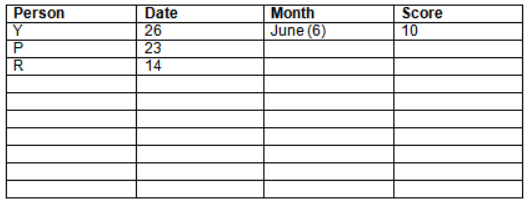
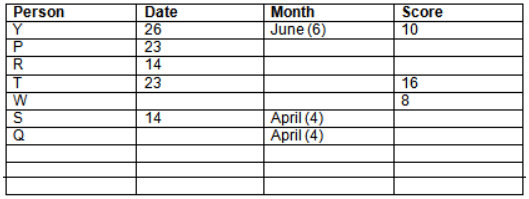
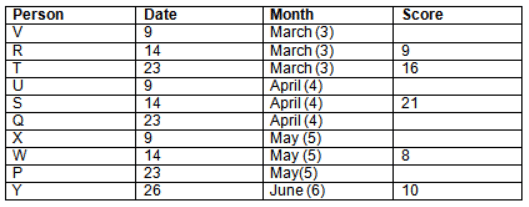
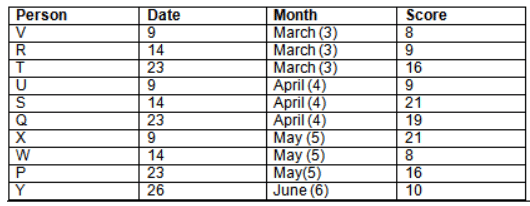
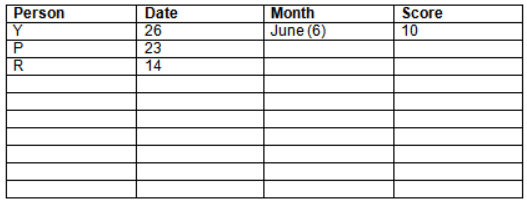
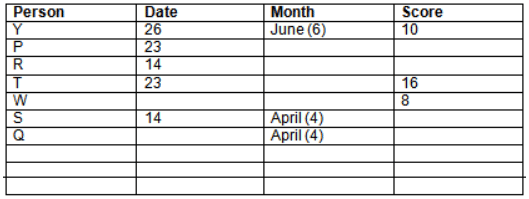
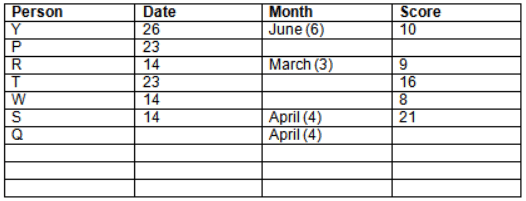
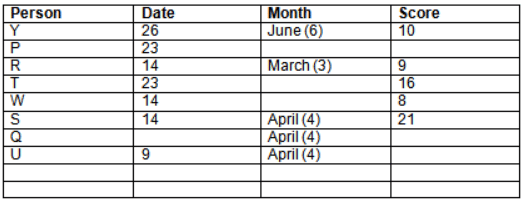
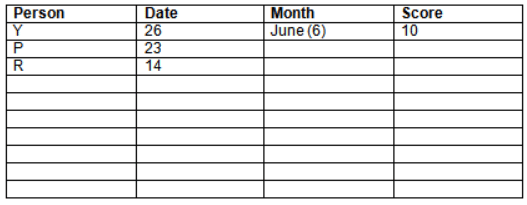
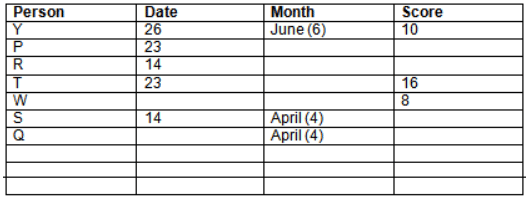
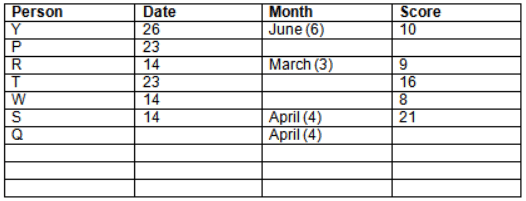
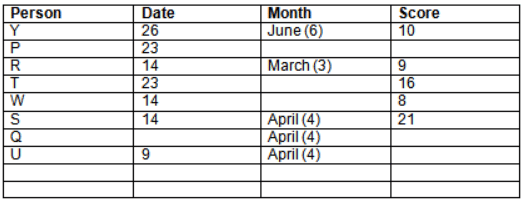
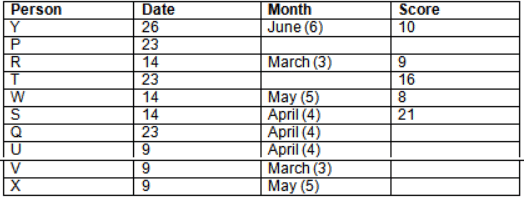
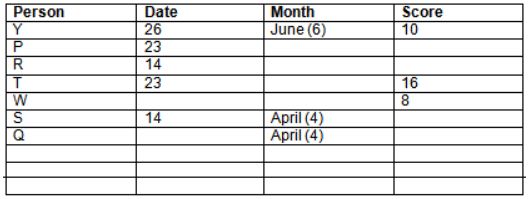
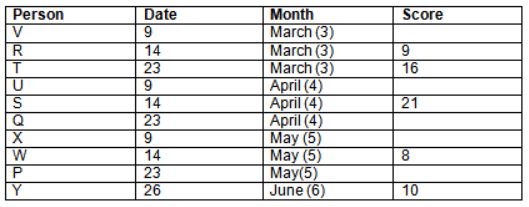
Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below:23th
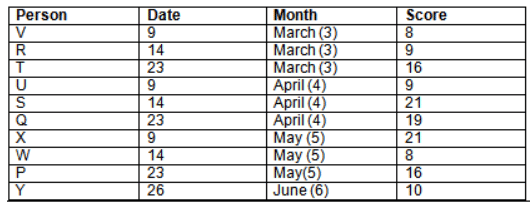
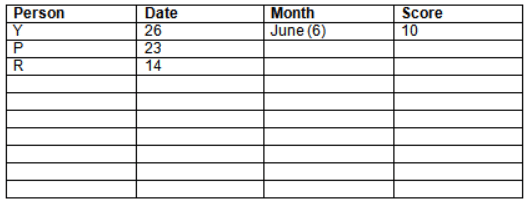
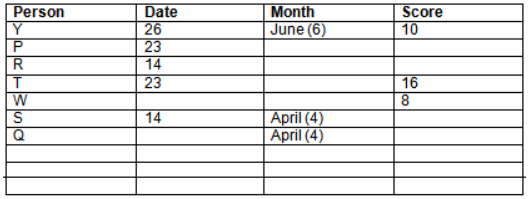
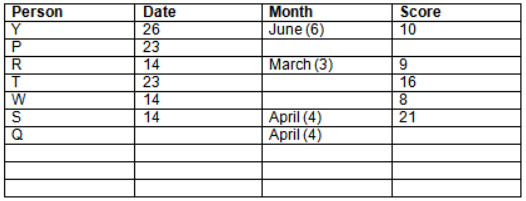
There are 10 persons – P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X and Y had exams on dates 9th, 14th, 23th
and 26th of each month – March, April, May and June but not necessarily in the same order. Not more than three persons have exam on same date and same month. Each person had different score viz. 16, 19, 21, 8, 9 and 10 but not necessarily in the same order.
The one who had exam on even number date scored 21. The one who had exam in March had a score of 8. P had exam on 23th. T scored two times that of W but does not have exam in same month. Q had exam on even number month. V’s exam was not in May. Only Y had exam in the month of June on 26th and scored 10 marks. Neither X nor W had exam in March. R had exam on 14th and had a score equal to the square of month number. S had exam on even date and in even month. T had exam on prime date and in prime number month. W had scored 6 marks less than his date of exam. The one who had exam on 23th had a prime score. The one who had exam earlier than Q had scored 5 marks more than its month number. X had scored same as sum of T’s score and its month number. The one who had exam after W had scored two times that of W. U had exam on date such that it is the square of earlier month number.
Q. Who among the following had exam in May?
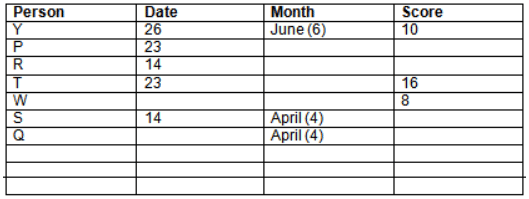
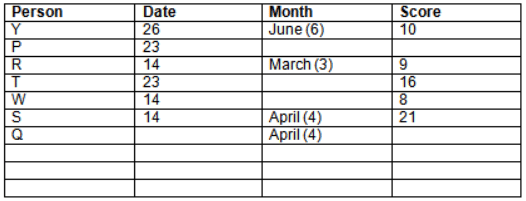
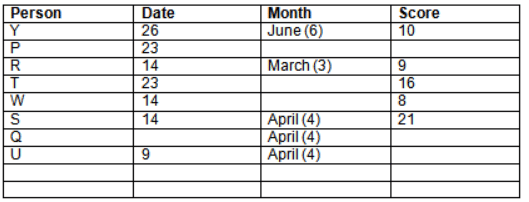
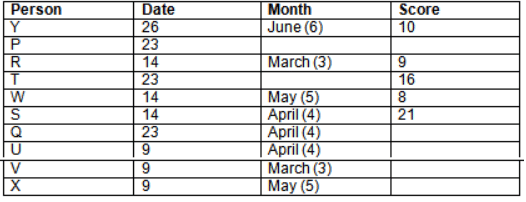
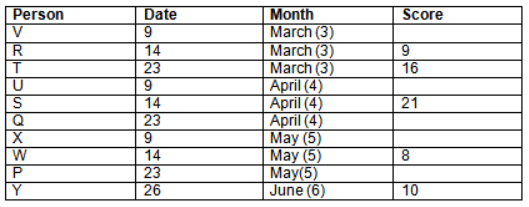
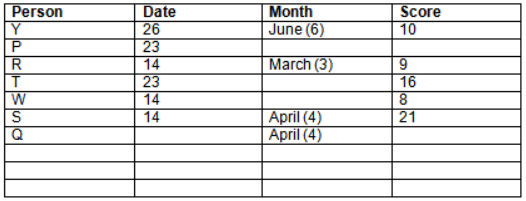
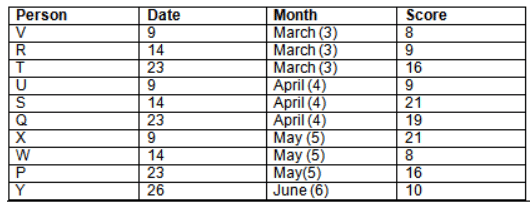
Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below:23th
There are 10 persons – P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X and Y had exams on dates 9th, 14th, 23th
and 26th of each month – March, April, May and June but not necessarily in the same order. Not more than three persons have exam on same date and same month. Each person had different score viz. 16, 19, 21, 8, 9 and 10 but not necessarily in the same order.
The one who had exam on even number date scored 21. The one who had exam in March had a score of 8. P had exam on 23th. T scored two times that of W but does not have exam in same month. Q had exam on even number month. V’s exam was not in May. Only Y had exam in the month of June on 26th and scored 10 marks. Neither X nor W had exam in March. R had exam on 14th and had a score equal to the square of month number. S had exam on even date and in even month. T had exam on prime date and in prime number month. W had scored 6 marks less than his date of exam. The one who had exam on 23th had a prime score. The one who had exam earlier than Q had scored 5 marks more than its month number. X had scored same as sum of T’s score and its month number. The one who had exam after W had scored two times that of W. U had exam on date such that it is the square of earlier month number.
Q. Who among the following had exam on same date as W?
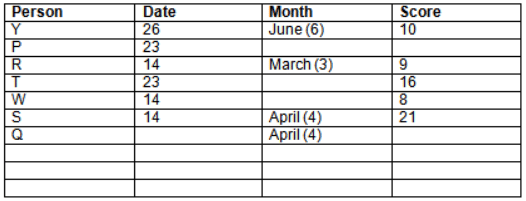
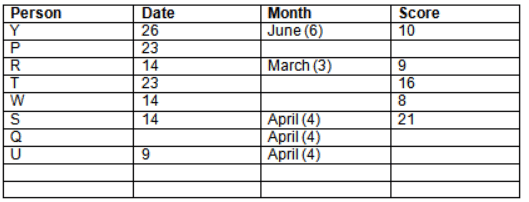
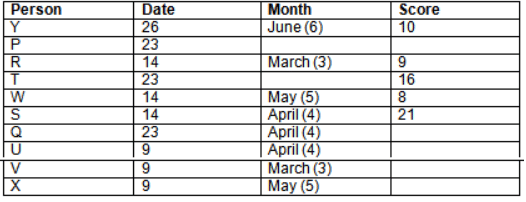
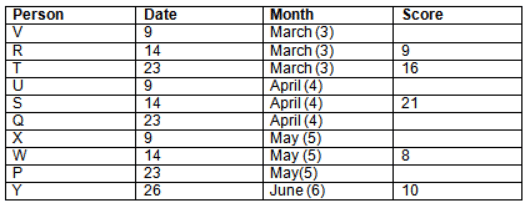
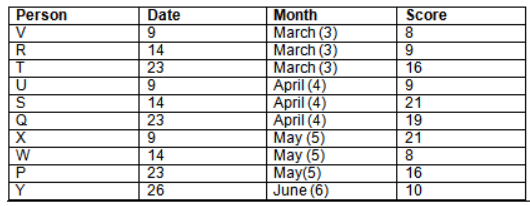
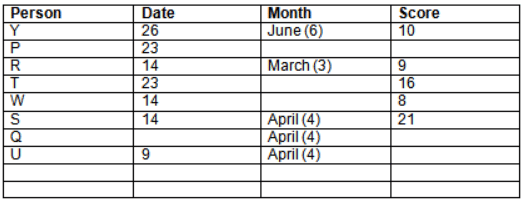
Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below:23th
There are 10 persons – P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X and Y had exams on dates 9th, 14th, 23th
and 26th of each month – March, April, May and June but not necessarily in the same order. Not more than three persons have exam on same date and same month. Each person had different score viz. 16, 19, 21, 8, 9 and 10 but not necessarily in the same order.
The one who had exam on even number date scored 21. The one who had exam in March had a score of 8. P had exam on 23th. T scored two times that of W but does not have exam in same month. Q had exam on even number month. V’s exam was not in May. Only Y had exam in the month of June on 26th and scored 10 marks. Neither X nor W had exam in March. R had exam on 14th and had a score equal to the square of month number. S had exam on even date and in even month. T had exam on prime date and in prime number month. W had scored 6 marks less than his date of exam. The one who had exam on 23th had a prime score. The one who had exam earlier than Q had scored 5 marks more than its month number. X had scored same as sum of T’s score and its month number. The one who had exam after W had scored two times that of W. U had exam on date such that it is the square of earlier month number.
Q. Who among the following had exam on 14th April?
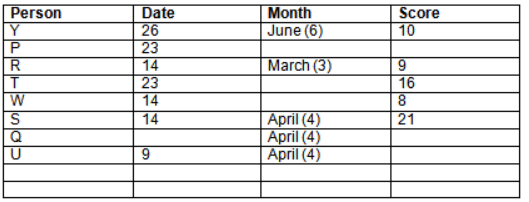
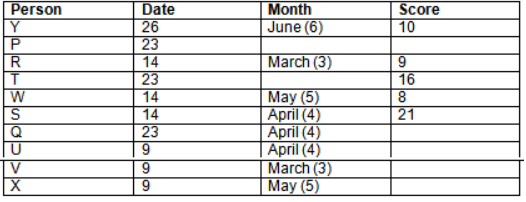
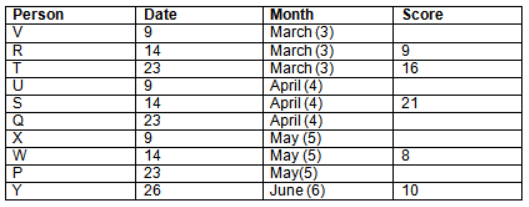
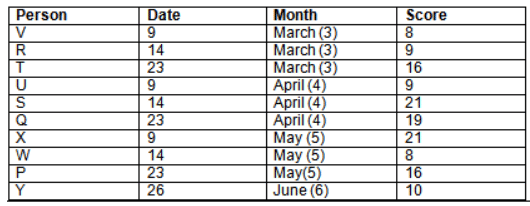
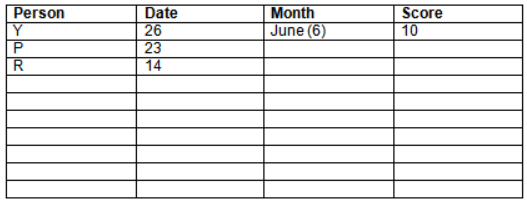
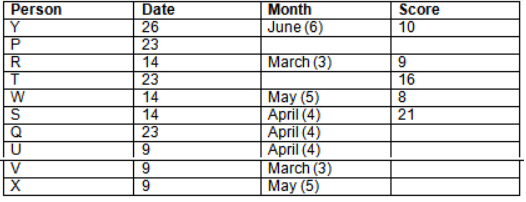
Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below:23th
There are 10 persons – P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X and Y had exams on dates 9th, 14th, 23th
and 26th of each month – March, April, May and June but not necessarily in the same order. Not more than three persons have exam on same date and same month. Each person had different score viz. 16, 19, 21, 8, 9 and 10 but not necessarily in the same order.
The one who had exam on even number date scored 21. The one who had exam in March had a score of 8. P had exam on 23th. T scored two times that of W but does not have exam in same month. Q had exam on even number month. V’s exam was not in May. Only Y had exam in the month of June on 26th and scored 10 marks. Neither X nor W had exam in March. R had exam on 14th and had a score equal to the square of month number. S had exam on even date and in even month. T had exam on prime date and in prime number month. W had scored 6 marks less than his date of exam. The one who had exam on 23th had a prime score. The one who had exam earlier than Q had scored 5 marks more than its month number. X had scored same as sum of T’s score and its month number. The one who had exam after W had scored two times that of W. U had exam on date such that it is the square of earlier month number.
Q. How many persons had exam before X?
Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below:23th
There are 10 persons – P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X and Y had exams on dates 9th, 14th, 23th
and 26th of each month – March, April, May and June but not necessarily in the same order. Not more than three persons have exam on same date and same month. Each person had different score viz. 16, 19, 21, 8, 9 and 10 but not necessarily in the same order.
The one who had exam on even number date scored 21. The one who had exam in March had a score of 8. P had exam on 23th. T scored two times that of W but does not have exam in same month. Q had exam on even number month. V’s exam was not in May. Only Y had exam in the month of June on 26th and scored 10 marks. Neither X nor W had exam in March. R had exam on 14th and had a score equal to the square of month number. S had exam on even date and in even month. T had exam on prime date and in prime number month. W had scored 6 marks less than his date of exam. The one who had exam on 23th had a prime score. The one who had exam earlier than Q had scored 5 marks more than its month number. X had scored same as sum of T’s score and its month number. The one who had exam after W had scored two times that of W. U had exam on date such that it is the square of earlier month number.
Q. Who among the following scored 16 marks?
Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below:23th
There are 10 persons – P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X and Y had exams on dates 9th, 14th, 23th
and 26th of each month – March, April, May and June but not necessarily in the same order. Not more than three persons have exam on same date and same month. Each person had different score viz. 16, 19, 21, 8, 9 and 10 but not necessarily in the same order.
The one who had exam on even number date scored 21. The one who had exam in March had a score of 8. P had exam on 23th. T scored two times that of W but does not have exam in same month. Q had exam on even number month. V’s exam was not in May. Only Y had exam in the month of June on 26th and scored 10 marks. Neither X nor W had exam in March. R had exam on 14th and had a score equal to the square of month number. S had exam on even date and in even month. T had exam on prime date and in prime number month. W had scored 6 marks less than his date of exam. The one who had exam on 23th had a prime score. The one who had exam earlier than Q had scored 5 marks more than its month number. X had scored same as sum of T’s score and its month number. The one who had exam after W had scored two times that of W. U had exam on date such that it is the square of earlier month number.
Q. What is the sum of scores of U and P?
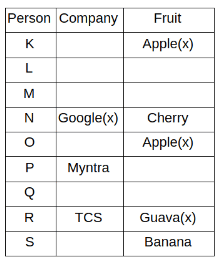
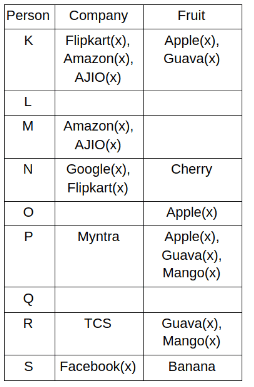
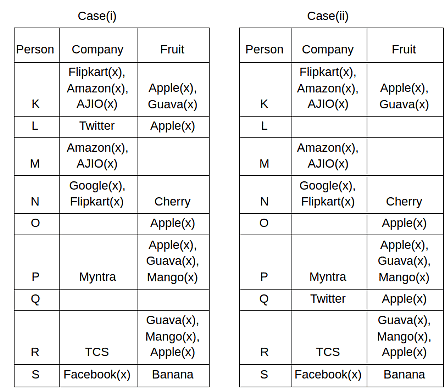
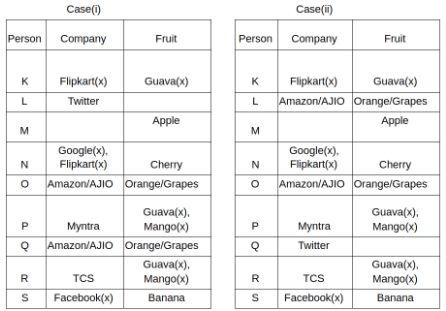
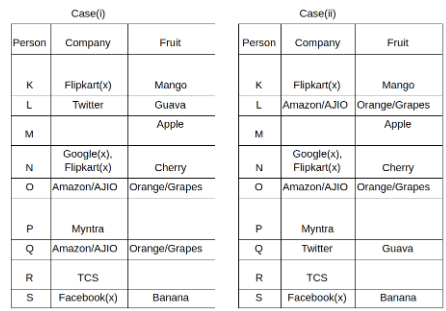
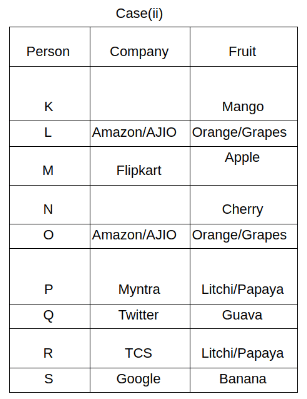
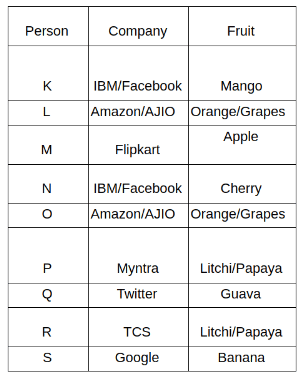
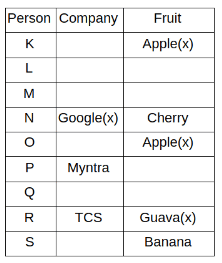
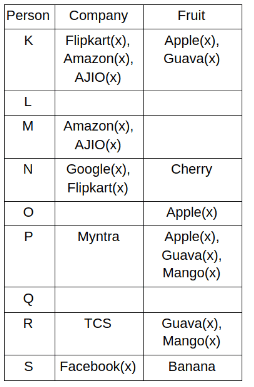
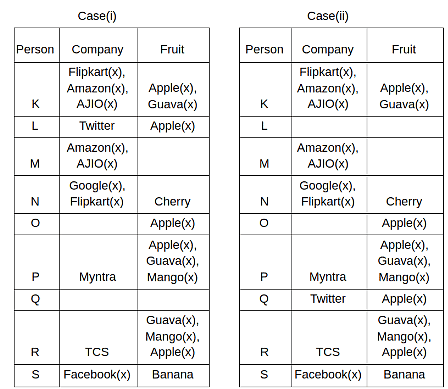
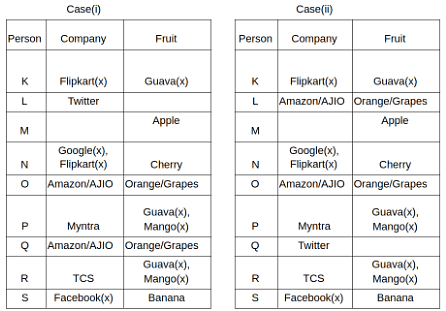
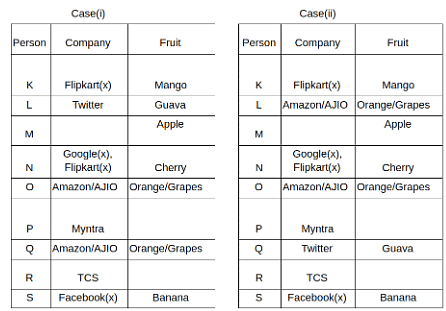
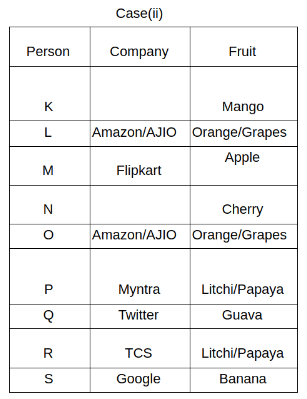
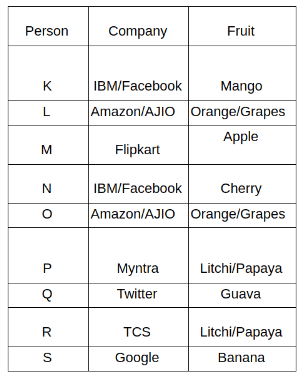
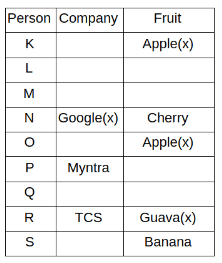
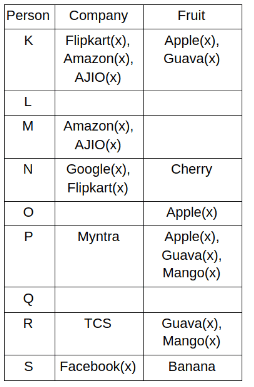
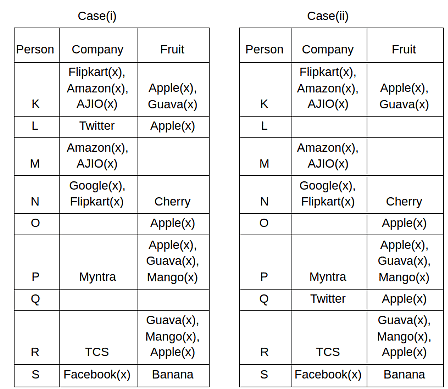
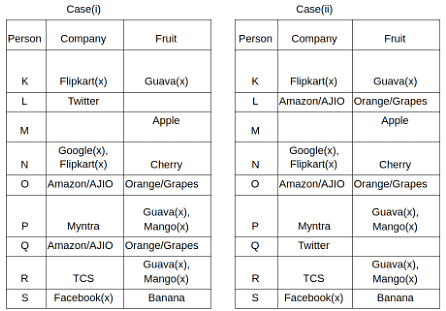
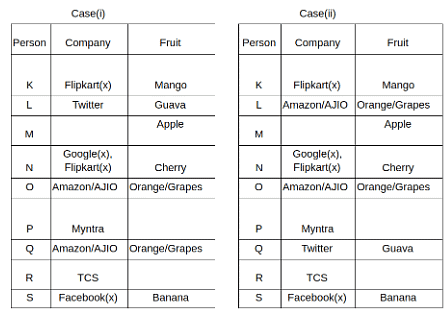
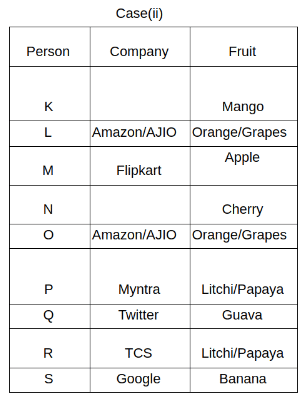
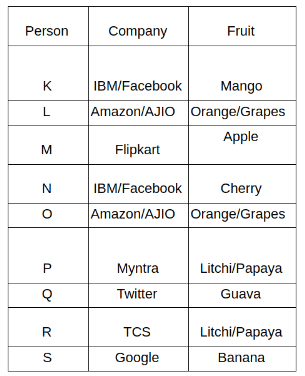
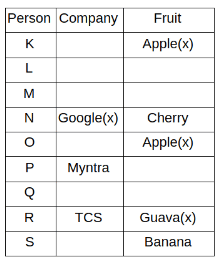
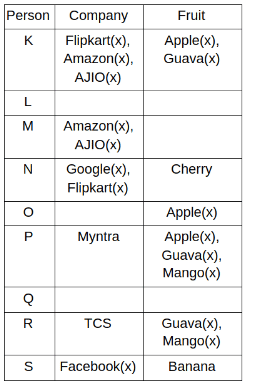
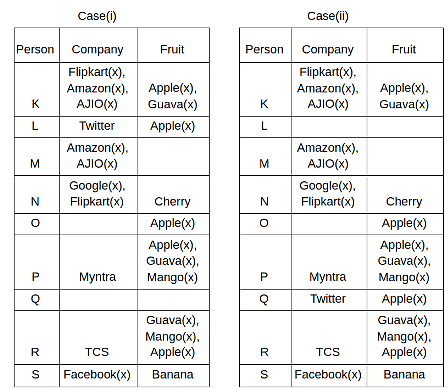
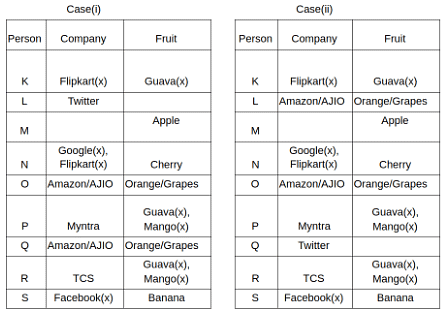
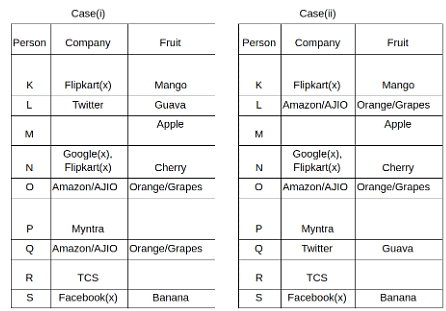
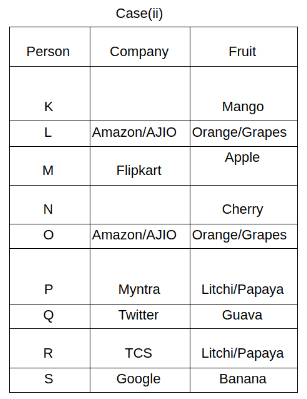
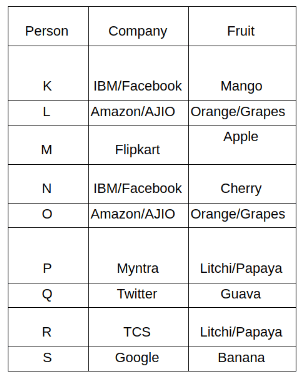
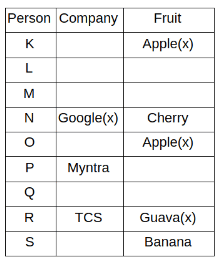
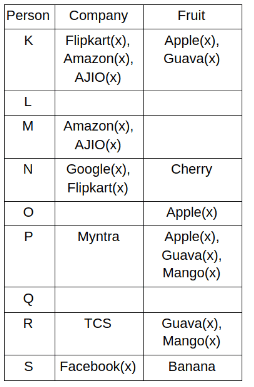
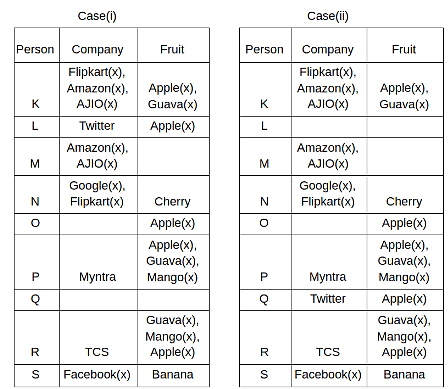
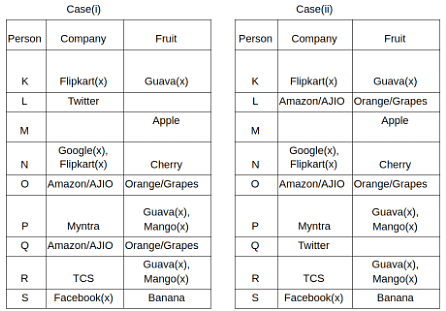
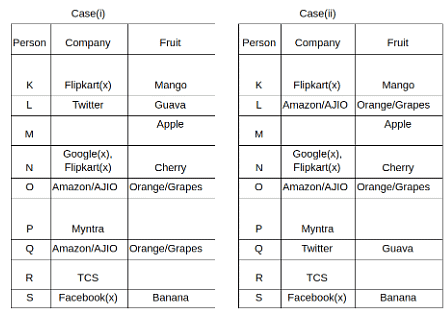
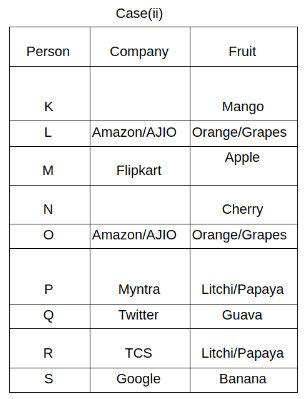
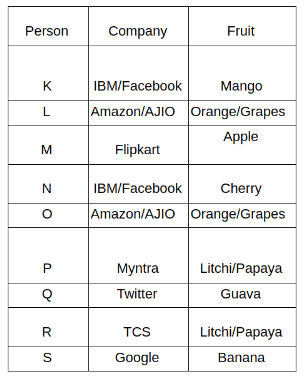
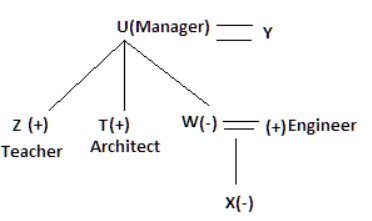
Nine people K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R and S are working in nine different companies namely Google, Facebook, Twitter, IBM, TCS, Myntra, Flipkart, Amazon and AJIO. Each person likes different fruits namely Apple, Banana, Grapes, Mango, Cherry, Litchi, Guava, Papaya and Orange. The one who is working in AJIO likes Grapes. R is working in TCS but doesn't like Guava. N likes Cherry but he is not working in Google. The one who likes Apple is not working in Myntra. Neither O nor K likes Apple. Either L or Q is working in Twitter. The one who likes Orange is working in Amazon. P is working in Myntra. S likes Banana. The one who likes Apple is not working in a company whose name starts with ‘T’. Neither M nor K is working in a company whose name starts with ‘A’. Neither K nor P likes Guava. Neither P nor R likes Mango. Both the one who likes Mango and the one who likes Apple are not working in Google. S is not working in Facebook. Neither K nor N is working in Flipkart. L doesn't like Guava.
Q. N is working in which of the following companies?
Nine people K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R and S are working in nine different companies namely Google, Facebook, Twitter, IBM, TCS, Myntra, Flipkart, Amazon and AJIO. Each person likes different fruits namely Apple, Banana, Grapes, Mango, Cherry, Litchi, Guava, Papaya and Orange. The one who is working in AJIO likes Grapes. R is working in TCS but doesn't like Guava. N likes Cherry but he is not working in Google. The one who likes Apple is not working in Myntra. Neither O nor K likes Apple. Either L or Q is working in Twitter. The one who likes Orange is working in Amazon. P is working in Myntra. S likes Banana. The one who likes Apple is not working in a company whose name starts with ‘T’. Neither M nor K is working in a company whose name starts with ‘A’. Neither K nor P likes Guava. Neither P nor R likes Mango. Both the one who likes Mango and the one who likes Apple are not working in Google. S is not working in Facebook. Neither K nor N is working in Flipkart. L doesn't like Guava.
Q. The one who is working in TCS likes which of the following fruits?
Nine people K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R and S are working in nine different companies namely Google, Facebook, Twitter, IBM, TCS, Myntra, Flipkart, Amazon and AJIO. Each person likes different fruits namely Apple, Banana, Grapes, Mango, Cherry, Litchi, Guava, Papaya and Orange. The one who is working in AJIO likes Grapes. R is working in TCS but doesn't like Guava. N likes Cherry but he is not working in Google. The one who likes Apple is not working in Myntra. Neither O nor K likes Apple. Either L or Q is working in Twitter. The one who likes Orange is working in Amazon. P is working in Myntra. S likes Banana. The one who likes Apple is not working in a company whose name starts with ‘T’. Neither M nor K is working in a company whose name starts with ‘A’. Neither K nor P likes Guava. Neither P nor R likes Mango. Both the one who likes Mango and the one who likes Apple are not working in Google. S is not working in Facebook. Neither K nor N is working in Flipkart. L doesn't like Guava.
Q. Which of the following statements is/are definitely true?
(i) O is working in Amazon.
(ii) P likes Papaya.
(iii) M is working in either Flipkart or Facebook.
Nine people K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R and S are working in nine different companies namely Google, Facebook, Twitter, IBM, TCS, Myntra, Flipkart, Amazon and AJIO. Each person likes different fruits namely Apple, Banana, Grapes, Mango, Cherry, Litchi, Guava, Papaya and Orange. The one who is working in AJIO likes Grapes. R is working in TCS but doesn't like Guava. N likes Cherry but he is not working in Google. The one who likes Apple is not working in Myntra. Neither O nor K likes Apple. Either L or Q is working in Twitter. The one who likes Orange is working in Amazon. P is working in Myntra. S likes Banana. The one who likes Apple is not working in a company whose name starts with ‘T’. Neither M nor K is working in a company whose name starts with ‘A’. Neither K nor P likes Guava. Neither P nor R likes Mango. Both the one who likes Mango and the one who likes Apple are not working in Google. S is not working in Facebook. Neither K nor N is working in Flipkart. L doesn't like Guava.
Q. Who among the following likes Mango?
Nine people K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R and S are working in nine different companies namely Google, Facebook, Twitter, IBM, TCS, Myntra, Flipkart, Amazon and AJIO. Each person likes different fruits namely Apple, Banana, Grapes, Mango, Cherry, Litchi, Guava, Papaya and Orange. The one who is working in AJIO likes Grapes. R is working in TCS but doesn't like Guava. N likes Cherry but he is not working in Google. The one who likes Apple is not working in Myntra. Neither O nor K likes Apple. Either L or Q is working in Twitter. The one who likes Orange is working in Amazon. P is working in Myntra. S likes Banana. The one who likes Apple is not working in a company whose name starts with ‘T’. Neither M nor K is working in a company whose name starts with ‘A’. Neither K nor P likes Guava. Neither P nor R likes Mango. Both the one who likes Mango and the one who likes Apple are not working in Google. S is not working in Facebook. Neither K nor N is working in Flipkart. L doesn't like Guava.
Q. Who among the following is working in AJIO?
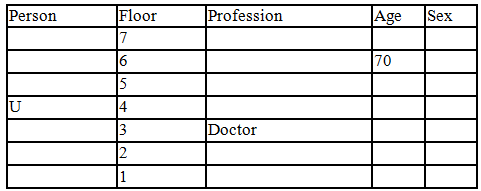
Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below:
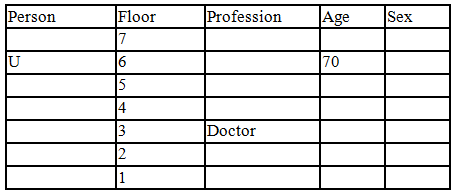
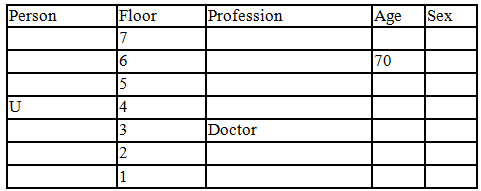
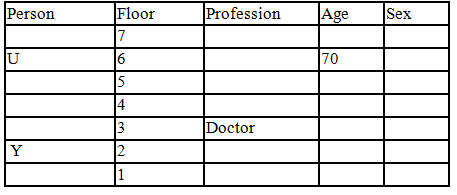
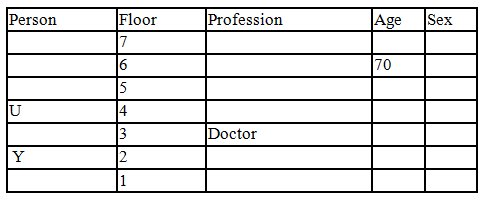
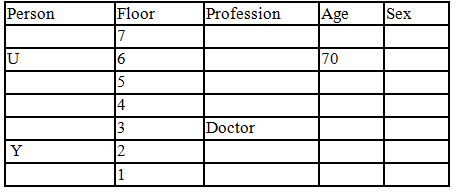
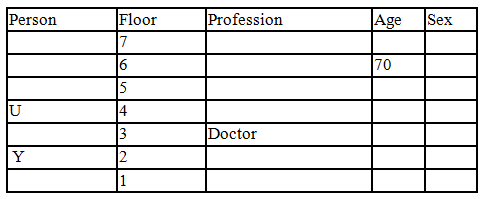
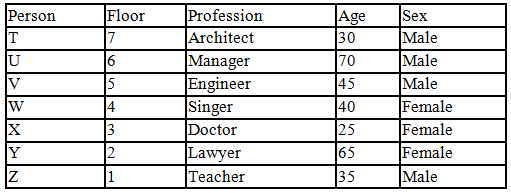
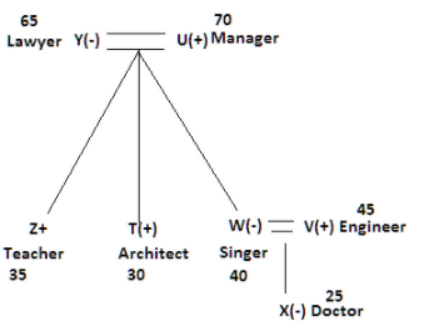
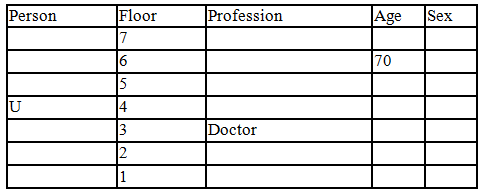
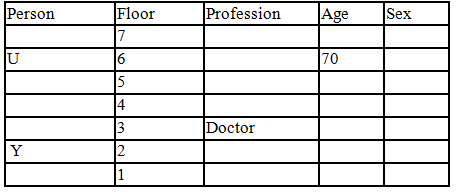
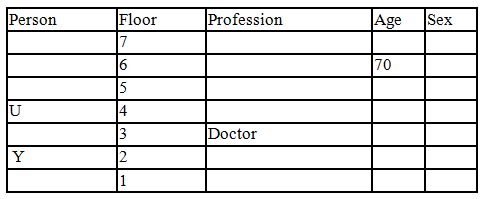
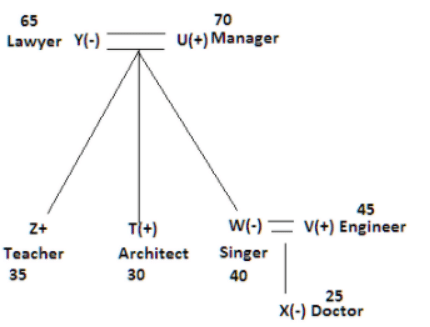
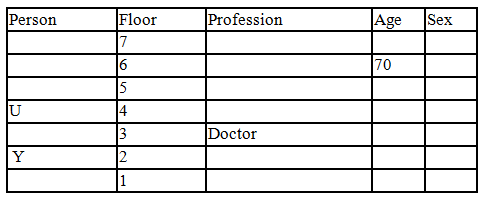
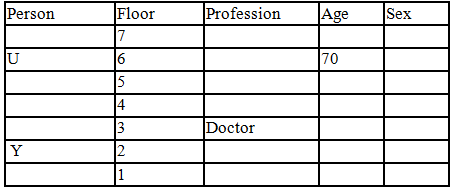
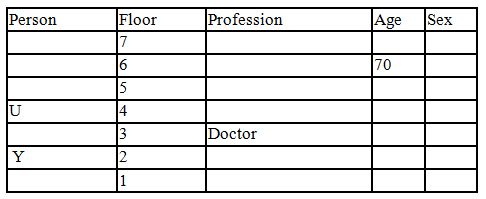
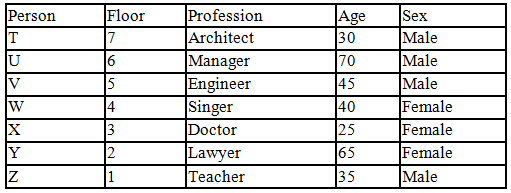
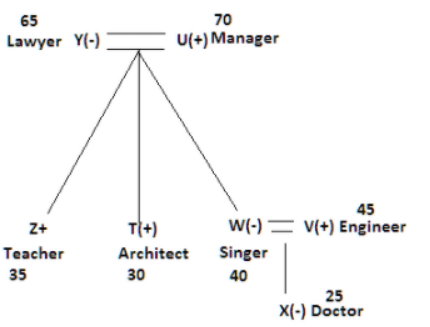
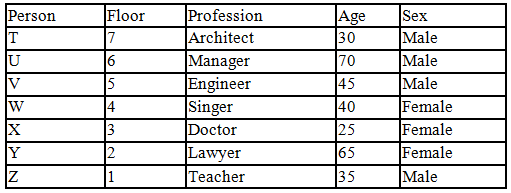
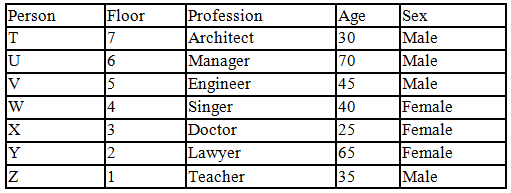
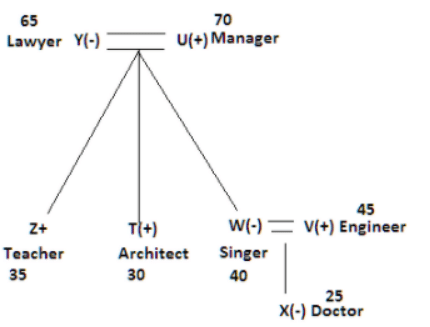
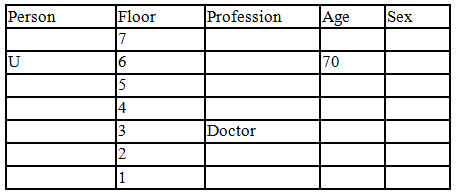
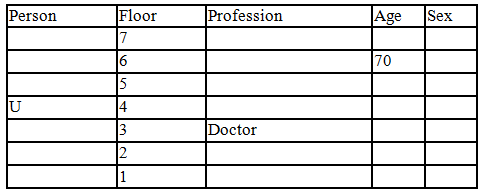
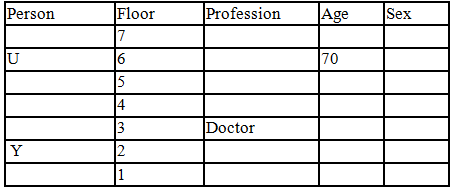
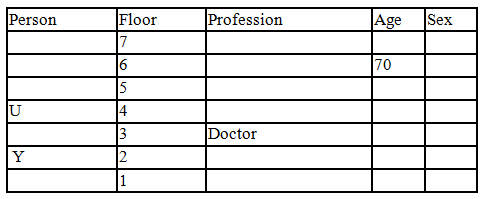
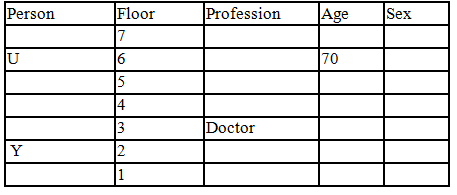
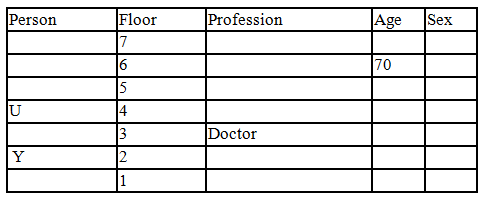
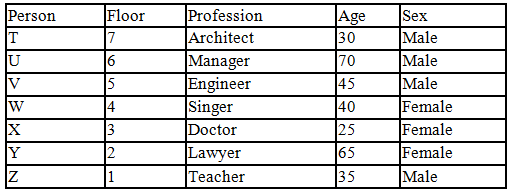
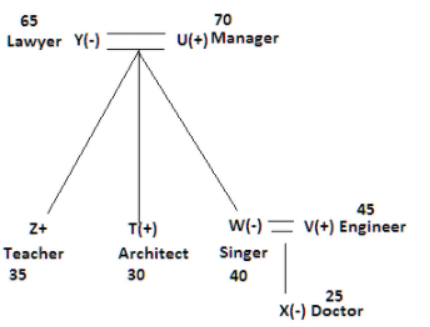
There seven family members T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z lives on different floors of a building in which the first floor is numbered 1 and the topmost floor is numbered 7. Each member has different age 65, 70, 45, 40, 35, 30 and 25. Each member has different profession Architecture, Engineer, Doctor, Lawyer, Teacher and Singer.
Manager is elder to Lawyer. Z is brother of T, who is Architect. One who lives on sixth floor is the oldest in the family. The one who is a Doctor lives on 3rd floor and unmarried also. W is sister of T, who is five year younger to his brother and lives in odd numbered floor but not immediately above Singer. Age of an Engineer is 45 years, and he is a son-in-law of Y who lives on 2nd floor. The one who is Teacher is brother-in-law of V who has a son whose profession is Doctor. U is a Manager, and he has two sons and one daughter. X is a female and is neither a Teacher nor a Singer. The one who is an Engineer lives in odd numbered floor, and he is ten years older to his brother-in-law. Z is not an Engineer nor lives on floor number more than 3. The singer is married and her age is ten times the number floor where she/he lives. The one who is the Teacher is the maternal uncle of X whose age is a perfect square and lives on immediately above who is Lawyer. Y is Lawyer and married to U who lives on even numbered floor above 3. Difference between the age of Manager and Lawyer is 5. The one who is Teacher is younger to Singer but older to one who is Architecture. There are only three females in the family and two married couples. Both Y and U whose age is LCM of a fourteen and five don’t have siblings.
Q. Which of the following combination is true?
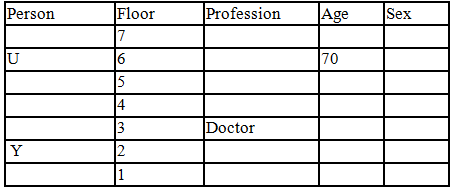
Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below:
There seven family members T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z lives on different floors of a building in which the first floor is numbered 1 and the topmost floor is numbered 7. Each member has different age 65, 70, 45, 40, 35, 30 and 25. Each member has different profession Architecture, Engineer, Doctor, Lawyer, Teacher and Singer.
Manager is elder to Lawyer. Z is brother of T, who is Architect. One who lives on sixth floor is the oldest in the family. The one who is a Doctor lives on 3rd floor and unmarried also. W is sister of T, who is five year younger to his brother and lives in odd numbered floor but not immediately above Singer. Age of an Engineer is 45 years, and he is a son-in-law of Y who lives on 2nd floor. The one who is Teacher is brother-in-law of V who has a son whose profession is Doctor. U is a Manager, and he has two sons and one daughter. X is a female and is neither a Teacher nor a Singer. The one who is an Engineer lives in odd numbered floor, and he is ten years older to his brother-in-law. Z is not an Engineer nor lives on floor number more than 3. The singer is married and her age is ten times the number floor where she/he lives. The one who is the Teacher is the maternal uncle of X whose age is a perfect square and lives on immediately above who is Lawyer. Y is Lawyer and married to U who lives on even numbered floor above 3. Difference between the age of Manager and Lawyer is 5. The one who is Teacher is younger to Singer but older to one who is Architecture. There are only three females in the family and two married couples. Both Y and U whose age is LCM of a fourteen and five don’t have siblings.
Q. Which of the following statement/s are true?
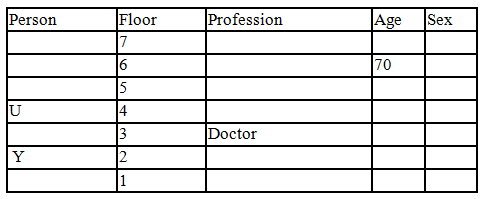
Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below:
There seven family members T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z lives on different floors of a building in which the first floor is numbered 1 and the topmost floor is numbered 7. Each member has different age 65, 70, 45, 40, 35, 30 and 25. Each member has different profession Architecture, Engineer, Doctor, Lawyer, Teacher and Singer.
Manager is elder to Lawyer. Z is brother of T, who is Architect. One who lives on sixth floor is the oldest in the family. The one who is a Doctor lives on 3rd floor and unmarried also. W is sister of T, who is five year younger to his brother and lives in odd numbered floor but not immediately above Singer. Age of an Engineer is 45 years, and he is a son-in-law of Y who lives on 2nd floor. The one who is Teacher is brother-in-law of V who has a son whose profession is Doctor. U is a Manager, and he has two sons and one daughter. X is a female and is neither a Teacher nor a Singer. The one who is an Engineer lives in odd numbered floor, and he is ten years older to his brother-in-law. Z is not an Engineer nor lives on floor number more than 3. The singer is married and her age is ten times the number floor where she/he lives. The one who is the Teacher is the maternal uncle of X whose age is a perfect square and lives on immediately above who is Lawyer. Y is Lawyer and married to U who lives on even numbered floor above 3. Difference between the age of Manager and Lawyer is 5. The one who is Teacher is younger to Singer but older to one who is Architecture. There are only three females in the family and two married couples. Both Y and U whose age is LCM of a fourteen and five don’t have siblings.
Q. Who is architect and by how much year he is younger to the person who is singer?
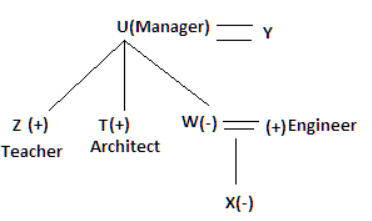
Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below:
There seven family members T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z lives on different floors of a building in which the first floor is numbered 1 and the topmost floor is numbered 7. Each member has different age 65, 70, 45, 40, 35, 30 and 25. Each member has different profession Architecture, Engineer, Doctor, Lawyer, Teacher and Singer.
Manager is elder to Lawyer. Z is brother of T, who is Architect. One who lives on sixth floor is the oldest in the family. The one who is a Doctor lives on 3rd floor and unmarried also. W is sister of T, who is five year younger to his brother and lives in odd numbered floor but not immediately above Singer. Age of an Engineer is 45 years, and he is a son-in-law of Y who lives on 2nd floor. The one who is Teacher is brother-in-law of V who has a son whose profession is Doctor. U is a Manager, and he has two sons and one daughter. X is a female and is neither a Teacher nor a Singer. The one who is an Engineer lives in odd numbered floor, and he is ten years older to his brother-in-law. Z is not an Engineer nor lives on floor number more than 3. The singer is married and her age is ten times the number floor where she/he lives. The one who is the Teacher is the maternal uncle of X whose age is a perfect square and lives on immediately above who is Lawyer. Y is Lawyer and married to U who lives on even numbered floor above 3. Difference between the age of Manager and Lawyer is 5. The one who is Teacher is younger to Singer but older to one who is Architecture. There are only three females in the family and two married couples. Both Y and U whose age is LCM of a fourteen and five don’t have siblings.
Q. Which of the flowing pairs represents two husbands of married couples?
Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below:
There seven family members T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z lives on different floors of a building in which the first floor is numbered 1 and the topmost floor is numbered 7. Each member has different age 65, 70, 45, 40, 35, 30 and 25. Each member has different profession Architecture, Engineer, Doctor, Lawyer, Teacher and Singer.
Manager is elder to Lawyer. Z is brother of T, who is Architect. One who lives on sixth floor is the oldest in the family. The one who is a Doctor lives on 3rd floor and unmarried also. W is sister of T, who is five year younger to his brother and lives in odd numbered floor but not immediately above Singer. Age of an Engineer is 45 years, and he is a son-in-law of Y who lives on 2nd floor. The one who is Teacher is brother-in-law of V who has a son whose profession is Doctor. U is a Manager, and he has two sons and one daughter. X is a female and is neither a Teacher nor a Singer. The one who is an Engineer lives in odd numbered floor, and he is ten years older to his brother-in-law. Z is not an Engineer nor lives on floor number more than 3. The singer is married and her age is ten times the number floor where she/he lives. The one who is the Teacher is the maternal uncle of X whose age is a perfect square and lives on immediately above who is Lawyer. Y is Lawyer and married to U who lives on even numbered floor above 3. Difference between the age of Manager and Lawyer is 5. The one who is Teacher is younger to Singer but older to one who is Architecture. There are only three females in the family and two married couples. Both Y and U whose age is LCM of a fourteen and five don’t have siblings.
Q. How is doctor related to the person who lives on 5th floor of the building?
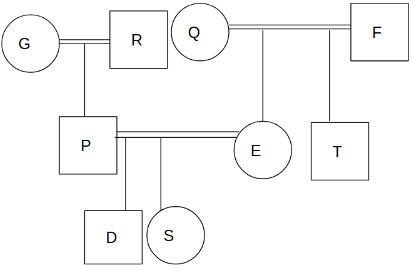
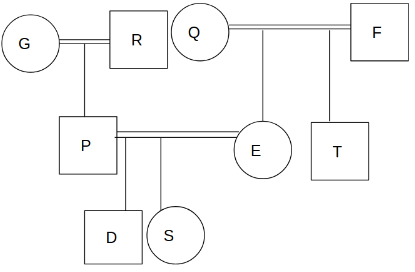
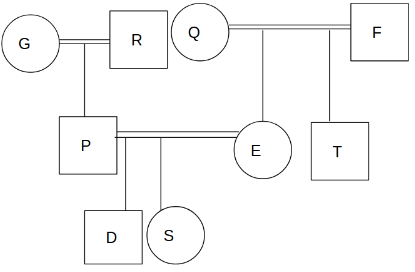
There are nine members P, Q, R, S, T, D, E, F and G in a family. R is the paternal grandfather of D. Q is the mother-in-law of P who has two children. E is the mother of S who is the sister of D. T who is the child of F is the brother-in-law of P. No one in the first generation is unmarried. The number of males are more than the number of females in the family. P has no sibling. Each couple is having at least one child.
Q. How is D related to T?
There are nine members P, Q, R, S, T, D, E, F and G in a family. R is the paternal grandfather of D. Q is the mother-in-law of P who has two children. E is the mother of S who is the sister of D. T who is the child of F is the brother-in-law of P. No one in the first generation is unmarried. The number of males are more than the number of females in the family. P has no sibling. Each couple is having at least one child.
Q. How many males are unmarried in the family?
There are nine members P, Q, R, S, T, D, E, F and G in a family. R is the paternal grandfather of D. Q is the mother-in-law of P who has two children. E is the mother of S who is the sister of D. T who is the child of F is the brother-in-law of P. No one in the first generation is unmarried. The number of males are more than the number of females in the family. P has no sibling. Each couple is having at least one child.
Q. How F is related to E?
Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below-
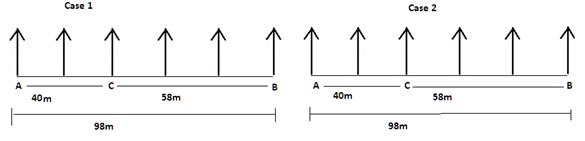
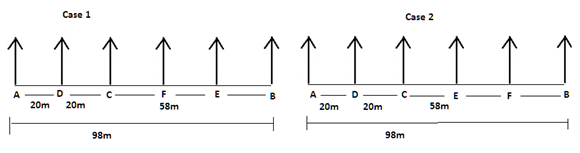
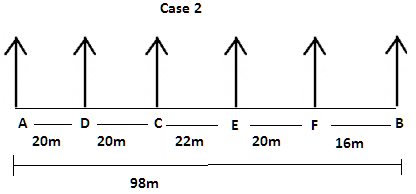
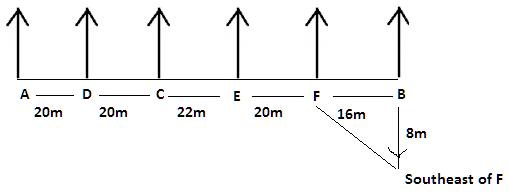
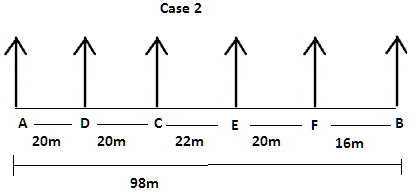
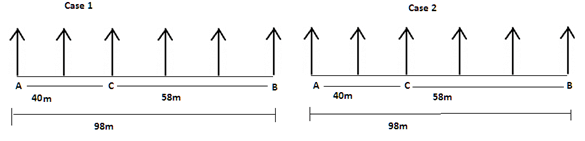
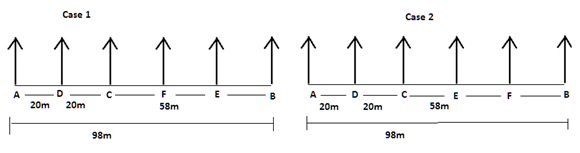
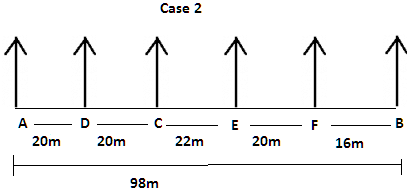
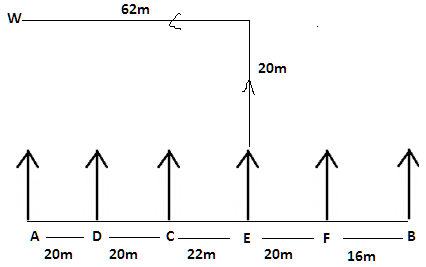
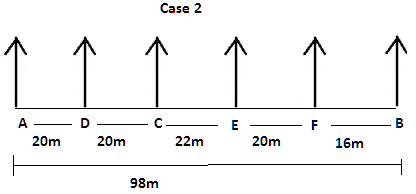
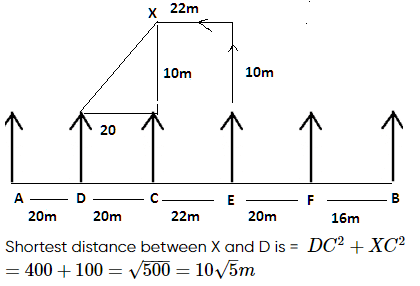
There are six children A, B, C, D, E and F playing in a park. Each of them is sitting in a row at a certain distance facing north but not necessarily in the same order. The total length of the row is 98 m. A and B sit at the extreme ends of the row. A doesn’t sit to right of D. Only two children sit between C and B. The distance between C and B is 58 m. The distance between A and D is same as the distance between C and D. The distance between C and E is 6 m more than the distance between B and F. sits to the right of C but not immediate right. The distance between E and F is 2 m less than the distance between C and E.
Q. If B walks 8m south to reach point Y, then in which direction is Y with respect to F?
Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below-
There are six children A, B, C, D, E and F playing in a park. Each of them is sitting in a row at a certain distance facing north but not necessarily in the same order. The total length of the row is 98 m. A and B sit at the extreme ends of the row. A doesn’t sit to right of D. Only two children sit between C and B. The distance between C and B is 58 m. The distance between A and D is same as the distance between C and D. The distance between C and E is 6 m more than the distance between B and F. sits to the right of C but not immediate right. The distance between E and F is 2 m less than the distance between C and E.
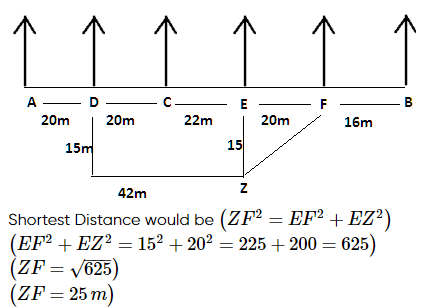
Q. If D walks 15m south, turn left to his left and walks 42m to reach Z, then what is the shortest distance between Z and F.
Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below-
There are six children A, B, C, D, E and F playing in a park. Each of them is sitting in a row at a certain distance facing north but not necessarily in the same order. The total length of the row is 98 m. A and B sit at the extreme ends of the row. A doesn’t sit to right of D. Only two children sit between C and B. The distance between C and B is 58 m. The distance between A and D is same as the distance between C and D. The distance between C and E is 6 m more than the distance between B and F. sits to the right of C but not immediate right. The distance between E and F is 2 m less than the distance between C and E.
Q. If E walks 20m north and turn left, after walking 62m he reach point W. He is in which direction respect with respect to point A and what is the distance between A and W.
Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below-
There are six children A, B, C, D, E and F playing in a park. Each of them is sitting in a row at a certain distance facing north but not necessarily in the same order. The total length of the row is 98 m. A and B sit at the extreme ends of the row. A doesn’t sit to right of D. Only two children sit between C and B. The distance between C and B is 58 m. The distance between A and D is same as the distance between C and D. The distance between C and E is 6 m more than the distance between B and F. sits to the right of C but not immediate right. The distance between E and F is 2 m less than the distance between C and E.
Q. If E walks 10m north, turns to his left and walks 22m to reach point X, then what is the shortest between X and D?
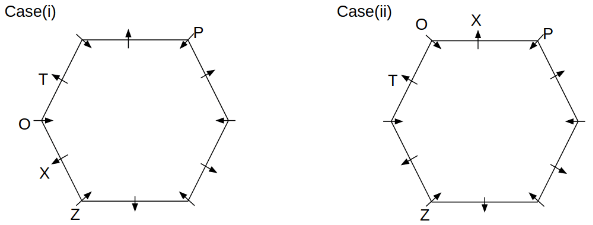
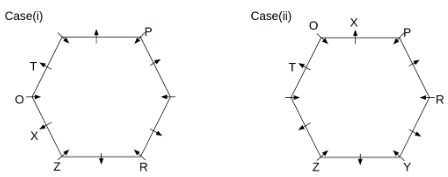
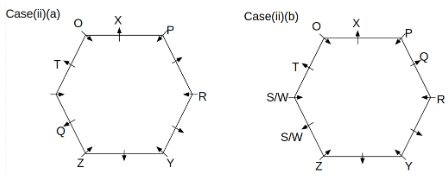
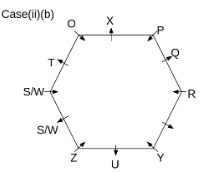
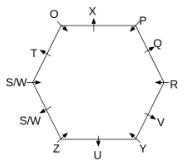
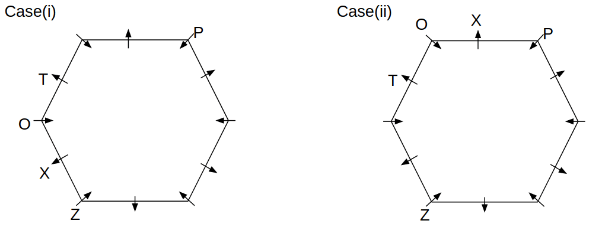
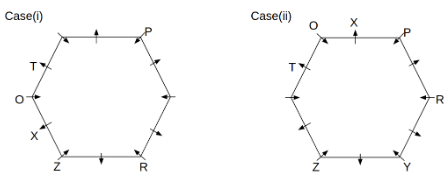
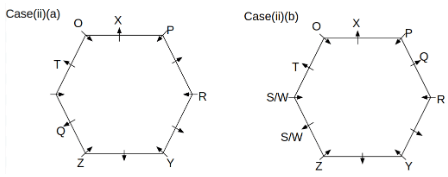
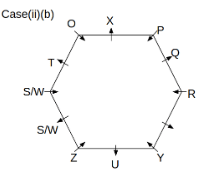
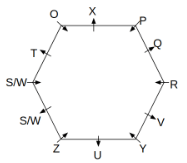
Twelve people O, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z are sitting around a hexagonal table. Six people sit at the corner of the table and face the center. While the remaining six people sit at the middle of the side of the table and face opposite to the center. S and W are immediate neighbours of each other. U is not an immediate neighbour of R. Two people are sitting between Y and Q. One person is sitting between T and X who is an immediate neighbour of O. P faces Z who is third to the left of T. Three people are sitting between O and R who is second to the right of Y.
Q. Who among the following sits opposite to T?
Twelve people O, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z are sitting around a hexagonal table. Six people sit at the corner of the table and face the center. While the remaining six people sit at the middle of the side of the table and face opposite to the center. S and W are immediate neighbours of each other. U is not an immediate neighbour of R. Two people are sitting between Y and Q. One person is sitting between T and X who is an immediate neighbour of O. P faces Z who is third to the left of T. Three people are sitting between O and R who is second to the right of Y.
Q. Which of the following is odd?