Geography: CUET Mock Test - 7 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Geography: CUET Mock Test - 7
Arun is interested in that aspect of human geography which studies each unit of Earth thoroughly to understand the entire planet.
Which stage of the evolution of human geography is this?
Which stage of the evolution of human geography is this?
The land left out of cultivation for one or less than one agriculture year is known by which of the following?
Match List I with List II
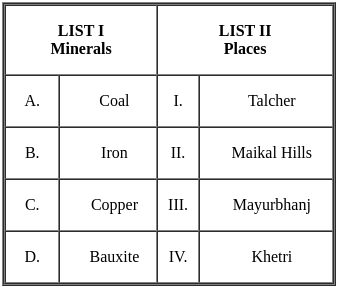
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:

The decades_______ are referred to as the period of population explosion in India.
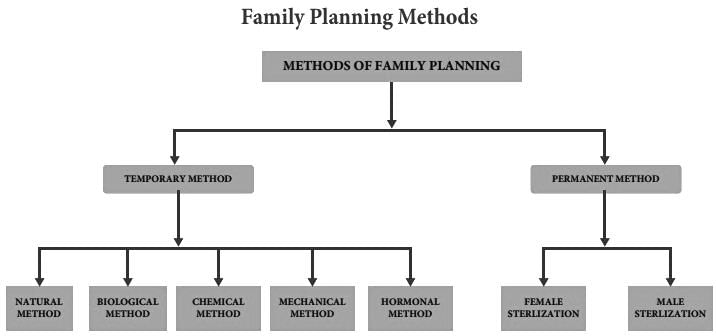
Which of the following statements is INCORRECT regarding the surgical methods of birth control?
Read the following and choose the correct sentence/sentences about the means of transport.
(A) Roadways are most commonly used means of transport especially for short distances.
(B) Waterways are the cheapest for carrying heavy and bulky goods over long distance.
(C) Railways are extremely useful in reaching inaccessible and difficult terrains
(D) Airways are most expensive and only mode to reach the most remote and distant areas.
Which of the following best describes primary activities?
Which factor influences the significance of primary activities in a region?
Which of the following is not an example of a primary activity?
Why is fishing considered an important economic activity?
What is the primary function of mining as a primary activity?
What is the main characteristic of subsistence agriculture?
Which of the following is an example of plantation agriculture?
Why is intensive farming more productive than extensive farming?
Which factor plays a crucial role in determining agricultural practices?
What distinguishes extensive farming from intensive farming?
Which of the following are the example(s) of human resource development?
P. Education loans
Q. Home loans
R. Computer training workshops
S. Cooking classes
Which of the following tribes practices 'Transhumance'?
There are two statements given below, marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct option.
Assertion (A): India's Green Revolution is an example of how the productivity of scarce land resources can be increased with improved production technology.
Reason (R): Because of the Green Revolution, farmers produced far larger quantities of food grains than was possible earlier, on the same piece of land.
Which of the following companies can be categorized under the 'electronics' industry?
Traditional ________ in rural areas is done by using surface storage bodies like lakes, ponds and irrigation tanks.
Which legume crop(s) increase(s) the natural fertility of soils through nitrogen fixation?
Why do we need to use our resources carefully?
I. Because our needs are increasing
II. Because all resources are not unlimited
III. Because the human population is increasing rapidly
IV. Because we need to make these resources last for use by future generations
Who among the following wrote the collection of essays known as 'Small Is Beautiful'?
What was the United States' estimated population during the Great Depression in 1930?