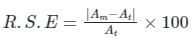Test: Measuring Instruments - SSS 2 MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Measuring Instruments
More power is required to operate a moving-iron meter than a PMMC meter because of the magnetic circuit's high _____.
The difference between the indicated value and the true value of a quantity is:
If a 100 watts bulb is used for 10 hours, then the amount of consumed electrical energy will be -
If a power transformer has a star-connected primary and a delta-connected secondary, then the CT connections on its primary and secondary sides should be:
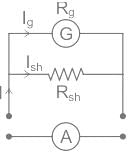
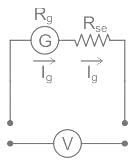
A galvanometer may be converted into ammeter or voltmeter. In which of the following cases the resistance of the device will be the largest?
The braking torque of induction type single-phase energy meter is:
When the pointer of an indicating instrument is in motion, then the deflecting torque is opposed by:
A meter reads 125 V and the true value of the voltage is 125.5 V. Find the static error of the instrument.


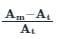
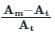 × 100
× 100