Test: Gyroscope - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Gyroscope
A rotating mass having a moment of inertia of 30 kgm2 rotates at 800 rpm and is travelling in a curve of a 170-metre radius at a speed of 240 km/hr. It will experience a gyroscopic reaction of _____.
The rotor of a ship with moment of inertia 200 kgm2 and rotational speed of 200 rad/s. What will be the gyroscopic couple when ship turns to left at radius of 100 m with speed 5 m/s?
A disc spinning on its axis at 20 rad/s will undergo precession when a torque 100 N-m is applied about an axis normal to it. If the mass moment of inertia is 1 kg-m2, then the angular velocity of precession is?
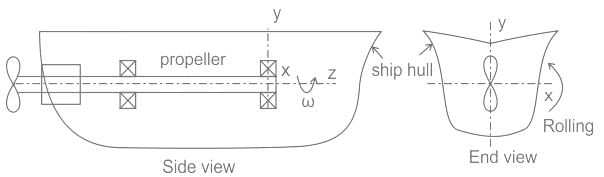
If the axes of the rolling of the ship and of the stabilizing rotor are parallel, it will result in
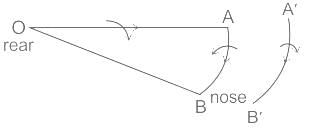
If the air screw of an aeroplane rotates clockwise when viewed from the rear and aeroplane takes a right turn, the gyroscopic effect will -
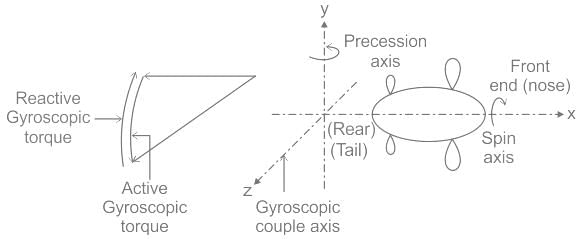
A flywheel weighs 981/π kgf and has a radius of gyration of 100 cm. It is given a spin of 100 r.p.m. about its horizontal axis. The whole assembly is rotating about a vertical axis at 6 rad/s. The gyroscopic couple experienced will be
Gyroscopic effect is not observed in which of the following actions performed by the ships?




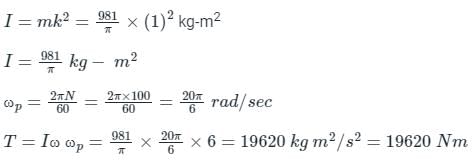
 1
1












