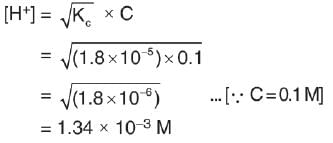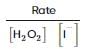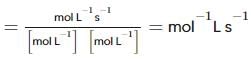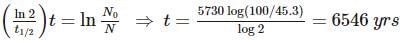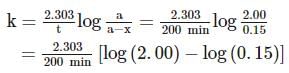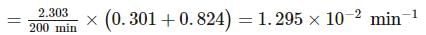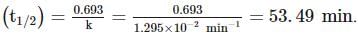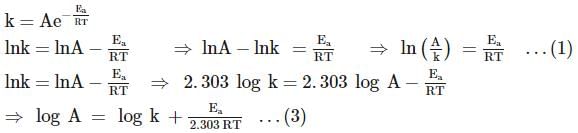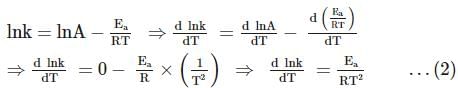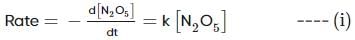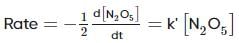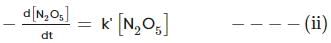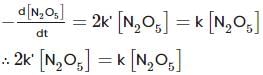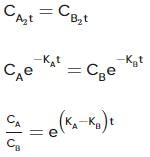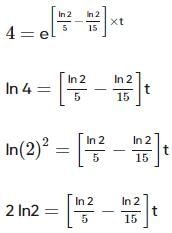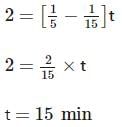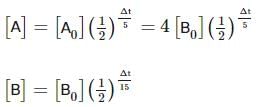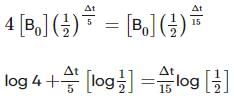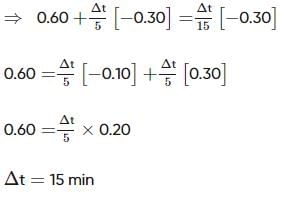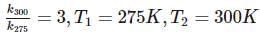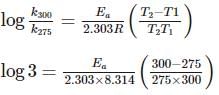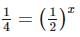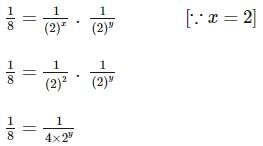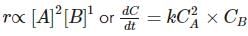BITSAT Chemistry Test - 1 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - BITSAT Chemistry Test - 1
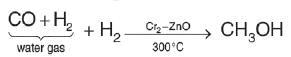
When primary amine is heated with CS2 in presence of excess of mercuric chloride, it produce isothiocyanate. This reaction is known as
Total number of electrons in all the p-orbitals of bromine will be
Ionization constant of acetic acid is 1.8 * 10-5. The concentration of H+ ions in 0.1 M solution is
On heating one end of a piece of metal, tlhe other end becomes hot because of
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine its order of reaction and the dimensions of the rate constant.
H2O2(aq)+3I−(aq)+2H+⟶2H2O(l)+I−3;Rate=k[H2O2][I−]
An archaeologist unearths a bone sample and wants to know the age of the bone. Her chemist friend determines the 45.3% of the initial amount of carbon-14 is present in the bone sample. If the half-life of carbon-14 is 5730 yrs, calculate the age (in years) of the bone.
A substance 'A' decomposes by a first order reaction starting initially with [A]=2.00 M and after 200 min, [A] becomes 0.15 M . For this reaction, t1/2 is
For the first-order decomposition reaction of N2O5 , it is observed that,
(i) N2O5(g)→2NO2(g)+1/2O2(g);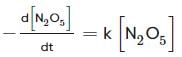
(ii) 2N2O5(g)→4NO2(g)+O2(g);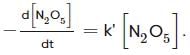
Which of the following is true?
What should be the age of the fossil for meaningful determination of its age?
Two substances A (t1/2=5 min) and B (t1/2=15 min) are taken in such a way that initially [A]=4[B] . The time after which both the concentration will be equal is : (Assume that reaction is first order)
In the start of summer, a given sample of milk turns sour at room temperature (27oC) in 48 hour . In a refrigerator at 2oC , milk can be stored three times before it sours.
For souring of milk, At 2oC , the reaction is three times slower than at 27oC . The activation energy of the souring of milk is (in kJ mol−1) .
A + B → Product
If concentration of A is doubled, rate increases 4 times. If concentration of A and B are doubled, rate increases 8 times. The differential rate equation of the reaction will be
According to quantum mechanics ψ2(r) the wave function squared gives
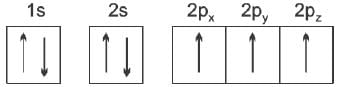
Spin quantum number with two spin states of the electron represented by two arrows, ↑ (spin up) and ↓ (spin down) was introduced to account for
The reagents to bring about the change from but – 2 – ene to ethanal
Which of the following reagents can be used to convert a carboxylic acid directly into its corresponding acid chloride derivative?
Commercial concentrated nitric acid is 15.6 M. To prepare 10 L of 6.0 M nitric acid from it,
Mole fraction of C3H5(OH)3 in a solution of 36 gm of water and 46 gm of glycerine is
AgNO3 sample is 85% by mass. To prepare 125 mL of 0.05 M AgNO3 solution, AgNO3 sample required is