NABARD Assistant Manager Grade 'A' Mock Test - 7 - Bank Exams MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - NABARD Assistant Manager Grade 'A' Mock Test - 7
Directions: These questions are based on the following information
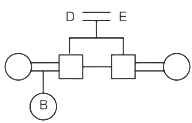
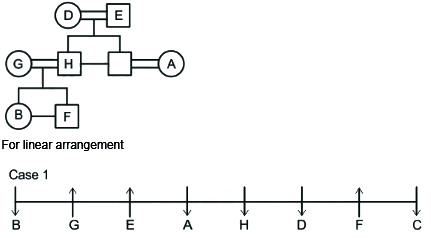
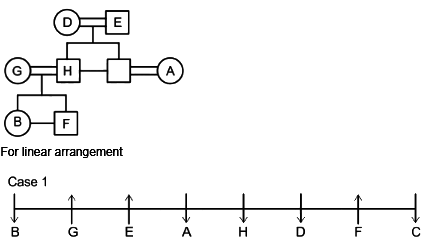
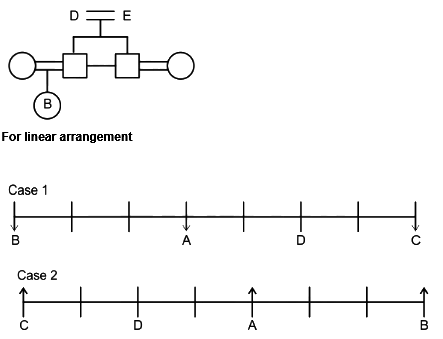
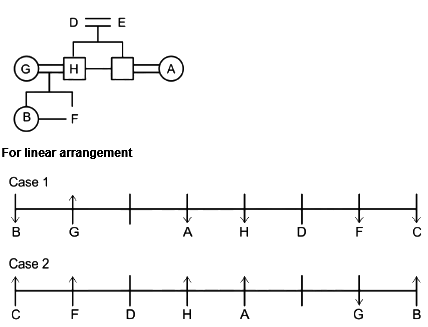
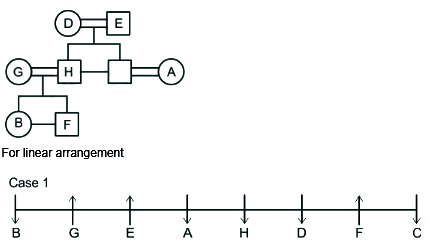
A family of 8 members A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting in a straight line facing both directions north as well as south. There are 3 generations having 3 married couples among them.
G and H do not face same direction. D sits 2nd to the left of A and 2nd to the right of C as well. E and his grandson face same direction. The son of H faces opposite direction to his grandmother but same direction as his mother. B is youngest female member of the family who sits on one of the ends of the line. G faces the opposite direction to her daughter. D is married to E and they have only two sons. H is father of F who sits 2nd to the left of H and faces north direction. A is the aunt of B and sits 3rd to her left. A faces same direction as B. G and H are married couples and two people sit between them. F is the grandson of D who is the mother of C. F is not immediate neighbor of A.
Q. How many female members are there in the family?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions accordingly:
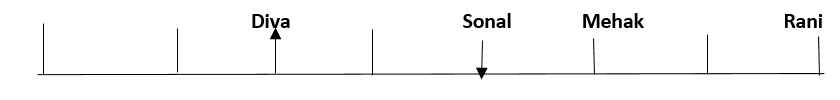
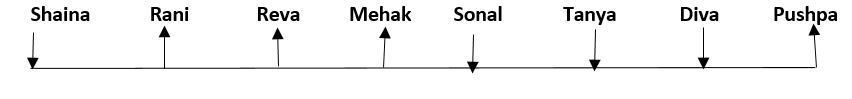
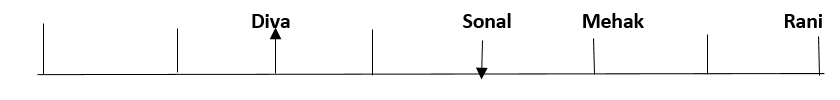
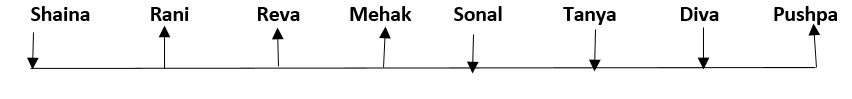
Eight friends, Shaina, Rani, Tanya, Reva, Sonal, Mehak, Pushpa and Diva are seated in a straight line but not necessarily in the same order. Some of them are facing south while some are facing north. Only two people sit between Sonal and Rani. Only three people sit to the left of Sonal. Sonal faces south. Mehak sits third to the right of Diva. Diva is not an immediate neighbour of neither Sonal nor Rani. Diva does not sit at any of the extreme ends of the line. Both the immediate neighbours of Reva face north. Reva is not an immediate neighbour of Diva. Only one person sits between Reva and Shaina. Shaina faces the same direction as Diva. The immediate neighbours of Rani face opposite directions (ie if one person is facing north then the other person faces south and vice versa). Persons sitting at the extreme ends face opposite directions. Tanya faces a direction opposite to that of Reva.
Q. How many persons are sitting between Pushpa and Mehak?
Directions: These questions are based on the following information
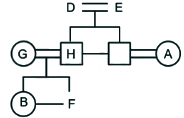
A family of 8 members A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting in a straight line facing both directions north as well as south. There are 3 generations having 3 married couples among them.
G and H do not face same direction. D sits 2nd to the left of A and 2nd to the right of C as well. E and his grandson face same direction. The son of H faces opposite direction to his grandmother but same direction as his mother. B is youngest female member of the family who sits on one of the ends of the line. G faces the opposite direction to her daughter. D is married to E and they have only two sons. H is father of F who sits 2nd to the left of H and faces north direction. A is the aunt of B and sits 3rd to her left. A faces same direction as B. G and H are married couples and two people sit between them. F is the grandson of D who is the mother of C. F is not immediate neighbor of A.
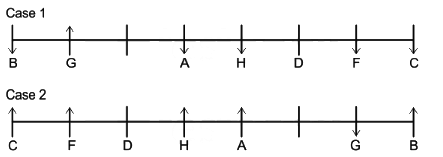
Q. Who sits 2nd to the left of grandfather?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions accordingly:
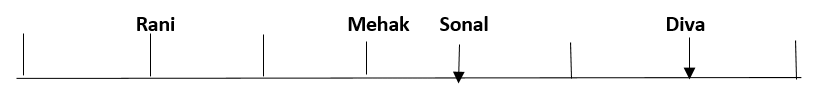
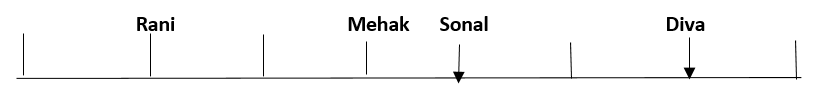
Eight friends, Shaina, Rani, Tanya, Reva, Sonal, Mehak, Pushpa and Diva are seated in a straight line but not necessarily in the same order. Some of them are facing south while some are facing north. Only two people sit between Sonal and Rani. Only three people sit to the left of Sonal. Sonal faces south. Mehak sits third to the right of Diva. Diva is not an immediate neighbour of neither Sonal nor Rani. Diva does not sit at any of the extreme ends of the line. Both the immediate neighbours of Reva face north. Reva is not an immediate neighbour of Diva. Only one person sits between Reva and Shaina. Shaina faces the same direction as Diva. The immediate neighbours of Rani face opposite directions (ie if one person is facing north then the other person faces south and vice versa). Persons sitting at the extreme ends face opposite directions. Tanya faces a direction opposite to that of Reva.
Q. What is the position of Sonal with respect of Rani?
Directions: These questions are based on the following information
A family of 8 members A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting in a straight line facing both directions north as well as south. There are 3 generations having 3 married couples among them.
G and H do not face same direction. D sits 2nd to the left of A and 2nd to the right of C as well. E and his grandson face same direction. The son of H faces opposite direction to his grandmother but same direction as his mother. B is youngest female member of the family who sits on one of the ends of the line. G faces the opposite direction to her daughter. D is married to E and they have only two sons. H is father of F who sits 2nd to the left of H and faces north direction. A is the aunt of B and sits 3rd to her left. A faces same direction as B. G and H are married couples and two people sit between them. F is the grandson of D who is the mother of C. F is not immediate neighbor of A.
Q. How is C related to the person who is 3rd to the left of F?
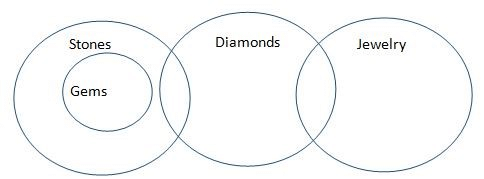
In each question below some statements followed by four conclusions numbered I, II, III and IV are given. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the two given statements, disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
All gems are stones.
Some stones are diamonds.
Some diamonds are jewelry.
Conclusions:
I. Some jewelry are stones
II. Some gems are jewelry.
III. Some diamonds are gems.
IV. All stones are gems.
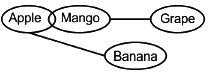
Directions: In the question below are given three statements followed by two conclusions I and II. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
Some Apple are Mango.
No Mango is Grapes.
No apple is Banana.
Conclusions:
I. Some Banana are Mango.
II. Some Grapes are Apple.
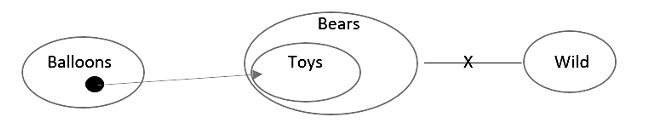
In each question below some statements followed by four conclusions numbered I, II, III and IV are given. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the two given statements, disregarding commonly known facts.
Statement:
A few balloons are not toys.
All toys are bear.
No bear is wild.
Conclusions:
I. No wild is a toy.
II. No wild is balloon.
III. Some Toys are not wild
IV. Some balloon is wild is a possibility
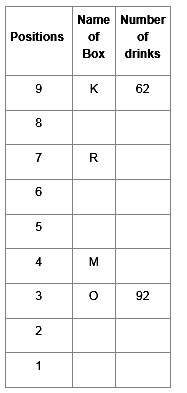
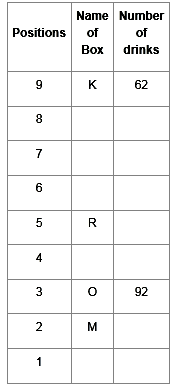
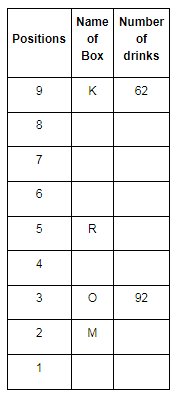
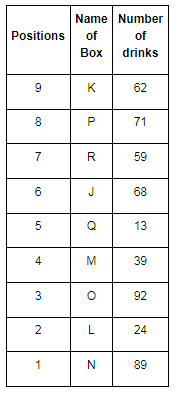
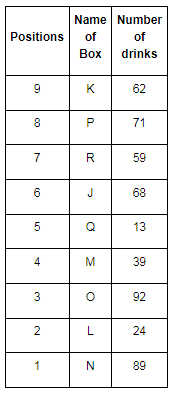
Direction: Read the given information and carefully answer the following questions.
There are nine boxes from J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R which are placed one above the other. Each box has adifferent number of drinks such as 71, 24, 68, 89, 39, 59, 62, 92 and 13. The lowermost box is numbered as one and above as two and so on. All the above information is not necessary in the same order.
The position of box M is even number. Box R has kept three boxes above the box M. Box P is kept one of the positions above box R. Box J is placed at even position above box M. The number of drinks inbox M is thrice the number of drinks in box Q. Box R has 35 drinks more than box L. Box K is placed at the topmost position. Box O has the highest amount of drinks and kept at the third position from the bottom. The difference between the number of drinks in box K and box O is 30. Box N has 89 drinks that are kept at one of the positions below box M but not immediately below it. Box L is kept one of the positions below box O but above N. There are even numbers of drinks in box J.
Q. Which box is kept at 1st position?
Read the following information carefully and answer the question that follows:
There are six persons Sumit, Alisha, Kavya, Helen, Aishwarya and Sonia, who got different marks in the examination. Sumit got less marks than only Kavya and Sonia. Alisha got more marks than Aishwarya, who did not get the lowest marks in the examination. The second lowest person got 65 marks.
Q. How many persons got more marks than Kavya?
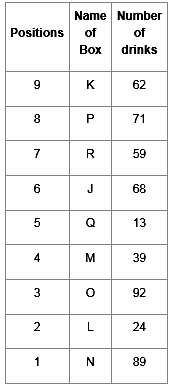
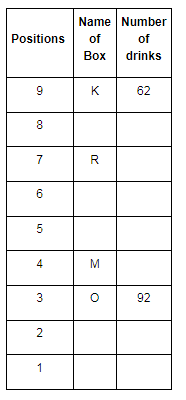
Direction: Read the given information and carefully answer the following questions.
There are nine boxes from J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R which are placed one above the other. Each box has a different number of drinks such as 71, 24, 68, 89, 39, 59, 62, 92 and 13. The lowermost box is numbered as one and above as two and so on. All the above information is not necessary in the same order.
The position of box M is even number. Box R has kept three boxes above the box M. Box P is kept one of the positions above box R. Box J is placed at even position above box M. The number of drinks inbox M is thrice the number of drinks in box Q. Box R has 35 drinks more than box L. Box K is placed at the topmost position. Box O has the highest amount of drinks and kept at the third position from the bottom. The difference between the number of drinks in box K and box O is 30. Box N has 89 drinks that are kept at one of the positions below box M but not immediately below it. Box L is kept one of the positions below box O but above N. There are even numbers of drinks in box J.
Q. Which box is kept immediately above the box M?
In these questions relationship between different elements is shown in the Statements. These Statements are followed by conclusions. You have to find out which of the conclusions logically follows from the given statements.
Statements: C ? Q, Q ? J, J > E, E ? I
Conclusion:
I. J < Q
II. I < J
III. Q< E
IV. J > C
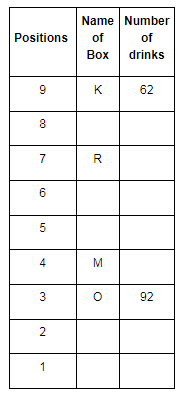
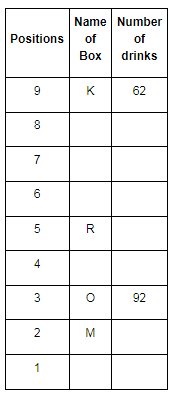
Direction: Read the given information and carefully answer the following questions.
There are nine boxes from J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q and R which are placed one above the other. Each box has adifferent number of drinks such as 71, 24, 68, 89, 39, 59, 62, 92 and 13. The lowermost box is numbered as one and above as two and so on. All the above information is not necessary in the same order.
The position of box M is even number. Box R has kept three boxes above the box M. Box P is kept one of the positions above box R. Box J is placed at even position above box M. The number of drinks inbox M is thrice the number of drinks in box Q. Box R has 35 drinks more than box L. Box K is placed at the topmost position. Box O has the highest amount of drinks and kept at the third position from the bottom. The difference between the number of drinks in box K and box O is 30. Box N has 89 drinks that are kept at one of the positions below box M but not immediately below it. Box L is kept one of the positions below box O but above N. There are even numbers of drinks in box J.
Q. How many drinks do box K have?
Study the following information and answer it carefully:
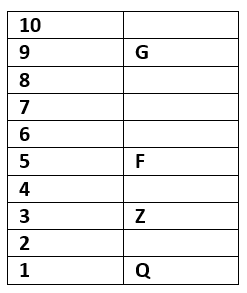
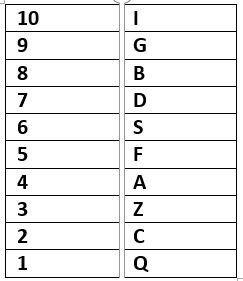
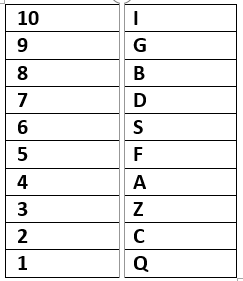
Ten persons F, B, D, S, I, A, Q, G, Z and C are lives on 10 floor building. The lowermost floor is numbered 1, above the floor numbered 2, & so on.
Three persons are living between G & F. G lives an odd numbered floor but above floor numbered 5. Only one person lives between Q & Z who is lives an odd numbered floor. One person lives between C & A. Two floors are there between D & I. Neither F nor G was immediately above or immediately below of C.B lives above S. I is not the immediate neighbour of B.
Q. Who are the immediate neighbours of A?
Directions: In the following question assuming the given statements to be True, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements: T ? M ? Q; G < O ? K; V > G ? T; C = O
Conclusions:
I. C = V
II. K ? M
III. G ? Q
Study the following information and answer it carefully:
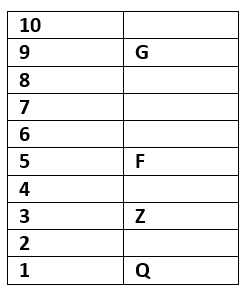
Ten persons F, B, D, S, I, A, Q, G, Z and C are lives on 10 floor building. The lowermost floor is numbered 1, above the floor numbered 2, & so on.
Three persons are living between G & F. G lives an odd numbered floor but above floor numbered 5. Only one person lives between Q & Z who is lives an odd numbered floor. One person lives between C & A. Two floors are there between D & I. Neither F nor G was immediately above or immediately below of C.B lives above S. I is not the immediate neighbour of B.
Q. Which among the following is not correct?
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions:
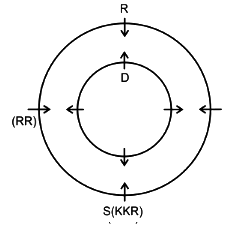
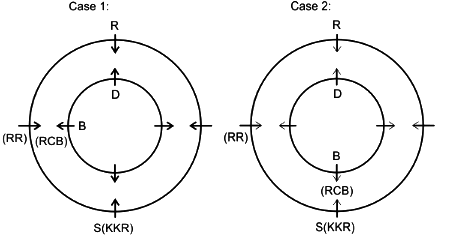
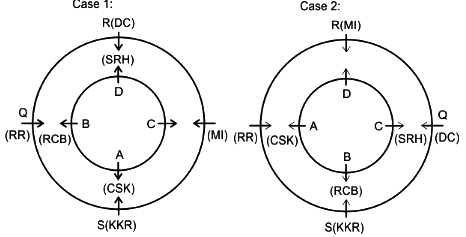
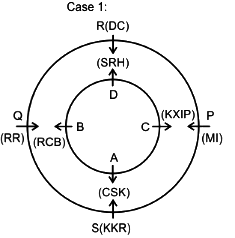
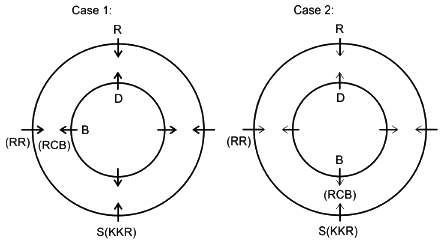
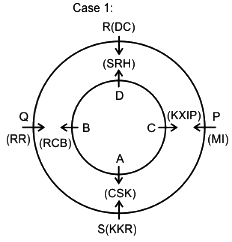
Eight friends A, B, C, D, P, Q, R and S are sitting in two circles in such a manner that each member of the inner circle sits exactly opposite to the member of the outer circle. The members sitting in the outer circle are P, Q, R and S and all of them are facing towards the Centre while the members of the inner circle are A, B, C and D and they are facing away from the Centre. Each of them likes different IPL teams DC, RCB, MI, CSK, KXIP, SRH, KKR and RR but not necessarily in the same order.
D likes neither RCB nor KXIP and faces R, who neither likes RR nor KKR. The person who likes SRH faces the person who likes DC. A, who likes CSK, faces the immediate neighbor of the person who likes MI. R sits second to the left of S. The person likes KXIP and DC are in a separate circle. The person who likes RR sits on the immediate left of S. Q, who does not like MI, does not face A. The person who likes RR and KKR are immediate neighbors, and one of them faces B, who likes RCB. The person who likes SRH and CSK sit in the same circle but they are not immediate neighbors. R does not like MI.
Q. Who among the following faces the one who like CSK?
Study the following information and answer it carefully:
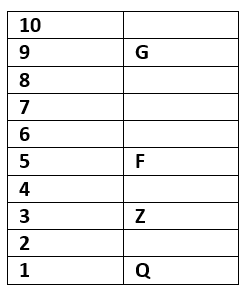
Ten persons F, B, D, S, I, A, Q, G, Z and C are lives on 10 floor building. The lowermost floor is numbered 1, above the floor numbered 2, & so on.
Three persons are living between G & F. G lives an odd numbered floor but above floor numbered 5. Only one person lives between Q & Z who is lives an odd numbered floor. One person lives between C & A. Two floors are there between D & I. Neither F nor G was immediately above or immediately below of C.B lives above S. I is not the immediate neighbour of B.
Q. If the number of persons above D are three then who is the person below which are also three persons?
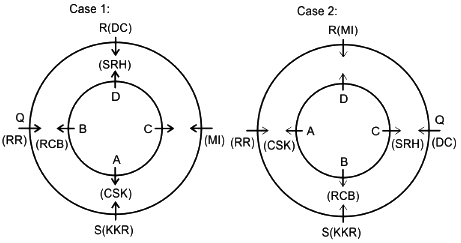
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions:
Eight friends A, B, C, D, P, Q, R and S are sitting in two circles in such a manner that each member of the inner circle sits exactly opposite to the member of the outer circle. The members sitting in the outer circle are P, Q, R and S and all of them are facing towards the Centre while the members of the inner circle are A, B, C and D and they are facing away from the Centre. Each of them likes different IPL teams DC, RCB, MI, CSK, KXIP, SRH, KKR and RR but not necessarily in the same order.
D likes neither RCB nor KXIP and faces R, who neither likes RR nor KKR. The person who likes SRH faces the person who likes DC. A, who likes CSK, faces the immediate neighbor of the person who likes MI. R sits second to the left of S. The person likes KXIP and DC are in a separate circle. The person who likes RR sits on the immediate left of S. Q, who does not like MI, does not face A. The person who likes RR and KKR are immediate neighbors, and one of them faces B, who likes RCB. The person who likes SRH and CSK sit in the same circle but they are not immediate neighbors. R does not like MI.
Q. Who faces the one who sits 2nd to the left of the one who likes RCB?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions below.
A certain number of people are sitting in a row facing North. S sits at one of the ends and there are two people between S and R. There are as many people to the right of V as there are to the left of V. W is third to the left of R who sits fourth from one of the extreme ends of the row. Q sits at one of the extreme ends of the row. W does not sit at any of the extreme ends of the row. There are five persons sitting between Q and T. U sits exactly in the middle of Q and T. Two persons sit between T and V. There are as many persons sitting between W and S as many are sitting between W and T.
Q. Who sits between W and T ?
Rearrange the following five sentences a, b, c, d and e in the proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph; then answer the questions given below them.
a) Users can be asked to pay a small price for the protection of vital environmental features, and more areas for nature tourism can also raise revenues.
b) This would ensure that tigers and other animals are not isolated, and can disperse strong genetic traits to other populations.
c) The National Tiger Conservation Authority should insist on modification of existing roads to provide crossings for animals at locations identified in various studies.
d) An assessment by the Wildlife Institute
of India states that tigers in at least 26 reserves face the destructive impact of roads and traffic.
e) A more robust approach would be to realign the roads away from all such landscapes.
Q. Which is the FIRST sentence of the paragraph?
Directions: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct/most appropriate options:
A Russian defence industry delegation will soon travel to India to carry forward long-drawn-out talks for an upgrade of the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) Sukhoi-30 MKI fleet. This proposed upgrade will include better radar, a more potent weapons package, a new cockpit system, and the integration of electronic warfare abilities. Russia is also hopeful that India will move ahead with plans to place an order for an additional 12 Su-30 MKIs to replace the fighter jets it lost to crashes over the years. Further, Moscow hopes to finalise the contract for 21 more MiG-29s meant to firm up the IAF’s depleting fleet strength. While the French-made Rafale is the frontrunner for a mega contract for 114 new fighters that the IAF is looking at, Russia believes it is the only country capable of offering a true Transfer of Technology (ToT) with over 60 per cent Indian content. The IAF is considering the acquisition of 114 fighters through the Make in India route.
“We have, several times, offered our vision of an upgrade programme (Su-30 MKI). It is a continuing discussion and we have put on the table our complete offer. We plan to visit India ____ the near future and have a meaningful discussion on that offer,” Yury Slyusar, CEO of Russia’s United Aircraft Corporation (UAC) said in response to a query by ThePrint at ARMY-2022, an international military exhibition being held here in Moscow. The UAC, a public joint stock company of which the Russian government owns a majority, is the largest manufacturer of aircraft in the country. In June, Russia’s flagship manufacturers, the Sukhoi and MiG aviation companies were merged into the UAC. New Delhi and Moscow have been in talks with each other about an upgrade for the Su-30 MKI, which India first ordered in 1996. The upgraded aircraft, if the proposal is approved, will be known as the Super Sukhoi.
The IAF has more than 160 Su-30 MKIs in its fleet, but talks regarding an upgrade have been stuck due to various issues — with cost being the most basic and important factor owing to the IAF’s plan to also procure 114 new fighters on a limited budget. While the exact numbers are not known, IAF sources have explained that the asking price for an upgrade is too high because it will involve a complete revamp and not just a simple extension of life. While the Su-30 MKI is the IAF’s frontline fighter, it is besieged by numerous issues, among them the inability to carry out electronic warfare and the lack of a more potent weapons system. The integration of about 40 Sukhois with the BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles — which have a range of over 300 kilometres — has, however, been a saving grace. As part of the proposed upgrade, the fighter jet’s N011 Bars passive radar will be replaced with ‘Uttam’, India’s own Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) radar.
The MKI version is the oldest member of the Su-30 family, which includes the Malaysian Su-30 MKM (2007 model) and the Russian Su-30 SM (2011 model). It is hoped that the upgrade will bring the MKI up to par with the Russian SM, which is equipped with multiple long-range missiles and smart bombs developed as part of Russia’s 2011-2020 State Armament Program for the Su-30 SM. UAC chief Slyusar said talks are also underway between India and Russia for the IAF’s 114 fighter jets programme, adding that the MiG is the only aircraft that can truly offer ToT with 60 per cent indigenous content. He was referring to the MiG-35, which Russia is keen to offer India. Asked about a possible collaboration with New Delhi — given India’s plan to develop its own fifth-generation fighter aircraft called AMCA (Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft) — the top Russian aviation official said that although there is no news on that front, Moscow is ready to collaborate if New Delhi so desires. Asking about the pending order for 12 Su-30 MKI and 21 MiG-29s, Slyusar said it was under consideration by India. Of the 1980s vintage, the jets are no longer in production, but 21 airframes built then remain in Russia. The jets purchased by India will be upgraded to the latest version before they are delivered.
Q. According to the passage, who is the frontrunner for a mega contract for 114 new fighters with the IAF?
Rearrange the following five sentences a, b, c, d and e in the proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph; then answer the questions given below them.
a) Users can be asked to pay a small price for the protection of vital environmental features, and more areas for nature tourism can also raise revenues.
b) This would ensure that tigers and other animals are not isolated, and can disperse strong genetic traits to other populations.
c) The National Tiger Conservation Authority should insist on modification of existing roads to provide crossings for animals at locations identified in various studies.
d) An assessment by the Wildlife Institute of India states that tigers in at least 26 reserves face the destructive impact of roads and traffic.
e) A more robust approach would be to realign the roads away from all such landscapes.
Q. Which is the THIRD sentence of the paragraph?
Directions: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct/most appropriate options:
A Russian defence industry delegation will soon travel to India to carry forward long-drawn-out talks for an upgrade of the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) Sukhoi-30 MKI fleet. This proposed upgrade will include better radar, a more potent weapons package, a new cockpit system, and the integration of electronic warfare abilities. Russia is also hopeful that India will move ahead with plans to place an order for an additional 12 Su-30 MKIs to replace the fighter jets it lost to crashes over the years. Further, Moscow hopes to finalise the contract for 21 more MiG-29s meant to firm up the IAF’s depleting fleet strength. While the French-made Rafale is the frontrunner for a mega contract for 114 new fighters that the IAF is looking at, Russia believes it is the only country capable of offering a true Transfer of Technology (ToT) with over 60 per cent Indian content. The IAF is considering the acquisition of 114 fighters through the Make in India route.
“We have, several times, offered our vision of an upgrade programme (Su-30 MKI). It is a continuing discussion and we have put on the table our complete offer. We plan to visit India ____ the near future and have a meaningful discussion on that offer,” Yury Slyusar, CEO of Russia’s United Aircraft Corporation (UAC) said in response to a query by ThePrint at ARMY-2022, an international military exhibition being held here in Moscow. The UAC, a public joint stock company of which the Russian government owns a majority, is the largest manufacturer of aircraft in the country. In June, Russia’s flagship manufacturers, the Sukhoi and MiG aviation companies were merged into the UAC. New Delhi and Moscow have been in talks with each other about an upgrade for the Su-30 MKI, which India first ordered in 1996. The upgraded aircraft, if the proposal is approved, will be known as the Super Sukhoi.
The IAF has more than 160 Su-30 MKIs in its fleet, but talks regarding an upgrade have been stuck due to various issues — with cost being the most basic and important factor owing to the IAF’s plan to also procure 114 new fighters on a limited budget. While the exact numbers are not known, IAF sources have explained that the asking price for an upgrade is too high because it will involve a complete revamp and not just a simple extension of life. While the Su-30 MKI is the IAF’s frontline fighter, it is besieged by numerous issues, among them the inability to carry out electronic warfare and the lack of a more potent weapons system. The integration of about 40 Sukhois with the BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles — which have a range of over 300 kilometres — has, however, been a saving grace. As part of the proposed upgrade, the fighter jet’s N011 Bars passive radar will be replaced with ‘Uttam’, India’s own Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) radar.
The MKI version is the oldest member of the Su-30 family, which includes the Malaysian Su-30 MKM (2007 model) and the Russian Su-30 SM (2011 model). It is hoped that the upgrade will bring the MKI up to par with the Russian SM, which is equipped with multiple long-range missiles and smart bombs developed as part of Russia’s 2011-2020 State Armament Program for the Su-30 SM. UAC chief Slyusar said talks are also underway between India and Russia for the IAF’s 114 fighter jets programme, adding that the MiG is the only aircraft that can truly offer ToT with 60 per cent indigenous content. He was referring to the MiG-35, which Russia is keen to offer India. Asked about a possible collaboration with New Delhi — given India’s plan to develop its own fifth-generation fighter aircraft called AMCA (Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft) — the top Russian aviation official said that although there is no news on that front, Moscow is ready to collaborate if New Delhi so desires. Asking about the pending order for 12 Su-30 MKI and 21 MiG-29s, Slyusar said it was under consideration by India. Of the 1980s vintage, the jets are no longer in production, but 21 airframes built then remain in Russia. The jets purchased by India will be upgraded to the latest version before they are delivered.
Q. In this question, a sentence (in bold) from the passage has been divided into four parts (A), (B), (C) and (D). Read the sentence to find out whether there is any grammatical error in it. The error if any will be in one part of the sentence. If there is No error the answer is 'No Error/(E)'. Ignore the error of punctuation if any.
Asking about the (A)/ pending order for 12 Su-30 MKI (B)/ and @1 MiG-29s, Slyusar said it (C)/ was under consideration by India. (D)/ No Error(E)
Rearrange the following five sentences a, b, c, d and e in the proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph; then answer the questions given below them.
a) Users can be asked to pay a small price for the protection of vital environmental features, and more areas for nature tourism can also raise revenues.
b) This would ensure that tigers and other animals are not isolated, and can disperse strong genetic traits to other populations.
c) The National Tiger Conservation Authority should insist on modification of existing roads to provide crossings for animals at locations identified in various studies.
d) An assessment by the Wildlife Institute of India states that tigers in at least 26 reserves face the destructive impact of roads and traffic.
e) A more robust approach would be to realign the roads away from all such landscapes.
Q. Which is the SECOND sentence of the paragraph?
Directions: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct/most appropriate options:
A Russian defence industry delegation will soon travel to India to carry forward long-drawn-out talks for an upgrade of the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) Sukhoi-30 MKI fleet. This proposed upgrade will include better radar, a more potent weapons package, a new cockpit system, and the integration of electronic warfare abilities. Russia is also hopeful that India will move ahead with plans to place an order for an additional 12 Su-30 MKIs to replace the fighter jets it lost to crashes over the years. Further, Moscow hopes to finalise the contract for 21 more MiG-29s meant to firm up the IAF’s depleting fleet strength. While the French-made Rafale is the frontrunner for a mega contract for 114 new fighters that the IAF is looking at, Russia believes it is the only country capable of offering a true Transfer of Technology (ToT) with over 60 per cent Indian content. The IAF is considering the acquisition of 114 fighters through the Make in India route.
“We have, several times, offered our vision of an upgrade programme (Su-30 MKI). It is a continuing discussion and we have put on the table our complete offer. We plan to visit India ____ the near future and have a meaningful discussion on that offer,” Yury Slyusar, CEO of Russia’s United Aircraft Corporation (UAC) said in response to a query by ThePrint at ARMY-2022, an international military exhibition being held here in Moscow. The UAC, a public joint stock company of which the Russian government owns a majority, is the largest manufacturer of aircraft in the country. In June, Russia’s flagship manufacturers, the Sukhoi and MiG aviation companies were merged into the UAC. New Delhi and Moscow have been in talks with each other about an upgrade for the Su-30 MKI, which India first ordered in 1996. The upgraded aircraft, if the proposal is approved, will be known as the Super Sukhoi.
The IAF has more than 160 Su-30 MKIs in its fleet, but talks regarding an upgrade have been stuck due to various issues — with cost being the most basic and important factor owing to the IAF’s plan to also procure 114 new fighters on a limited budget. While the exact numbers are not known, IAF sources have explained that the asking price for an upgrade is too high because it will involve a complete revamp and not just a simple extension of life. While the Su-30 MKI is the IAF’s frontline fighter, it is besieged by numerous issues, among them the inability to carry out electronic warfare and the lack of a more potent weapons system. The integration of about 40 Sukhois with the BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles — which have a range of over 300 kilometres — has, however, been a saving grace. As part of the proposed upgrade, the fighter jet’s N011 Bars passive radar will be replaced with ‘Uttam’, India’s own Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) radar.
The MKI version is the oldest member of the Su-30 family, which includes the Malaysian Su-30 MKM (2007 model) and the Russian Su-30 SM (2011 model). It is hoped that the upgrade will bring the MKI up to par with the Russian SM, which is equipped with multiple long-range missiles and smart bombs developed as part of Russia’s 2011-2020 State Armament Program for the Su-30 SM. UAC chief Slyusar said talks are also underway between India and Russia for the IAF’s 114 fighter jets programme, adding that the MiG is the only aircraft that can truly offer ToT with 60 per cent indigenous content. He was referring to the MiG-35, which Russia is keen to offer India. Asked about a possible collaboration with New Delhi — given India’s plan to develop its own fifth-generation fighter aircraft called AMCA (Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft) — the top Russian aviation official said that although there is no news on that front, Moscow is ready to collaborate if New Delhi so desires. Asking about the pending order for 12 Su-30 MKI and 21 MiG-29s, Slyusar said it was under consideration by India. Of the 1980s vintage, the jets are no longer in production, but 21 airframes built then remain in Russia. The jets purchased by India will be upgraded to the latest version before they are delivered.
Q. What is the Tone of the passage?
In each question below, a sentence is given with a part of it printed in bold type. That part contains an idiom/phrasal verb that may be correct or erroneous. Each sentence is followed by phrases (A), (B), (C) and (D). Find out which is the correct idiom that should replace the error in bold, if there is any, and which makes the sentence grammatically meaningful and correct. If the sentence is correct as it is and ‘No improvement required’, mark (E) as the answer.
And while you should not drop the base too early, you should also be able to recognize when it's time to call it quits.
Directions: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct/most appropriate options:
A Russian defence industry delegation will soon travel to India to carry forward long-drawn-out talks for an upgrade of the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) Sukhoi-30 MKI fleet. This proposed upgrade will include better radar, a more potent weapons package, a new cockpit system, and the integration of electronic warfare abilities. Russia is also hopeful that India will move ahead with plans to place an order for an additional 12 Su-30 MKIs to replace the fighter jets it lost to crashes over the years. Further, Moscow hopes to finalise the contract for 21 more MiG-29s meant to firm up the IAF’s depleting fleet strength. While the French-made Rafale is the frontrunner for a mega contract for 114 new fighters that the IAF is looking at, Russia believes it is the only country capable of offering a true Transfer of Technology (ToT) with over 60 per cent Indian content. The IAF is considering the acquisition of 114 fighters through the Make in India route.
“We have, several times, offered our vision of an upgrade programme (Su-30 MKI). It is a continuing discussion and we have put on the table our complete offer. We plan to visit India ____ the near future and have a meaningful discussion on that offer,” Yury Slyusar, CEO of Russia’s United Aircraft Corporation (UAC) said in response to a query by ThePrint at ARMY-2022, an international military exhibition being held here in Moscow. The UAC, a public joint stock company of which the Russian government owns a majority, is the largest manufacturer of aircraft in the country. In June, Russia’s flagship manufacturers, the Sukhoi and MiG aviation companies were merged into the UAC. New Delhi and Moscow have been in talks with each other about an upgrade for the Su-30 MKI, which India first ordered in 1996. The upgraded aircraft, if the proposal is approved, will be known as the Super Sukhoi.
The IAF has more than 160 Su-30 MKIs in its fleet, but talks regarding an upgrade have been stuck due to various issues — with cost being the most basic and important factor owing to the IAF’s plan to also procure 114 new fighters on a limited budget. While the exact numbers are not known, IAF sources have explained that the asking price for an upgrade is too high because it will involve a complete revamp and not just a simple extension of life. While the Su-30 MKI is the IAF’s frontline fighter, it is besieged by numerous issues, among them the inability to carry out electronic warfare and the lack of a more potent weapons system. The integration of about 40 Sukhois with the BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles — which have a range of over 300 kilometres — has, however, been a saving grace. As part of the proposed upgrade, the fighter jet’s N011 Bars passive radar will be replaced with ‘Uttam’, India’s own Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) radar.
The MKI version is the oldest member of the Su-30 family, which includes the Malaysian Su-30 MKM (2007 model) and the Russian Su-30 SM (2011 model). It is hoped that the upgrade will bring the MKI up to par with the Russian SM, which is equipped with multiple long-range missiles and smart bombs developed as part of Russia’s 2011-2020 State Armament Program for the Su-30 SM. UAC chief Slyusar said talks are also underway between India and Russia for the IAF’s 114 fighter jets programme, adding that the MiG is the only aircraft that can truly offer ToT with 60 per cent indigenous content. He was referring to the MiG-35, which Russia is keen to offer India. Asked about a possible collaboration with New Delhi — given India’s plan to develop its own fifth-generation fighter aircraft called AMCA (Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft) — the top Russian aviation official said that although there is no news on that front, Moscow is ready to collaborate if New Delhi so desires. Asking about the pending order for 12 Su-30 MKI and 21 MiG-29s, Slyusar said it was under consideration by India. Of the 1980s vintage, the jets are no longer in production, but 21 airframes built then remain in Russia. The jets purchased by India will be upgraded to the latest version before they are delivered.
Q. Which of the following is/are correct according to the given passage?
A. Moscow hopes to finalise the contract for 21 more MiG-29s meant to firm up the IAF’s depleting fleet strength.
B. The integration of about 40 Sukhois with the BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles has, however, been a saving grace.
C. As part of the proposed upgrade, the fighter jet’s N011 Bars passive radar will be damaged with ‘Uttam’, India’s own Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) radar.
Which of the following sentences is grammatically correct?
Directions: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct/most appropriate options:
A Russian defence industry delegation will soon travel to India to carry forward long-drawn-out talks for an upgrade of the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) Sukhoi-30 MKI fleet. This proposed upgrade will include better radar, a more potent weapons package, a new cockpit system, and the integration of electronic warfare abilities. Russia is also hopeful that India will move ahead with plans to place an order for an additional 12 Su-30 MKIs to replace the fighter jets it lost to crashes over the years. Further, Moscow hopes to finalise the contract for 21 more MiG-29s meant to firm up the IAF’s depleting fleet strength. While the French-made Rafale is the frontrunner for a mega contract for 114 new fighters that the IAF is looking at, Russia believes it is the only country capable of offering a true Transfer of Technology (ToT) with over 60 per cent Indian content. The IAF is considering the acquisition of 114 fighters through the Make in India route.
“We have, several times, offered our vision of an upgrade programme (Su-30 MKI). It is a continuing discussion and we have put on the table our complete offer. We plan to visit India ____ the near future and have a meaningful discussion on that offer,” Yury Slyusar, CEO of Russia’s United Aircraft Corporation (UAC) said in response to a query by ThePrint at ARMY-2022, an international military exhibition being held here in Moscow. The UAC, a public joint stock company of which the Russian government owns a majority, is the largest manufacturer of aircraft in the country. In June, Russia’s flagship manufacturers, the Sukhoi and MiG aviation companies were merged into the UAC. New Delhi and Moscow have been in talks with each other about an upgrade for the Su-30 MKI, which India first ordered in 1996. The upgraded aircraft, if the proposal is approved, will be known as the Super Sukhoi.
The IAF has more than 160 Su-30 MKIs in its fleet, but talks regarding an upgrade have been stuck due to various issues — with cost being the most basic and important factor owing to the IAF’s plan to also procure 114 new fighters on a limited budget. While the exact numbers are not known, IAF sources have explained that the asking price for an upgrade is too high because it will involve a complete revamp and not just a simple extension of life. While the Su-30 MKI is the IAF’s frontline fighter, it is besieged by numerous issues, among them the inability to carry out electronic warfare and the lack of a more potent weapons system. The integration of about 40 Sukhois with the BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles — which have a range of over 300 kilometres — has, however, been a saving grace. As part of the proposed upgrade, the fighter jet’s N011 Bars passive radar will be replaced with ‘Uttam’, India’s own Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) radar.
The MKI version is the oldest member of the Su-30 family, which includes the Malaysian Su-30 MKM (2007 model) and the Russian Su-30 SM (2011 model). It is hoped that the upgrade will bring the MKI up to par with the Russian SM, which is equipped with multiple long-range missiles and smart bombs developed as part of Russia’s 2011-2020 State Armament Program for the Su-30 SM. UAC chief Slyusar said talks are also underway between India and Russia for the IAF’s 114 fighter jets programme, adding that the MiG is the only aircraft that can truly offer ToT with 60 per cent indigenous content. He was referring to the MiG-35, which Russia is keen to offer India. Asked about a possible collaboration with New Delhi — given India’s plan to develop its own fifth-generation fighter aircraft called AMCA (Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft) — the top Russian aviation official said that although there is no news on that front, Moscow is ready to collaborate if New Delhi so desires. Asking about the pending order for 12 Su-30 MKI and 21 MiG-29s, Slyusar said it was under consideration by India. Of the 1980s vintage, the jets are no longer in production, but 21 airframes built then remain in Russia. The jets purchased by India will be upgraded to the latest version before they are delivered.
Q. Choose the Synonym of the word 'potent'.





 \
\