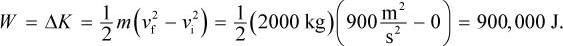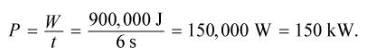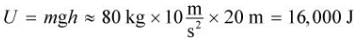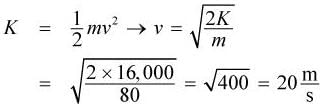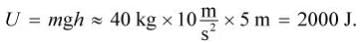Test: Work and Energy - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Work and Energy
A weight lifter lifts a 275 kg barbell from the ground to a height of 2.4 m. How much work has he done in lifting the barbell, and how much work is required to hold the weight at that height?
A 2000 kg experimental car can accelerate from 0 to 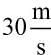 in 6 s. What is the average power of the engine needed to achieve this acceleration?
in 6 s. What is the average power of the engine needed to achieve this acceleration?
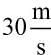 in 6 s. What is the average power of the engine needed to achieve this acceleration?
in 6 s. What is the average power of the engine needed to achieve this acceleration?5 m3 of a gas are brought from an initial pressure of 1 kPa to a pressure of 3 kPa through an isochoric process. During this process, the work performed by the gas is:
Which of the following best characterizes the work–energy theorem?
Josh, who has a mass of 80 kg, and Sarah, who has a mass of 50 kg, jump off a 20 m tall building and land on a fire net. The net compresses, and they bounce back up at the same time. Which of the following statements is NOT true?
Mechanical advantage and efficiency are both ratios. Which of the following is true regarding the quantities used in these ratios?
A consumer is comparing two new cars. Car A exerts 250 horsepower, while Car B exerts 300 horsepower. The consumer is most concerned about the peak velocity that the car can reach. Which of the following statements would best inform the consumer's decision? (Note: 1 horsepower = 745.7 W)
A tractor pulls a log with a mass of 500 kg along the ground for 100 m. The rope (between the tractor and the log) makes an angle of 30° with the ground and is acted on by a tensile force of 5000 N. How much work does the tractor perform in this scenario? (Note: sin 30° = 0.5, cos 30° = 0.866, tan 30° = 0.577)
A 40 kg block is resting at a height of 5 m off the ground. If the block is released and falls to the ground, which of the following is closest to its total mechanical energy at a height of 2 m, assuming negligible air resistance?


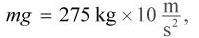 or about 2750 N, it follows that the weightlifter must exert an equal and opposite force of 2750 N on the barbell. The work done in lifting the barbell is therefore W = Fd cos θ = (2750 N)(2.4 m)(cos 0) ≈ 7000 J. Using the same equation, it follows that the work done to hold the barbell in place is W = Fd cos θ = (2750 N)(0 m)(cos θ) = 0 J. Because the barbell is held in place and there is no displacement, the work done is zero.
or about 2750 N, it follows that the weightlifter must exert an equal and opposite force of 2750 N on the barbell. The work done in lifting the barbell is therefore W = Fd cos θ = (2750 N)(2.4 m)(cos 0) ≈ 7000 J. Using the same equation, it follows that the work done to hold the barbell in place is W = Fd cos θ = (2750 N)(0 m)(cos θ) = 0 J. Because the barbell is held in place and there is no displacement, the work done is zero.