Test: Fluids in Motion - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Fluids in Motion
Objects A and B are submerged at a depth of 1 m in a liquid with a specific gravity of 0.877. Given that the density of object B is one-third that of object A and that the gauge pressure of object A is 3 atm, what is the gauge pressure of object B? (Note: Assume atmospheric pressure is 1 atm and g = 9.8 m/s2).
Two wooden balls of equal volume but different density are held beneath the surface of a container of water. Ball A has a density of 0.5 g/m3, and ball B has a density of 0.7 g/cm3. When the balls are released, they will accelerate upward to the surface. What is the relationship between the acceleration of ball A and that of ball B?
A hydraulic lever is used to lift a heavy hospital bed, requiring an amount of work W. When the same bed with a patient is lifted, the work required is doubled. How can the cross-sectional area of the platform on which the bed is lifted be changed so that the pressure on the hydraulic lever remains constant?
The speed of blood in the aorta is much higher than the speed of blood through a capillary bed. How can this fact be explained using the continuity equation, assuming that we are interested in average flow and that there is no net fluid loss?
A large cylinder is filled with equal volumes of two immiscible fluids. A balloon is submerged in the first fluid; the gauge pressure in the balloon at the deepest point in the first fluid is found to be 3 atm. Next, the balloon is lowered all the way to the bottom of the second fluid, where the hydrostatic pressure in the balloon reads 8 atm. What is the ratio of the gauge pressure accounted for by the first fluid to the gauge pressure accounted for by the second fluid?
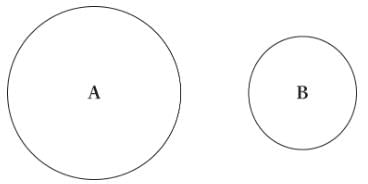
Balls A and B of equal mass are floating in a swimming pool, as shown below. Which will produce a greater buoyant force?
A low-pressure weather system can decrease the atmospheric pressure from 1 atm to 0.99 atm. By what percent will this decrease the force on a rectangular window from the outside? (Note: Assume the window is 6 m by 3 m and the glass is 3 cm thick.)
A water tower operator is interested in increasing the pressure of a column of water that is applied to a piston. She hopes that increasing the pressure will increase the force being applied to the piston. The only way to increase the pressure is to alter the speed of the water as it flows through the pipe to the piston. How should the speed of the water be changed to increase the pressure and force?
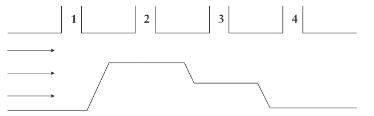
The figure shown represents a section through a horizontal pipe of varying diameters into which four open vertical pipes connect. If water is allowed to flow through the pipe in the direction indicated, in which of the vertical pipes will the water level be lowest?
Which of the following data sets is sufficient to determine the linear speed through an area of a rigid pipe?















