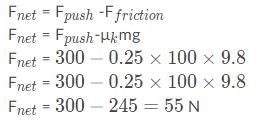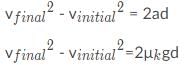Test: Vector Analysis and Forces Acting on an Object - 1 - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Vector Analysis and Forces Acting on an Object - 1
A 100 kg block of wood is traveling with a constant velocity on ice. What is its normal force?
A rock has a mass of 100 kg. A man pushes the rock on its side with a force of 300 N, moving the rock. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the rock and the ground is 0.25, what is the net force of the rock?
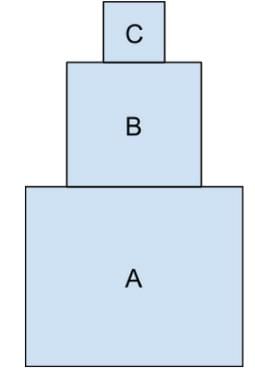
Box A has a mass of 100 kg, box B has a mass of 50 kg, and box C has a box a mass of 25 kg. The boxes are arranged in the following arrangement. What is the normal force, exerted by the ground, experienced by Box A?

A child pushes a 100 kg refrigerator with a force of 50 N, but the refrigerator does not move. Suppose the coefficient of static friction between the floor and the refrigerator is 0.4. What is the force due to friction in this scenario?
An elevator’s motion is through the action of a single cable. The elevator has a gravitational force of 2000 N. When the elevator is moving downwards at a constant velocity, how much tension is in this cable?
For a three second period of time, a 50 kg wooden crate slides across the concrete floor at exactly 5 m/s. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the wooden crate and the concrete floor is 0.2. What is the net force of this crate during this three second period?
Jennifer presses her finger down on a coin and exerts a 2 N force. The coin has a mass of 5 grams. What is the normal force on the coin exerted by the table in which Jennifer presses against?
If the forces acting on an object are balanced, then which of the following must be true about the object?
An elevator with a passenger accelerates upwards from rest at a value of 3 m/s2 squared. What is the normal force of the elevator on the passenger if the passenger has a mass of 50 kg?
The coefficient of kinetic friction for a car against a road is 0.05. If a car moving at 10 m/s suddenly stops its wheels from moving, how far will the car go before it comes to a complete stop?