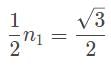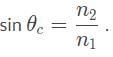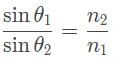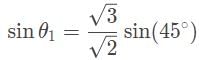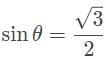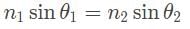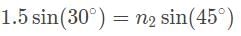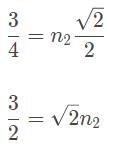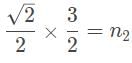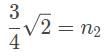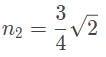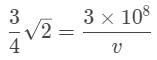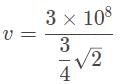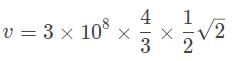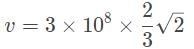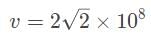Test: Reflection and Refraction - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Reflection and Refraction
Which of the following is true of reflected light rays from a surface?
I. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection for diffuse reflections.
II. The angle measured between the surface and the ray is the same magnitude as the angle of reflection
III. The angle of incidence is found by subtracting the angle made with the surface from the normal
I. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection for diffuse reflections.
II. The angle measured between the surface and the ray is the same magnitude as the angle of reflection
III. The angle of incidence is found by subtracting the angle made with the surface from the normal
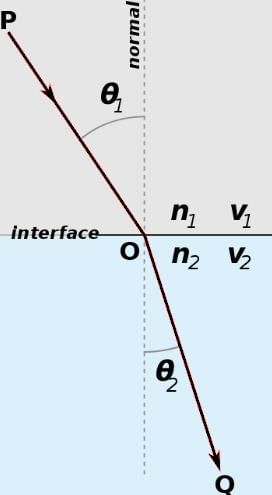
In the figure below, from P → Q a ray of light passes from air through glass with a refraction index of 1.5. If the angle of reflection is 30° , what is sin of the angle of refraction?

A diamond has an index of refraction of 2.4, point, 4. What is the speed of light within the diamond?
A ray of light refracts as it passes from glass into a vacuum. It’s angle of incidence is 30°, and its angle of refraction is 60° what is the index of refraction of the glass?
A prism is used to separate white light into a rainbow. Which color of the visible spectrum would have the smallest angle of refraction (the angle between the ray and a line normal to the surface of the prism)?
What would the critical angle be for a flare lit underneath the surface ocean, if the index of refraction for ocean water is 1.33?
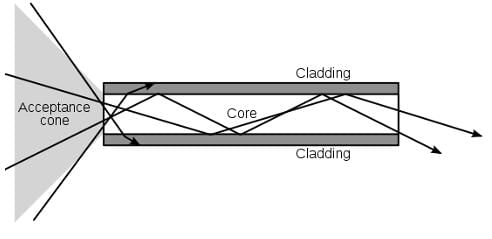
Above is a schematic of a fiber optic cable, which maintains total internal reflection throughout the length of the cable. The index of refraction of the cladding of a cable is generally 1.52, while the core has an index of refraction of 1.62 Choosing from the list below, what is the smallest angle of incidence light could have to enter from the acceptance cone that would be able to ‘escape’ the fiber optic cable?
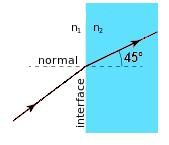
A laser beam is refracted in a prism with an index of refraction (n2) of √3/√2. The angle of refraction is measured to be 45°. If the prism is in a vacuum, what is the angle between the incoming ray of light and the surface of the prism?
Which of the following is true concerning total internal reflection?
I. Light traveling from a lower index of refraction to a higher one can experience total internal refraction.
II. If the angle of incidence equals the critical angle then light will not be refracted
III. If an angle of incidence is larger than the critical angle, it will not experience total internal reflection.
A ray of light passing through a gel with an index of refraction of 1.5 has an incidence angle of 30° as it transitions through a pane of glass. The angle of refraction is 45°. What is the speed of light within the glass?


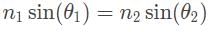

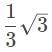 cannot be an answer.
cannot be an answer.