Test: Stereochemistry - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Stereochemistry
What is the total number of isomers with the formula C3H6O that are either cyclic or chiral?
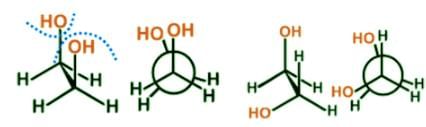
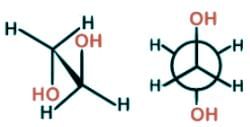
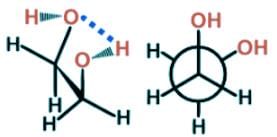
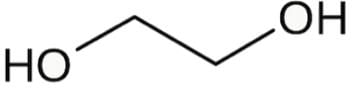
Ethylene glycol is known to most Americans as antifreeze and to some for having a sweet syrupy taste. For scientists, it can be used as a protecting group for carbonyls. Which is the most stable conformer of the compound ethylene glycol depicted below?

Which of the following cyclic hydrocarbon structures would be NOT categorized as an achiral compound?
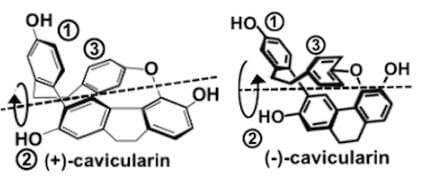
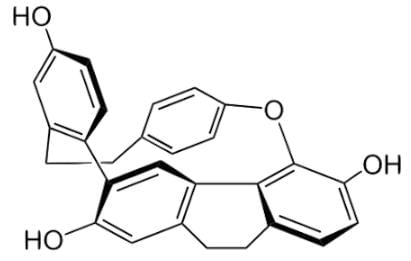
Cavicularin is a natural phenolic secondary metabolite isolated from the liverwort Cavicularia densa, and the structure is depicted below. Your research group discovers that the sample rotates plane-polarized light 168.2 degrees. Based on the findings, which of the following statements can be deduced about the stereochemistry of this compound?
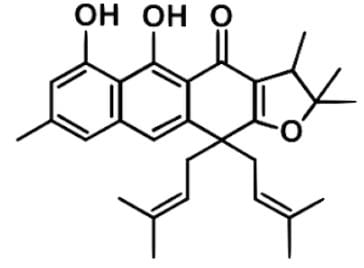
Plant extracts are widely used in many parts of Cameroon to treat infectious diseases or related symptoms including abdominal pains, itching, urinary and respiratory ailments, fever and coughing, diarrhea. Harunmadagascarin C as depicted below is an extract from the plant Harungana madagascariensis that has been studied for potential antimicrobial activity. Which statement best describes the stereochemistry of the compound?
Which of the following statements most accurately describes the characteristics of diastereomers, enantiomers, and meso compounds?
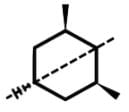
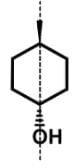
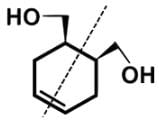
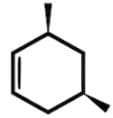
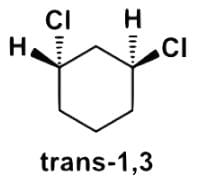
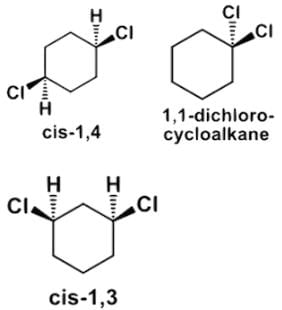
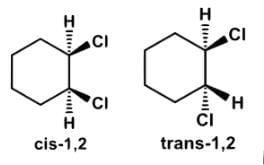
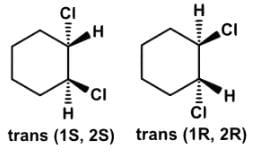
Which of the following statements most accurately describes the stereochemistry between the various cyclohexanes?
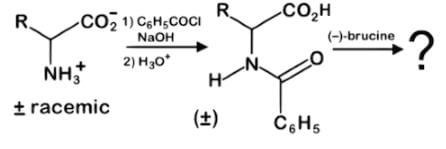
While brucine is a naturally occurring alkaloid related to strychnine and hence poisonous, it can be used as a tool for stereospecific chemical syntheses. Which of the following statements best describes the result of this reaction series with a racemic mixture of an amino acid?
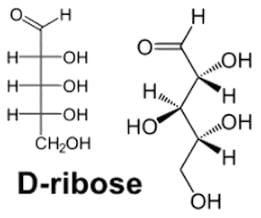
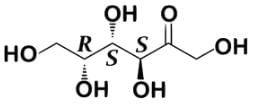
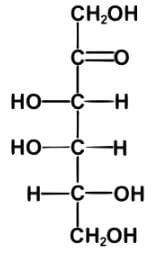
Tagalose is a functional sweetener and can be found in milk in small amounts. Commercially, Tagalose is produced from lactose, whereby galactose is isomerized under alkaline conditions to D-tagatose (shown below) by calcium hydroxide. Based on the Fischer projection, which of the following wedge-dash structures correctly represents D-tagatose?
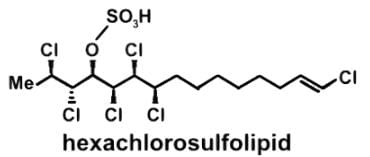
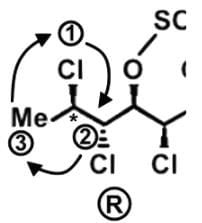
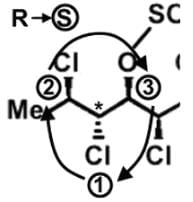
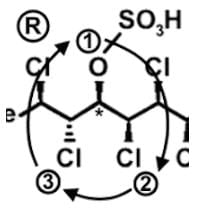
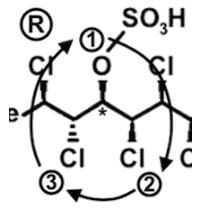
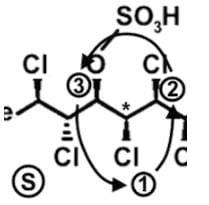
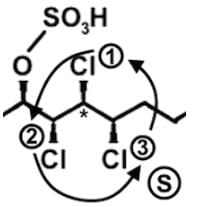
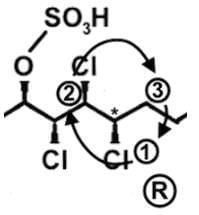
The compound hexachlorosulfolipid belongs to a class of compounds called chlorosulfolipids, which are integral components of algal membranes and are known to inhibit protein kinases. Some have been isolated from mussels and are linked to diarrhetic shellfish poisoning. Based on the wedge and dash structure below, what are the R and S designations from left to right for the stereocenters of this toxin?