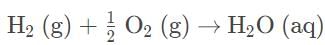Test: Thermochemistry - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Thermochemistry
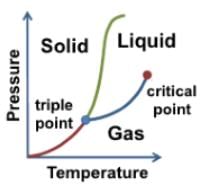
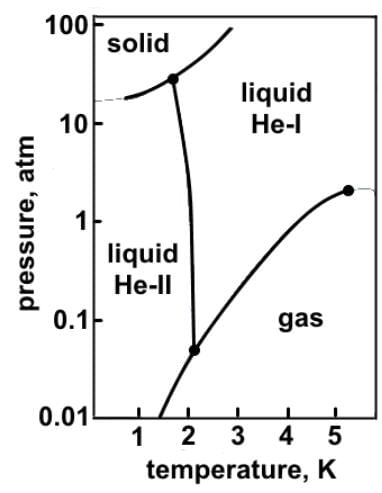
Which of the following statements can reasonably be deduced from the phase diagram of helium below?

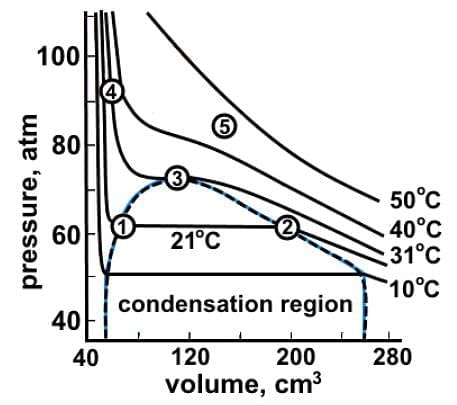
Which of the following statements best characterizes the data represented in the liquid-vapor phase diagram of carbon dioxide where the dotted line represents phase change?

Which of the following reactions is most likely to be spontaneous only at high temperatures?
Which of the following statements accurately describes thermochemistry?
According to Hess's law, which of the following statements is true?
The standard enthalpy of formation (ΔHf°) of an element in its most stable form is:
Which of the following equations represents a formation reaction?
Which of the following processes is associated with a positive entropy change?
Which of the following statements is true about the first law of thermodynamics?