Test: Conservative & Non Conservative Forces - Grade 9 MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Conservative & Non Conservative Forces
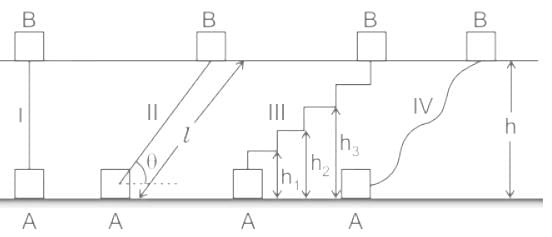
If the work of the force is independent of the path and depends only on the force’s initial and final position on the path, that force is known as _____________ force.
Which of the following forces is non-conservative in nature?
Which one belongs to a different class?
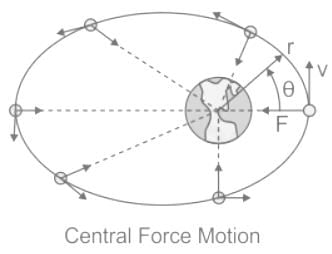
For a particle moving under a central force, it's motion will be
Pick the incorrect statement from the following
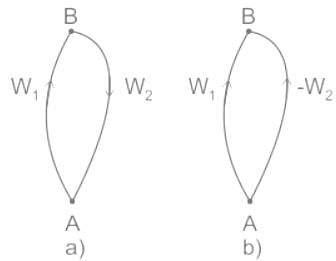
Which of the given statements are correct for a conservative force field
(p) The total mechanical energy is conserved.
(q) The work done around a closed path is zero.
(r) Gain in kinetic energy = Loss in potential energy.
Which of the following forces is an example of a conservative force?
When is the work done by a conservative force equal to zero?
Which of the following is a characteristic of conservative forces?
Which of the following statements about non-conservative forces is correct?