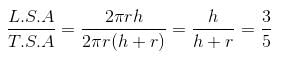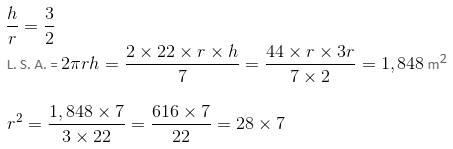ECGC PO Mock Test - 7 - Bank Exams MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - ECGC PO Mock Test - 7
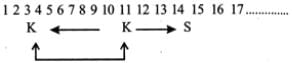
In a row of 40 girls, when Komal was shifted to her left by 4 places her number from the left end of the row become 10. What was the number of Swati from the right end of the row, if Swati was three places to the right of Komal’s original position?
Directions to Solve
In each of the following questions find out the alternative which will replace the question mark.
Question -
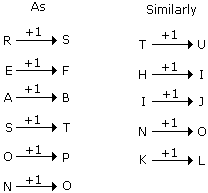
REASON : SFBTPO :: THINK : ?
Directions to Solve: In each of the questions below consists of a question and two statements numbered I and II given below it. You have to decide whether the data provided in the statements are sufficient to answer the question. Read both the statements and
Give answer:
- (A) If the data in statement I alone are sufficient to answer the question, while the data in statement II alone are not sufficient to answer the question
- (B) If the data in statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question, while the data in statement I alone are not sufficient to answer the question
- (C) If the data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question
- (D) If the data given in both statements I and II together are not sufficient to answer the question and
- (E) If the data in both statements I and II together are necessary to answer the question.
Question: On a T.V. channel, four serials A, B, C, and D were screened, one on eacn days, on four consecutive days but not necessarily in that order. On which day was serial C screened?
Statements:
I. The first serial was screened on 23rd, Tuesday and was followed by serial D.
II. Serial A was not screened on 25th and one serial was screened between serials A and B.
- (A) If the data in statement I alone are sufficient to answer the question, while the data in statement II alone are not sufficient to answer the question
- (B) If the data in statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question, while the data in statement I alone are not sufficient to answer the question
- (C) If the data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question
- (D) If the data given in both statements I and II together are not sufficient to answer the question and
- (E) If the data in both statements I and II together are necessary to answer the question.
Statements:
I. The first serial was screened on 23rd, Tuesday and was followed by serial D.
II. Serial A was not screened on 25th and one serial was screened between serials A and B.
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the given question.
In a certain code:
'chest teeth gap limb' is coded as Q&2 C%3 U#4 I?4
'borrow some corn people' is coded as F@3 0#3 X!5 F*5
'eat bank scheme tomato' is coded as P?5 L!3 U^2 F@5
'gossible come person gones' is coded as F#3 T&4 F&7 O*5
What will be the code for 'linguist paraglide emperor'?
Directions: These questions are based on the following information, read the comprehension carefully to answer the given questions.
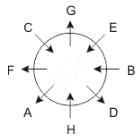
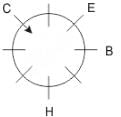
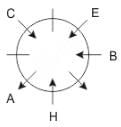
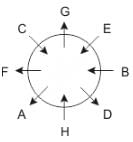
Eight people A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting around a circular table but not necessarily in the same order. Some are facing inside and some are facing outside. Not more than two people facing same direction are sitting together.
H sits third to the right of C who is not facing outside. Immediate neighbours of H are facing same directions with respect to each other but opposite direction with respect to H who is facing inside. B is the immediate neighbor of E and both are facing same direction. E sits second to the left of C who is not the immediate neighbor of B. There are equal number of persons facing inside and outside direction. B sits third to the left of A and both are facing opposite directions to each other. H sits to the immediate right of D. F sits second to the left of G.
Q. What is the position of F with respect to E?
Directions: Read the information given below to answer these questions:
(i) Aarti is older than Sanya.
(ii) Muskan is elder than Aarti but younger than Kashish.
(iii) Kashish is elder than Sanya.
(iv) Sanya is younger than Muskan.
(v) Gargi is the eldest.
Q. Daksh is taller than Manick but not as tall as Rohan. Somesh is shorter than Daksh but taller than Farhan. Who among them is the shortest?
A man goes to his office from his house at a speed of 3 km/hr and returns at a speed of 2 km/hr. If he takes 5 hours in going and coming, what is the distance between his house and office?
The odds in favour of standing first of three students Amit, Vikas and Vivek appearing at an examination are 1 : 2. 2 : 5 and 1 : 7 respectively. What is the probability that either of them will stand first (assume that a tie for the first place is not possible).
How is A related to B?
I. B is the only brother of R, whose father is Q.
II. A is the only son of G, who is only sister of R.
What is A’s position from the left end in a row of children facing South?
I. B is tenth to the left of A and fifteenth from the right end of the row.
II. There are 44 children besides A in the row
Ratio between the lateral surface area and the total surface area of a right circular cylinder is 3 : 5. If the lateral surface area is 1848 sq. m, then volume of the cylinder is (in cubic m).
Directions : Study the following bar chart carefully and answer the questions given below:
Given line graph shows the data of washing machines of different price range of various brands during Diwali festival.

Q. How many washing machines of price up to Rs. 10000 were sold in the festival?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given beside.
Three online hotel booking website A,B and C listed some hotels on their websites. The all listed 3 star, 4 star and 5 star hotels. One hotel can be listed on exactly one website.
Further it is known that
- Total number of hotels listed on all three website together is 720.
- Total number of 4 star hotels is twice the total number of 3 star hotels on all the three websites taken together. Further, total number of 5 star hotels is thrice the total number of 4 star hotels on all three sites together.
- Out of 200 hotels listed on Websites A, 30% are 3 star hotels.
- Ratio of 5 star hotels on sites A,B and C are 1 : 1 : 2.
- Number of 5 star hotels on B website is 20% more than number of 4 star hotels on the same website.
- Number of 3 star hotels on website B and C are same.
Q. Website D also started listing of Hotels on their site. Number of 3 star hotels on site D is 50% more than number of 4 star hotels on site A. Total number of hotels (3 star, 4 star and 5 star) on site D are 500, out of which 50% are 4 star. Find the number of 5 star hotels listed on site D.
Read the each sentence to find out whether there is any grammatical error in it. The error, if any will be in one part of the sentence. The letter of that part is the answer. If there is no error, the answer is 'D'. (Ignore the errors of punctuation, if any).
The rate of metabolism of (a) / a body is comparatively lowest when (b) / it is at rest and is (c) / thus optimum for examination (d) / No error (e)
He is the most (a) / intelligent and also (b) / the very talented (c) / student of the college (d) / No error (e)
Each species has its special place or habitat. An (31)____ bird watcher can look at (32)____forest, meadow, lake , swamp or field and (33)____ almost exactly what birds he (34)____find there (35)____birds are found all over the world; others (36)____ themselves to certain areas. Still (37)____migrate from one country to another in (38)____in search of warmth and (39)____, and then return in spring,(40)____the season is more favourable.
Q. Find the word most appropriate for Blank No. 35
Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions that follow:
Paragraph 1: The government has announced a list of ‘Institutes of Eminence’ (IoE) among India’s institutions of higher education. This was awaited for the simple reason that finding a place on it would save an educational institution from the clutches of a dreaded regulator. Regulators are meant to ensure that we have a socially desirable outcome, but in the case of higher education in India the opposite seems to have been the case. The University Grants Commission (UGC) has over half a century micro-managed this space to an unimaginable level of silliness. The result has been publicly-funded universities that are cavernous wastes, shattering the aspirations of our youth and producing low-level ‘knowledge’. Evidence of the role of India’s higher-education regulator may be seen in the feature that the few instances when this is not the case the institutions have enjoyed privilege that leaves them protected from its depredations.
Paragraph 2: The latest offering is in the form of a proposed Higher Education Commission of India (HECI). The intention is to leave the HECI to focus on quality while leaving funding of public institutions to the Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD). Even as we observe the progress of the HECI and wonder if it is going to be any more than old wine in a new bottle, we already have an inkling of what could go wrong. This springs from the government’s announcement of a list of IoEs. The government has chosen three public and three private institutions for this status. The public institutions are the Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru, and the Indian Institutes of Technology at Delhi and Mumbai. The private ones are the Birla Institute of Technology and Science Pilani, the JIO Institute and the Manipal Academy of Higher Education. This list suffers from a serious lack of credibility. Where in it are the universities of India? We understand that the government’s aim is to rectify the low presence of Indian institutions in the global rankings of universities.
Paragraph 3: While the early European universities may have started as academies of the arts they were soon to have medicine and astronomy as areas that they pursued with vigour. Somewhere along the line we seem to have lost this breadth and come to revel in a landscape dominated by engineering schools. These engineering schools, notably the IITs, have done us proud but cannot be equated with the great universities of the world for the simple reason that they are focussed on a narrow domain. Also, if the idea behind IoEs is that they will be left alone and given enhanced financial support, it must be acknowledged that until very recently the IITs have not been meddled with neither have they been starved of resources. The IISc is of course broader than the IITs but does not embrace the social sciences and the humanities, the presence of which would be considered necessary for a university.
Paragraph 4 : If a list of eminent institutions in the country is at all needed, the absence of the Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU) from the first list of IoEs is striking. Its faculty has brought many of the world’s leading ideas to Indian students and in at least area came close to building a new school of thought, however controversial. It is not as if similar efforts in the social sciences have not occurred elsewhere in India but JNU has perhaps sustained its reputation as a university for longer. It already had schools of Computer Science and the Life Sciences over four decades ago when these were fledgling disciplines giving it a certain breadth early on.
Paragraph 5 : Even as we may wonder at the exclusion of JNU from the list of IoEs released by the government one might wonder at how the private institutions that are on it made the cut. While BITS Pilani may have made a significant contribution to the country at a time when it desperately needed engineers, but is yet not what may be considered a university, the presence of the two others on the list leave one nonplussed. One of them, we are told, has been conferred the status on grounds of its promise, a dubious position to take as this institute has little to show except for the financial heft that will surely undergird it. The other is known largely for its association with the practice of charging capitation fees for education.
Q. Which of the following may be inferred from paragraph 3?
I. Universities should embody knowledge across a wide range of disciplines.
II. There is an emphasis on a depth of knowledge across a broad horizon in Indian Universities today.
III. In India, a lot of focus is given to Institutions which are focused on only few areas.
Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions that follow:
Paragraph 1 : The government has announced a list of ‘Institutes of Eminence’ (IoE) among India’s institutions of higher education. This was awaited for the simple reason that finding a place on it would save an educational institution from the clutches of a dreaded regulator. Regulators are meant to ensure that we have a socially desirable outcome, but in the case of higher education in India the opposite seems to have been the case. The University Grants Commission (UGC) has over half a century micro-managed this space to an unimaginable level of silliness. The result has been publicly-funded universities that are cavernous wastes, shattering the aspirations of our youth and producing low-level ‘knowledge’. Evidence of the role of India’s higher-education regulator may be seen in the feature that the few instances when this is not the case the institutions have enjoyed privilege that leaves them protected from its depredations.
Paragraph 2 : The latest offering is in the form of a proposed Higher Education Commission of India (HECI). The intention is to leave the HECI to focus on quality while leaving funding of public institutions to the Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD). Even as we observe the progress of the HECI and wonder if it is going to be any more than old wine in a new bottle, we already have an inkling of what could go wrong. This springs from the government’s announcement of a list of IoEs. The government has chosen three public and three private institutions for this status. The public institutions are the Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru, and the Indian Institutes of Technology at Delhi and Mumbai. The private ones are the Birla Institute of Technology and Science Pilani, the JIO Institute and the Manipal Academy of Higher Education. This list suffers from a serious lack of credibility. Where in it are the universities of India? We understand that the government’s aim is to rectify the low presence of Indian institutions in the global rankings of universities.
Paragraph 3 : While the early European universities may have started as academies of the arts they were soon to have medicine and astronomy as areas that they pursued with vigour. Somewhere along the line we seem to have lost this breadth and come to revel in a landscape dominated by engineering schools. These engineering schools, notably the IITs, have done us proud but cannot be equated with the great universities of the world for the simple reason that they are focussed on a narrow domain. Also, if the idea behind IoEs is that they will be left alone and given enhanced financial support, it must be acknowledged that until very recently the IITs have not been meddled with neither have they been starved of resources. The IISc is of course broader than the IITs but does not embrace the social sciences and the humanities, the presence of which would be considered necessary for a university.
Paragraph 4 : If a list of eminent institutions in the country is at all needed, the absence of the Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU) from the first list of IoEs is striking. Its faculty has brought many of the world’s leading ideas to Indian students and in at least area came close to building a new school of thought, however controversial. It is not as if similar efforts in the social sciences have not occurred elsewhere in India but JNU has perhaps sustained its reputation as a university for longer. It already had schools of Computer Science and the Life Sciences over four decades ago when these were fledgling disciplines giving it a certain breadth early on.
Paragraph 5 : Even as we may wonder at the exclusion of JNU from the list of IoEs released by the government one might wonder at how the private institutions that are on it made the cut. While BITS Pilani may have made a significant contribution to the country at a time when it desperately needed engineers, but is yet not what may be considered a university, the presence of the two others on the list leave one nonplussed. One of them, we are told, has been conferred the status on grounds of its promise, a dubious position to take as this institute has little to show except for the financial heft that will surely undergird it. The other is known largely for its association with the practice of charging capitation fees for education.
Q. As per your understanding of the passage studied above, what can be some reasons for lack of quality in higher education?
I. State universities recruited a lot of faculty members on contract basis who have little incentive to perform.
II. Public universities are insulated from political pressure.
III. The amount spent on research is very less as compared to foreign Institutions.
Directions: Out of the given alternatives, choose the one which can be substituted for the given words/sentence.
A person who pretends to have more knowledge or skill than he really has:
Directions: Out of the given alternatives, choose the one which can be substituted for the given words/sentence.
One who knows two languages:
Which of the following programming language was used in the First Generation of Computers?
Which of the following programming languages is used to create web pages and web applications?
Which postal organizations signed a bilateral Tracked Packet agreement to start International Tracked Packet Service?
What was the objective of the MoU signed between the National Anti-Doping Agency, India, and the South Asia Regional Anti-Doping Organization (SARADO)?
Who has been re-appointed as the Solicitor General of India?
What is the significance of the Quit India Movement (QIM) commemorated on August Kranti Day?