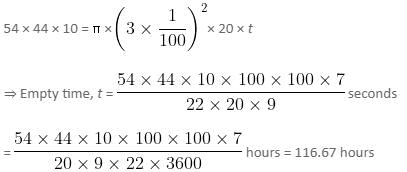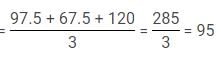BSF Head Constable Mock Test - 9 - CDS MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - BSF Head Constable Mock Test - 9
How many runs did Sachin Tendulkar was scored in his ODI debut?
Which one of the following glands produces the growth hormone (somatotrophin)?
Mount Abu is a hill station located in ______ ranges.
Which authority recommends the principles gov erring the grantsin-aid of the revenues of the States out of the Consolidated Fund of India?
What is the objective of the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) signed between the Ministry of Defence (MoD) and the Food Safety & Standards Authority of India (FSSAI)?
Which company has signed a contract with the Government e-Marketplace (GeM) for developing, implementing, operating, and maintaining the GeM portal?
Study the following line graph and answer the questins.
Exports from Three Companies Over the Years (in Rs. crore)
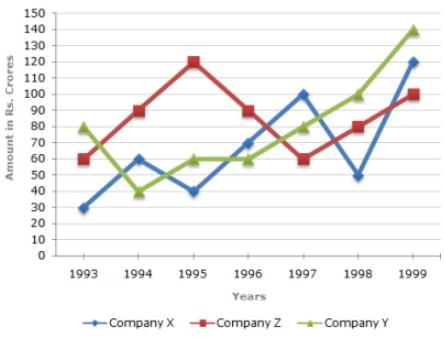
Q. In how many of the given years, were the exports from Company Z more than the average annual exports over the given years?
The average rainfall for the first 3 days out of five days was recorded to be 0.45 inches. The rainfall on the last two days was in the ratio 2:3. The average of five days was 0.40 inches. What was the rainfall on the last day?
The average price of a share is the average of 5 readings taken at regular intervals in a day. The index price is taken by a weighted arithmetic average price of a class A and class B stock. The respective weights are 1.1 and 0.9 for the two kinds of stocks. If the five readings of a class A stock were 19, 26, 31, 35, 39 and for a class B stock the readings were 7, 8, 17, 20, 23 then what was the index price that day?
What is the rate of simple interest for the first 4 years if the sum of Rs. 360 becomes Rs. 540 in 9 years and the rate of interest for the last 5 years is 6%?
When the price of rice is increased by 30 percent, a family reduces its consumption such that the expenditure is only 20 percent more than before. If 50 kg of rice is consumed by family before, then find the new consumption of family (approx.)
A man has 4000 rupees in his account two years ago. In the first year he deposited 20 percent of the amount in his account. In the next year he deposited 10 percent of the increased amount in the account. Find the total amount in the account of the person after 2 years.
A 60 year old father in his will divides his money among his three sons in the ratio of their ages. The first (eldest) son is 8 years older than the third son. The second son is 4 years younger to the first son. The third son's age is 1/3rd of his father's age. If the father had Rs. 12,00,000, the share of second son is:
Brian and Sam are two brothers who work at a multinational company in the New York City. The ratio of monthly incomes of Brian and Sam is 3 : 4 and the ratio of their monthly savings is 2 : 3, respectively. It is known that Brian spends two-thirds of his income each month. Find the respective ratio of their monthly expenditures.
Vijay bought some pens for Rs. 540. He lost 2 pens on his way back to the shop. Then, he sold the rest of the pens at Rs. 6 more (per pen) than what he paid for them. On the whole transaction, Vijay gained 10% on his outlay. How many pens did Vijay buy?
Gopal, a cunning milkman, buys milk from Frontier Dairy Junction and sells it to gullible housewives. He buys milk at Rs. 35 per litre and adds 250 ml of pure water to a litre of the thick creamy milk. He sells the mixture so formed at Rs. 45 per litre. What is his approximate profit percentage? It is to be assumed that it costs him next to nothing to mix the milk in water.
A rectangular reservoir has dimensions 54 meters × 44 meters × 10 meters. An outlet pipe of circular cross-section has a radius of 3 centimeters and the water runs through the pipe at a rate of 20 meters/second. What is the time taken by the outlet pipe to empty the reservoir full of water?
Out of the four sectors given, how many sectors showed a consistent trend(increase or decrease) in percentage in the allocation between the fourth plan and the seventh plan
Directions: Study the following bar chart carefully and answer the questions given beside.
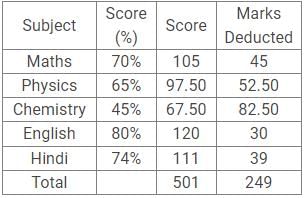
The chart given below shows the percentage marks of a student in five different subjects. The maximum marks in each subject are 150.
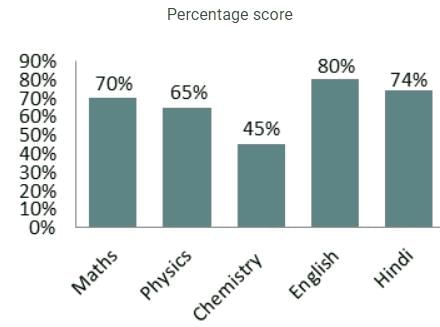
What is the average score of Physics, Chemistry and English?
Find out the Synonym of the following word:
STRINGENT
Find out the Synonym of the following word:
HESITATED
Read the each sentence to find out whether there is any grammatical error in it. The error, if any will be in one part of the sentence. The letter of that part is the answer. If there is no error, the answer is 'D'. (Ignore the errors of punctuation, if any).
In the following questions four alternatives are given for the idiom/phrase italicised and underlined in the sentence. Choose the alternative which best expresses the meaning of idiom/phrase.
Q. Sanjay is very different about passing the Civil Services Examination this year.
The Great Wall Space Agency’s recent attempts to launch a man into space, a majorgoal of their space program for the past few years, has not substantially decreasedthe gaps existing between the technology-rich and technology-poor cities aroundthe space center.
Direction: Each question below has one blank, which is indicating that something has been omitted. Find out which option can be used to fill up the blank in the sentence in the same sequence to make it meaningfully complete.
There has been _____________ interest among retail investors in ETF, thanks to the underperformance of the actively-managed large-cap equity funds.
Directions: Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
There is now no denying that the new government takes office amid a clear economic slowdown. The first macro data set released showed an under-performing economy with GDP growth falling to 5.8% in the fourth quarter of 2018-19 and pulling down the overall growth for the fiscal to a five-year low of 6.8%. Growth in gross value added (GVA), which is GDP minus taxes and subsidies, fell to 6.6% in 2018-19, pointing to a serious slowdown. If further confirmation were needed, the growth in core sector output — a set of eight major industrial sectors — fell to 2.6% in April, compared to 4.7% in the same month last year. And finally, unemployment data, controversially suppressed by the Union government so far, showed that joblessness was at a 45-year high of 6.1% in 2017-18. These numbers highlight the challenges ahead in drafting the Budget for 2019-20. The economy is beset by a consumption slowdown as reflected in the falling sales of everything from automobiles to consumer durables, even fast-moving consumer goods. Private investment is not taking off, while government spending, which kept the economy afloat during the last NDA government, was cut back in the last quarter of 2018-19 to meet the fiscal deficit target of 3.4%.
The good news is that inflation is undershooting the target and oil prices are on the retreat again. But the rural economy remains in distress, as seen by the 2.9% growth in agriculture last fiscal; the sector needs a good monsoon this year to bounce back. Overall economic growth in the first quarter of this fiscal is likely to remain subdued, and any improvement is unlikely until the late second quarter or the early third. There are not too many options before the new Finance Minister. In the near term, she has to boost consumption, which means putting more money in the hands of people. That, in turn, means cutting taxes, which is not easy given the commitment to rein in the fiscal deficit. In the medium term, Ms. Sitharaman has to take measures to boost private investment even as she opens up public spending again. These call for major reforms, starting with land acquisition and labour, corporate taxes by reducing exemptions and dropping rates, and nursing banks back to health. On the table will be options such as further recapitalisation of the ailing banks, and consolidation. The question, though, is where the money will come from. With tax revenues likely to be subdued owing to the slowdown, the Centre will have to look at alternative sources such as disinvestment. There may be little choice but to go big on privatisation. A rate cut by the Reserve Bank of India, widely expected this week, would certainly help boost sentiment. But it is the Budget that will really set the tone for the economy
Q. As per the passage, which of the following reforms has NOT been mentioned in the passage to improve the investment climate?
Directions: Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
There is now no denying that the new government takes office amid a clear economic slowdown. The first macro data set released showed an under-performing economy with GDP growth falling to 5.8% in the fourth quarter of 2018-19 and pulling down the overall growth for the fiscal to a five-year low of 6.8%. Growth in gross value added (GVA), which is GDP minus taxes and subsidies, fell to 6.6% in 2018-19, pointing to a serious slowdown. If further confirmation were needed, the growth in core sector output — a set of eight major industrial sectors — fell to 2.6% in April, compared to 4.7% in the same month last year. And finally, unemployment data, controversially suppressed by the Union government so far, showed that joblessness was at a 45-year high of 6.1% in 2017-18. These numbers highlight the challenges ahead in drafting the Budget for 2019-20. The economy is beset by a consumption slowdown as reflected in the falling sales of everything from automobiles to consumer durables, even fast-moving consumer goods. Private investment is not taking off, while government spending, which kept the economy afloat during the last NDA government, was cut back in the last quarter of 2018-19 to meet the fiscal deficit target of 3.4%.
The good news is that inflation is undershooting the target and oil prices are on the retreat again. But the rural economy remains in distress, as seen by the 2.9% growth in agriculture last fiscal; the sector needs a good monsoon this year to bounce back. Overall economic growth in the first quarter of this fiscal is likely to remain subdued, and any improvement is unlikely until the late second quarter or the early third. There are not too many options before the new Finance Minister. In the near term, she has to boost consumption, which means putting more money in the hands of people. That, in turn, means cutting taxes, which is not easy given the commitment to rein in the fiscal deficit. In the medium term, Ms. Sitharaman has to take measures to boost private investment even as she opens up public spending again. These call for major reforms, starting with land acquisition and labour, corporate taxes by reducing exemptions and dropping rates, and nursing banks back to health. On the table will be options such as further recapitalisation of the ailing banks, and consolidation. The question, though, is where the money will come from. With tax revenues likely to be subdued owing to the slowdown, the Centre will have to look at alternative sources such as disinvestment. There may be little choice but to go big on privatisation. A rate cut by the Reserve Bank of India, widely expected this week, would certainly help boost sentiment. But it is the Budget that will really set the tone for the economy
Q. As per the passage, which of the following would lead to ‘putting more money in the hands of people’?
I. Decrease in tax rates.
II. Increase in inflation
III. Increase in private investment
Directions: Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
There is now no denying that the new government takes office amid a clear economic slowdown. The first macro data set released showed an under-performing economy with GDP growth falling to 5.8% in the fourth quarter of 2018-19 and pulling down the overall growth for the fiscal to a five-year low of 6.8%. Growth in gross value added (GVA), which is GDP minus taxes and subsidies, fell to 6.6% in 2018-19, pointing to a serious slowdown. If further confirmation were needed, the growth in core sector output — a set of eight major industrial sectors — fell to 2.6% in April, compared to 4.7% in the same month last year. And finally, unemployment data, controversially suppressed by the Union government so far, showed that joblessness was at a 45-year high of 6.1% in 2017-18. These numbers highlight the challenges ahead in drafting the Budget for 2019-20. The economy is beset by a consumption slowdown as reflected in the falling sales of everything from automobiles to consumer durables, even fast-moving consumer goods. Private investment is not taking off, while government spending, which kept the economy afloat during the last NDA government, was cut back in the last quarter of 2018-19 to meet the fiscal deficit target of 3.4%.
The good news is that inflation is undershooting the target and oil prices are on the retreat again. But the rural economy remains in distress, as seen by the 2.9% growth in agriculture last fiscal; the sector needs a good monsoon this year to bounce back. Overall economic growth in the first quarter of this fiscal is likely to remain subdued, and any improvement is unlikely until the late second quarter or the early third. There are not too many options before the new Finance Minister. In the near term, she has to boost consumption, which means putting more money in the hands of people. That, in turn, means cutting taxes, which is not easy given the commitment to rein in the fiscal deficit. In the medium term, Ms. Sitharaman has to take measures to boost private investment even as she opens up public spending again. These call for major reforms, starting with land acquisition and labour, corporate taxes by reducing exemptions and dropping rates, and nursing banks back to health. On the table will be options such as further recapitalisation of the ailing banks, and consolidation. The question, though, is where the money will come from. With tax revenues likely to be subdued owing to the slowdown, the Centre will have to look at alternative sources such as disinvestment. There may be little choice but to go big on privatisation. A rate cut by the Reserve Bank of India, widely expected this week, would certainly help boost sentiment. But it is the Budget that will really set the tone for the economy
Q. Which of the following is / are true as per the passage?
I. There is going to be a definite rate cut by the RBI in the coming week.
II. The rural economy is in better shape than the urban economy.
III. Government spending has increased in the last quarter of 2018-19.



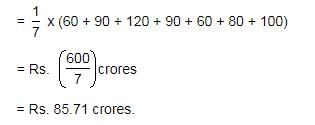
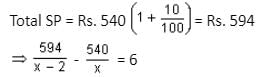 On simplifying, we get
On simplifying, we get