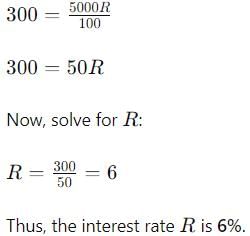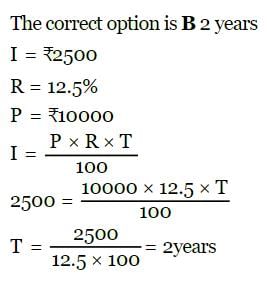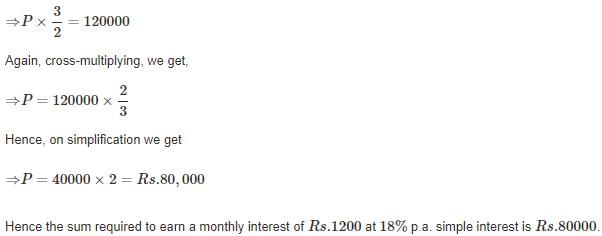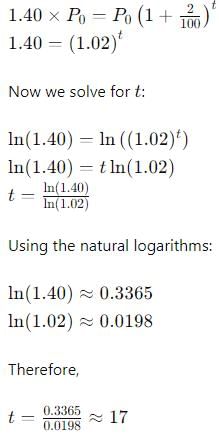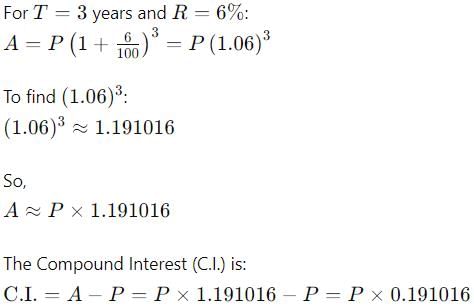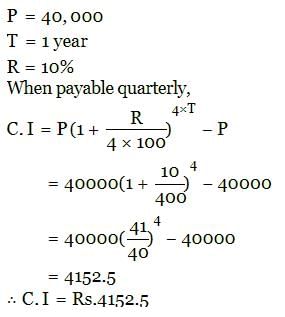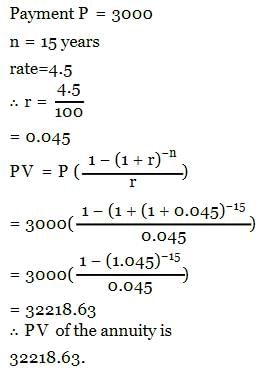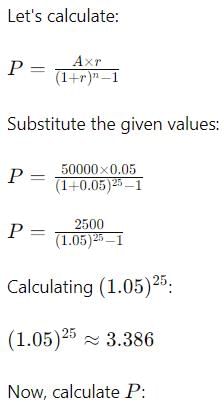Test: Simple And Compound Interest Including Annuity - 1 - CA Foundation MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Simple And Compound Interest Including Annuity - 1
Choose the most appropriate option (a) (b) (c) (d)
S.I on Rs. 3500 for 3 years at 12% per annum is
P = 5000, R = 15, T = 4 ½ using I = PRT/100, I will be
If P = 5000, T = 1, I = Rs. 300, R will be
Find the compound interest on Rs. 7500 at 4% per annum for 2 years, compounded annually.
P = Rs. 12000, A = Rs. 16500, T = 2 ½ years. Rate percent per annum simple interest will be P = Rs. 12000.
P = Rs. 10000, I = Rs. 2500, R = 12 ½% SI. The number of years T will be
P = Rs. 8500, A = Rs. 10200, R = 12 ½ % SI, t will be.
The sum required to earn a monthly interest of Rs 1200 at 18% per annum SI is
In simple interest, a sum of money amounts to ₹ 6,200 in 2 years and ₹ 6,800 in 3 years. Find the principal and rate of interest.
A sum of money doubles itself in 10 years. The number of years it would triple itself is
If P = Rs. 1000, R = 5% p.a, n = 4; Amount and C.I. is
Rs. 100 will become after 20 years at 5% p.a compound interest calculated annually
The effective rate of interest corresponding to a nominal rate 3% p.a payable half yearly is
A machine is depreciated at the rate of 20% on reducing balance. The original cost of the machine was Rs. 100000 and its ultimate scrap value was Rs. 30000. The effective life of the machine is
If A = Rs. 1000, n = 2 years, R = 6% p.a compound interest payable half-yearly, then principal (P) is
The population of a town increases every year by 2% of the population at the beginning of that year. The number of years by which the total increase of population be 40% is
The difference between C.I and S.I on a certain sum of money invested for 3 years at 6% p.a is Rs. 110.16. the sum is
The useful life of a machine is estimated to be 10 years and cost Rs.10,000. Rate of depreciation is 10% p.a. The scrap value at the end of its life is
The effective annual rate of interest corresponding to a nominal rate of 6% per annum payable half-yearly is
The C.I on Rs. 16000 for 1 ½ years at 10% p.a payable half -yearly is
The C.I on Rs. 40000 at 10% p.a for 1 year when the interest is payable quarterly is
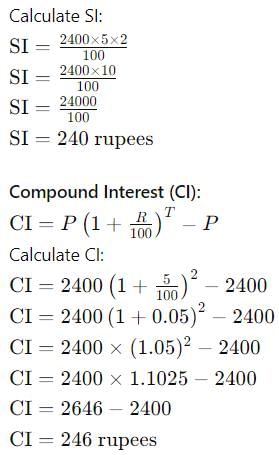
The difference between the S.I and the C.I on Rs. 2400 for 2 years at 5% p.a is
The annual birth and death rates per 1000 are 39.4 and 19.4 respectively. The number of years in which the population will be doubled assuming there is no immigration or emigration is
The C.I on Rs. 4000 for 6 months at 12% p.a payable quarterly is
The present value of an annuity of Rs. 3000 for 15 years at 4.5% p.a CI is
The amount of an annuity certain of Rs. 150 for 12 years at 3.5% p.a C.I is
A loan of Rs. 10.000 is to be paid back in 30 equal instalments. The amount of each installment to cover the principal and at 4% p.a CI is
A = Rs. 1200 n = 12 yrs i = 0.08 v = ?
a = Rs. 100 , n = 10 , i = 5%. find the FV of the annuity
Using the formula FV = a / {(1 + i) n – 1}, M is equal to
If the amount of an annuity after 25 years at 5% p.a C.I is Rs. 50000 the annuity will be