Test: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - 2 - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - 2
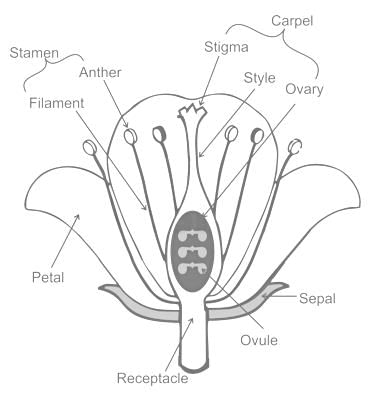
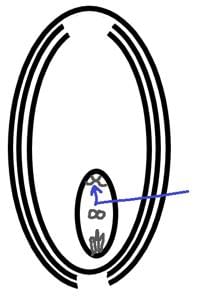
Label the part marked with a blue arrow.


Label the part marked by the blue arrow.

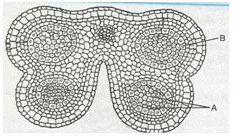
Identify “A” and “B” in the T.S of mature anther:
What happen to haploid megaspores formed by megaspore mother cell in an angiospermic plant?
A bilobed dithecous anther had 100 microspore mother cells per microsporangium. How many male gametes can this anther produce?
Pollen grain of large number of species can be stored in:
Continued self pollination results in
Abundant occurrence of fossilized pollen grain is due to resistant:
At the _______ end, embryogenesis happens.
The correct sequence of parts of female reproductive organ in plants
If an endosperm cell of angiosperm contain 24 chromosome, the number of chromosome in each cell of root is?
The meiocyte of an onion plant contains 32 chromosomes. Calculate the number of chromosomes found in its endosperm?
A typical angiospemic embryo sac is though 8 nucleate is 7-celled. 8 nuclei includes______.
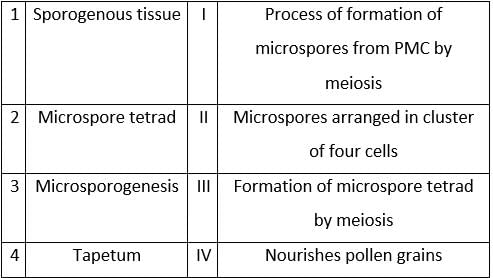
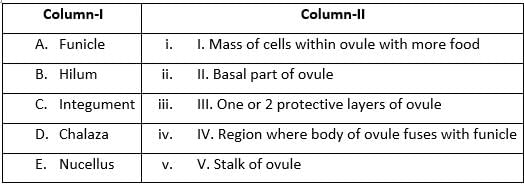
Match the Column-I to Column-II
In which of the following plants fruit contain larger number of seed?
From the statements given below choose the option that are not true for a typical female gametophyte of a flowering plant:
(i) It is 8-nucleate and 7-celled at maturity
(ii) It is cellular during the development
(iii) It is situated inside the nucellus
(iv) It has an egg apparatus situated at the chalazal end
Which one of the following statements is false in respect of flowering plants?
1. Parthenocarpy can be induced through the application of growth hormones
2. Integuments encircle the ovule except at the tip where a small opening called the germ pore is organized
3. Endosperm development precedes embryo development
4. Apomixis have several advantages in horticulture and agriculture
Find the incorrect statement:
1. A polycarpellary, apocarpous gynoecium is found in Michelia
2. Many ovules are present in an ovary of papaya and orchids
3. Yellowish, powdery pollen grains found in Hibiscus
4. The more pistils may be fused together to form monocarpellary syncarpous gynoecium