Test: Biomolecules - 1 - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Biomolecules - 1
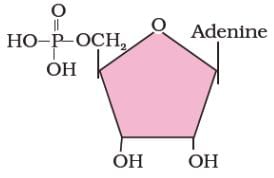
Identify the biomolecule shown in the structural diagram given below.

Proteins are polymers of amino acids that are connected by __________
Which of the following nitrogenous base produces nucleoside only with ribose sugar?
Directions: In the following question, two statements are given. One is assertion and the other is reason. Examine the statements carefully and mark the correct option.
Assertion: Both amino group and acidic group act as substituents on the same carbon called α-amino acids.
Reason: Amino acids are inorganic compounds containing an amino group.
Assertion (A): The formation of the enzyme-substrate complex is a transient phenomenon crucial for catalysis.
Reason (R): The transition state structure is the most stable state during the conversion of substrate to product.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
i. Polysaccharides are composed of long chains of monosaccharides and can be classified as homopolymers or heteropolymers.
ii. Cellulose is a homopolymer made only of glucose and forms complex helical structures.
iii. Starch serves as an energy reserve in plants and can form helical structures that bind iodine, producing a blue color.
iv. Glycogen, found in animals, is a linear polysaccharide that does not have branches.
Which of the following statements given above is/are correct?
i. In the absence of any enzyme, the formation of H2CO3 is very slow, with about 200 molecules produced in an hour.
ii. Carbonic anhydrase accelerates the reaction rate by approximately 10 million times, producing about 600,000 molecules of H2CO3 every second.
iii. The metabolic pathway from glucose to pyruvic acid involves ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
iv. Under anaerobic conditions in skeletal muscle, pyruvic acid is formed instead of lactic acid.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
i. Lipids are generally water soluble and include simple fatty acids.
ii. Fatty acids can be either saturated (without double bonds) or unsaturated (with one or more double bonds).
iii. Glycerol is a simple sugar that can be esterified with fatty acids to form triglycerides.
iv. Phospholipids are found in cell membranes and contain phosphorus.
Which of the following statements regarding nucleic acids is/are correct?
i. Nucleic acids are comprised of polynucleotides that contain ribose or deoxyribose sugars.
ii. The building blocks of nucleic acids are amino acids.
iii. The nitrogenous bases adenine, guanine, uracil, cytosine, and thymine are found in nucleic acids.
iv. DNA is a type of nucleic acid that contains ribose sugar.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
i. All amino acids contain an amino group and a carboxyl group attached to the same carbon atom.
ii. There are only twenty types of amino acids that are found in proteins.
iii. The R group in amino acids can vary and influences the properties of the amino acid.
iv. Amino acids can only be classified as acidic or basic.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
i. Enzymes require cofactors for catalytic activity, and the protein portion is known as the apoenzyme.
ii. Prosthetic groups are loosely associated with the apoenzyme and can be easily removed.
iii. Coenzymes are transiently associated with the apoenzyme and often derived from vitamins.
iv. Metal ions serve as cofactors and are essential for the activity of certain enzymes.
Which type of enzyme catalyzes the transfer of a group (other than hydrogen) between substrates?
Assertion (A): Competitive inhibitors bind to the active site of an enzyme, preventing substrate binding.
Reason (R): Due to its close structural similarity with the substrate, the inhibitor competes with the substrate for the substratebinding site of the enzyme
Which of the following statements regarding the catalytic cycle of enzyme action is/are correct?
i. The substrate binds to the active site of the enzyme, fitting perfectly into it.
ii. The enzyme changes shape to fit more tightly around the substrate after binding occurs.
iii. The enzyme-product complex is formed when the active site breaks the chemical bonds of the substrate.
iv. The enzyme remains permanently altered after releasing the products of the reaction.
Assertion (A): The acid insoluble fraction of biomolecules includes proteins, nucleic acids, polysaccharides, and lipids, which are all classified as macromolecules.
Reason (R): Lipids, despite having lower molecular weights than 800 Da, are classified as macromolecules because they exhibit polymeric characteristics.