Test: Cell Cycle & Cell Division - 1 - ACT MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Cell Cycle & Cell Division - 1
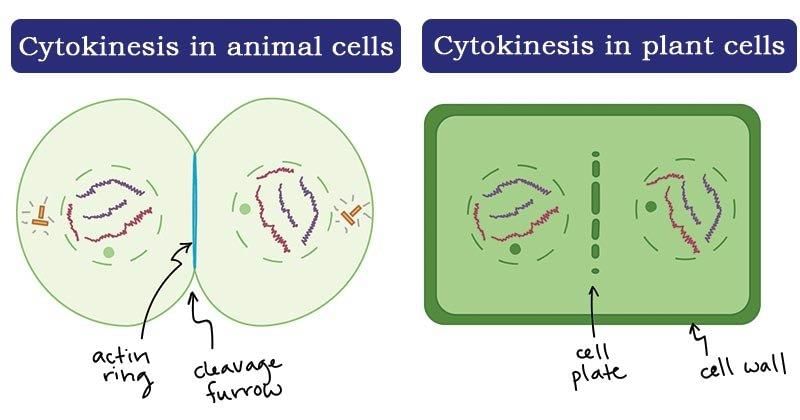
Plant Cytokinesis differ from animals Cytokinesis in having
Cell growth results in disturbing the ratio between
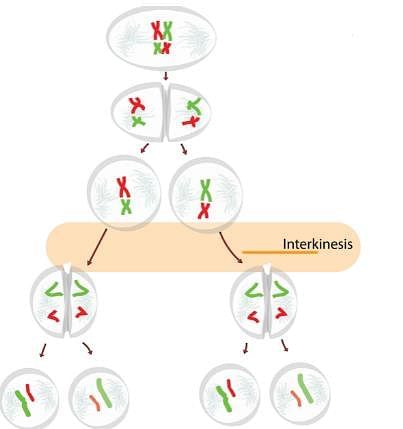
The transition period between M- phase I and M- phase II without DNA replication
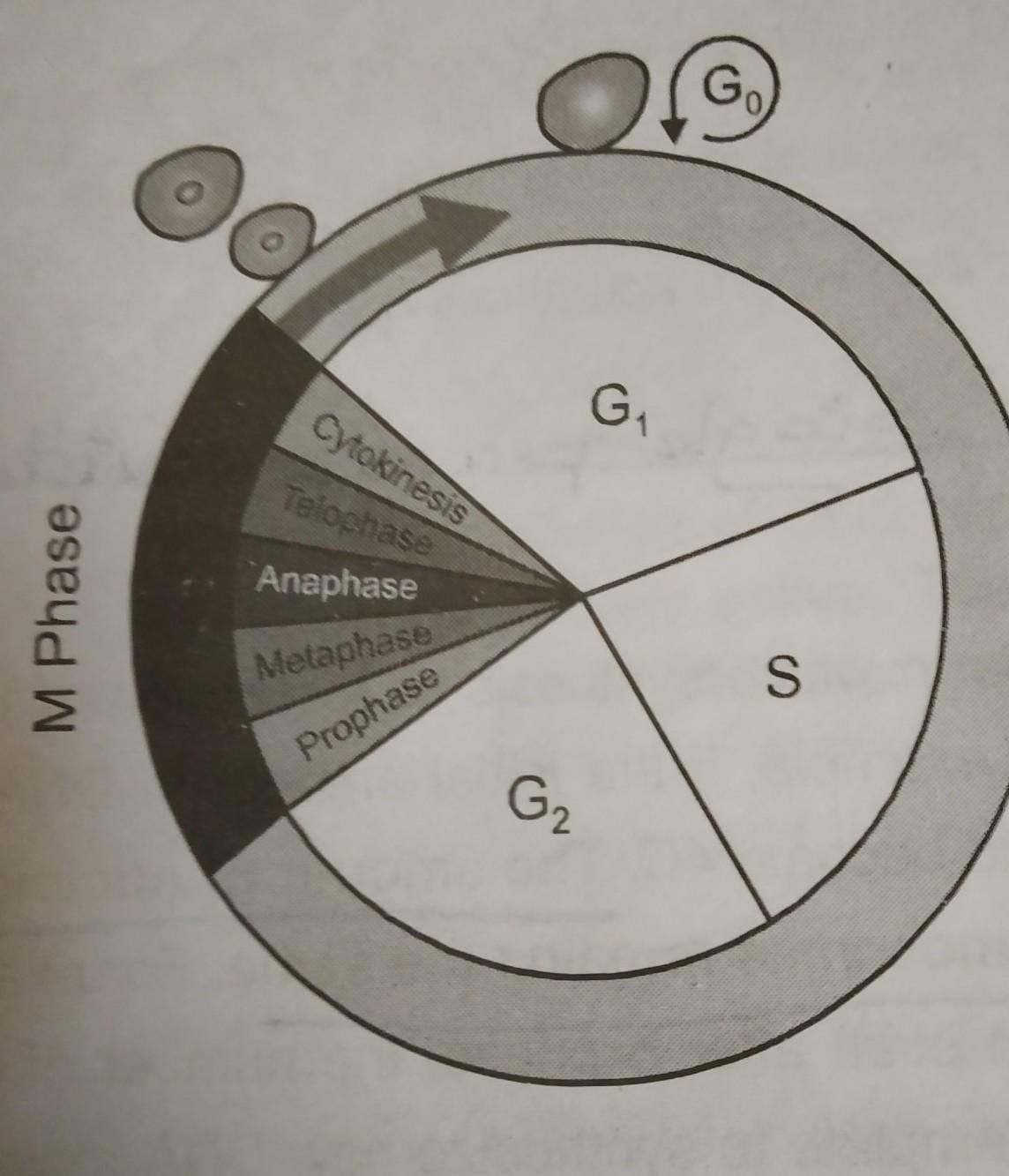
What is the average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell?
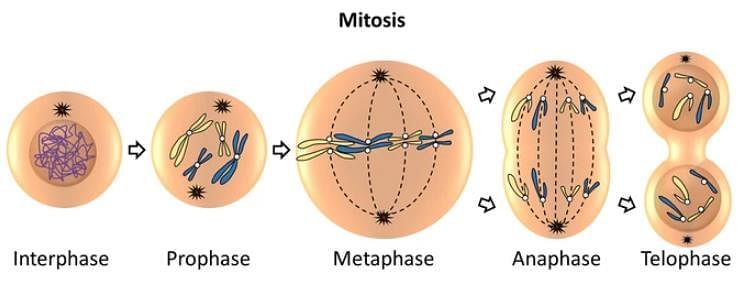
During which stage do the chromatids of a bivalent become distinct?
In some lower plants and social insects, the haploid cells are divided by
During which stage of prophase I the crossing over takes place?
M- phase in mitosis undergoes which type of division?
In yeast the cell cycle is progressed through
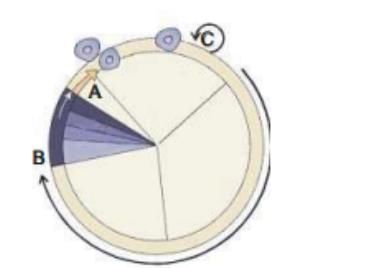
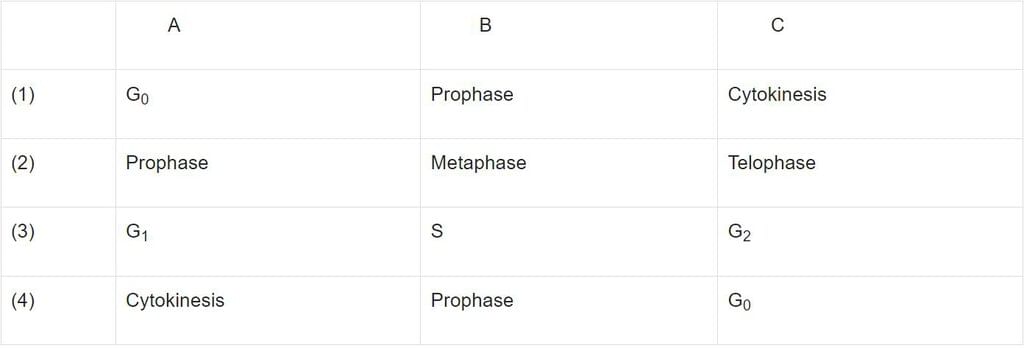
Identify the symbols A, B and C in the figure given below
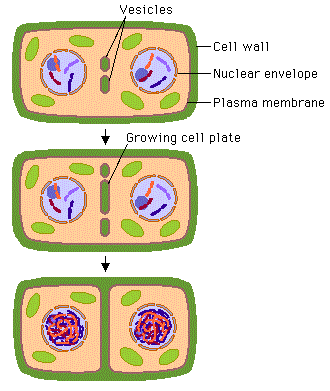
In plant cells, the new cell wall begins by the
Crossing over results in the exchange of genetic material, which occurs between:
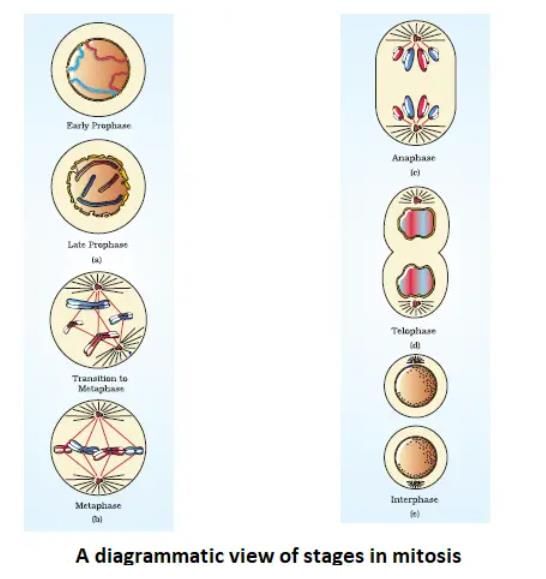
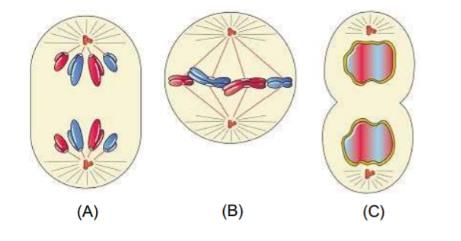
The figures below shows 3 phases of mitosis select the option given correct identification together with the correct event ?
In between two walls of adjacent cells are seen
Which is the longest phase of the cell cycle?
If the DNA content of an onion tip cell is 2C at the end of the M-phase, what would be its DNA content at the end of the S-phase?
I. During G1 phase, the cell is metabolically active and continuously grows but does not replicate its DNA.
II. During G2 phase, proteins are synthesized in preparation for mitosis while cell growth continues.
Which of the following is correct?
“The synaptonemal complex is formed during A stage and dissolves during B stage”.
Complete the above statement by choosing the correct option for A and B.