Test: Excretory Products & their Elimination - 1 - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Excretory Products & their Elimination - 1
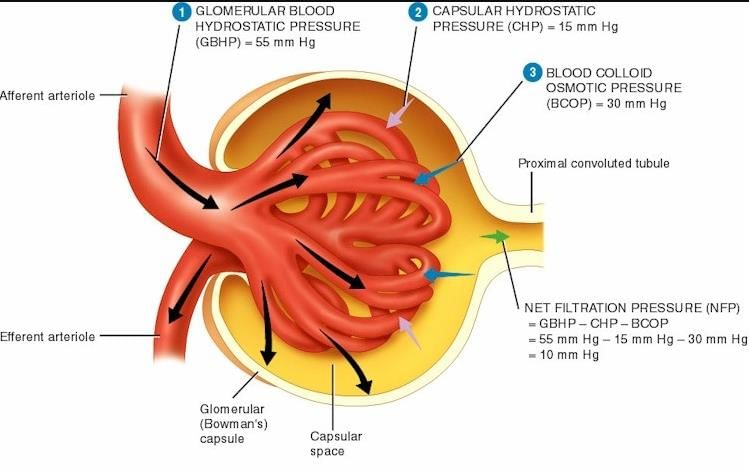
Blood enters glomerular capillaries through _____ arteriole and leaves through _____ arteriole:
The following substances are the excretory products in animals. Choose the least toxic form among them?
During micturition, the muscles of urinary bladder and urethral sphincters will
pH of urine under healthy conditions is :
The presence of ketone bodies is an indication of which of the following diseases?
The condition where urea accumulates in blood is:
Which of the following substances is not reabsorbed by renal Tubules?
Juxtaglomerular apparatus is a special sensitive region formed by cellular modifications in the:
Which of the following is not accumulated by the body of living organisms?
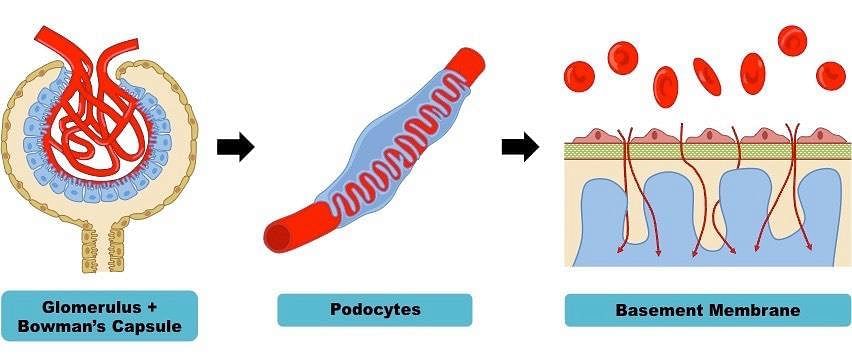
The epithelial cells of Bowman’s capsule are called:
All of the following organs help in excretion except :
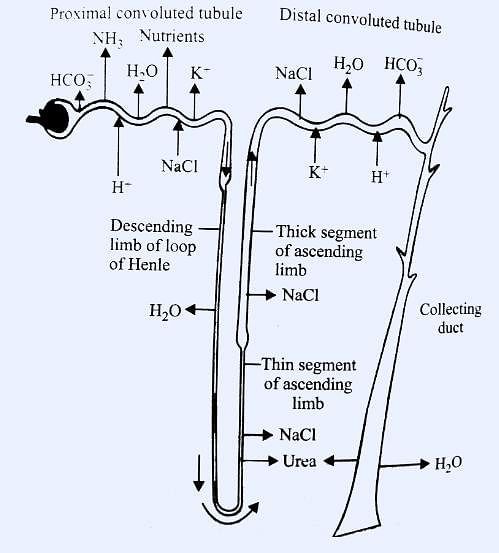
Ascending limb of Henle’s loop is not permeable for :
Conditional reabsorption of sodium ions and water takes place in
What activates osmoreceptors in the body?
Uricotelic mode of passing out nitrogenous wastes is found in?
Which hormone is released by the hypothalamus in response to excessive fluid loss from the body?
What effect does ADH have on the kidney function?
Which hormone is released by the JG cells in response to a fall in glomerular blood flow?
During urine formation, the tubular cells secrete ______________ into the filtrate.