Test: Organisms & Populations - 2 - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Organisms & Populations - 2
Which of the following groups will be able thrive in hypersaline lagoons?
Which of the following should not be characteristic feature of any xerophytes?
Which type of interaction does a mycorrhiza show?
Which should be considered more realistic growth model?
Mediterranean orchid Ophrysensures pollination by :
“In Competition, the superior competitor eliminates the inferior one”, this statement is called?
Statement I: Age pyramid of expanding population is broader at base and thin upwards.
Statement II: Number of individuals in pre-reproductive age is more than post reproductive age.
Statement III: population size is technically called as population density.
Species facing competition might evolve mechanism that promotes co-existence rather than exclusion and that mechanism can be
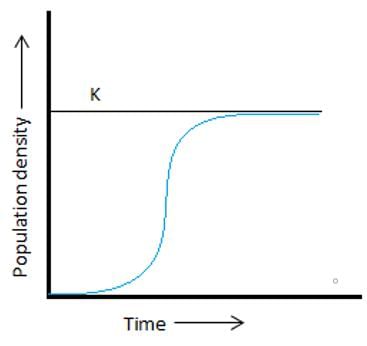
What does the blue line in the given figure indicate?
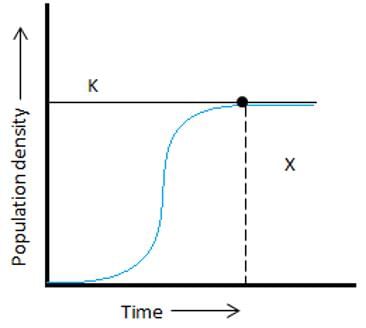
Which phase does ‘X’ in the given figure of the sigmoidal curve indicate?