Test: Neural Control & Coordination - 1 - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Neural Control & Coordination - 1
Injury localised to the hypothalamus would most likely disrupt ______.
Which of the following integrates all the activities of the organs?
Which of the following cells secrete a myelin sheath?
The………. difference across the resting membrane is called as Resting potential.
Brain stem is the support system of brain and is the collective name for:
The rise in stimulus-induced permeability to
a. Potassium ions
b. Sodium ions
c. Restoring RMP
d. Diffusion of potassium ions
Arrange them in order.
Assertion (A): The human brain functions as the primary control center for both voluntary and involuntary actions in the body.
Reason (R): The brain is protected by the skull and meninges, which provide physical barriers against external damage.
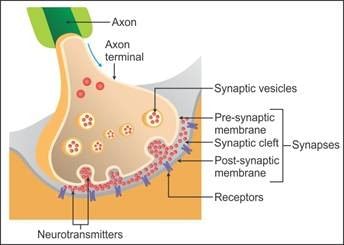
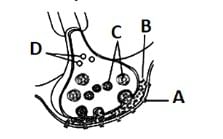
A diagram showing the axon terminal and synapse is given. Identify correctly at least two of A-D:
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding electrical synapses?
What are the short repeatedly branched fibres called?
What does each branch of axon terminate into?
Where are the specific receptors of neurotransmitters present?
Which of the following statements are correct?
(A). Depolarization of an axonal membrane is caused due to rise in stimulus-induced permeability to Na⁺ and its rapid influx into axoplasm.
(B). Diffusion of K⁺ outside the axonal membrane restores the resting potential of the membrane.
(C). Sodium-potassium pump maintains active transport of 2 Na⁺ outwards for 3 K⁺ into the axoplasm across the resting membrane.