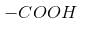Test: Aldehydes Ketones & Carboxylic Acids - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Aldehydes Ketones & Carboxylic Acids
Give the name of the following compound:
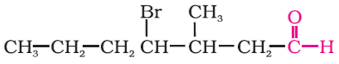
Arrange the following alcohols, hydrocarbon and ether in order of their increasing boiling points Pentan – 1 – ol, n – butane, pentanal, ethoxyethane.
The compound formed as a result of oxidation of ethyl benzene by KMnO4 is
Give IUPAC names of the following compound:
The reagents to bring about the change from but – 2 – ene to ethanal
A strong base can abstract an α – hydrogen from
Which of the following reagents can be used to convert a carboxylic acid directly into its corresponding acid chloride derivative?
The appropriate reagent for the transformation:
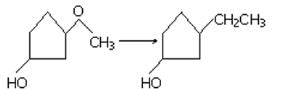
What compound is produced when cyclohexene is treated with concentrated KMnO4?
Arrange the following compounds in decreasing order of their acid strength: i) trichloroacetic acid ii) trifluoroacetic acid iii) acetic acid and iv) formic acid
The combination of a carbonyl group and a hydroxyl group on the same carbon atom is called a __________ group.
CH3CHO and C6H5CH2CHO can be distinguished chemically by:
The common name for pentanedioic acid is:
Which of the following acids does not exhibit optical isomerism?
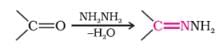
Aldehydes are produced on reduction of the following by DIBAL – H
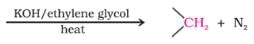
Which of the following statements is not correct?
What compound is produced when (CH3)2CHCH2Br is subjected to the following sequence of steps:
1. Mg, Et2O
2. CO2
3. H3O+?
The oxidation of toluene to benzoic acid can be stopped at the aldehyde stage, to give benzadehyde, The reagent used for the purpose is one of the following.
The oxidation of toluene to benzoic acid can be stopped at the aldehyde stage. The reaction is called?
The compound obtained when acetaldehyde reacts with dilute aqueous sodium hydroxide exhibits:
In Hell – Volhard Zelinsky reaction, halogen reacts with
Many naturally occurring aldehydes and ketones are used in the blending of perfumes and flavouring agents. But the preferred ones are



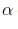 - position.
- position.