Test: Enthalpy Change ∆rH of a Reaction – Reaction Enthalpy (June 14) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Enthalpy Change ∆rH of a Reaction – Reaction Enthalpy (June 14)
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-9) This section contains 9 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. The difference between ΔrH° and ΔrE° (in kcal) for the reaction
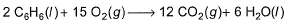
at 298 K in kcal is
Enthalpies of formation of CO(g) , CO2 (g) , N2O (g) and N2O4 (g) are -110, - 393, 81 and 9.7 kJ mol-1. Thus, ΔrU for the reaction at 298 K is,
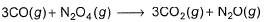
Given
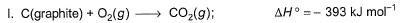
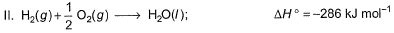
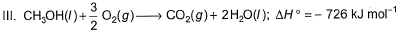
Q. Thus, heat of formation of CH3OH(/)is
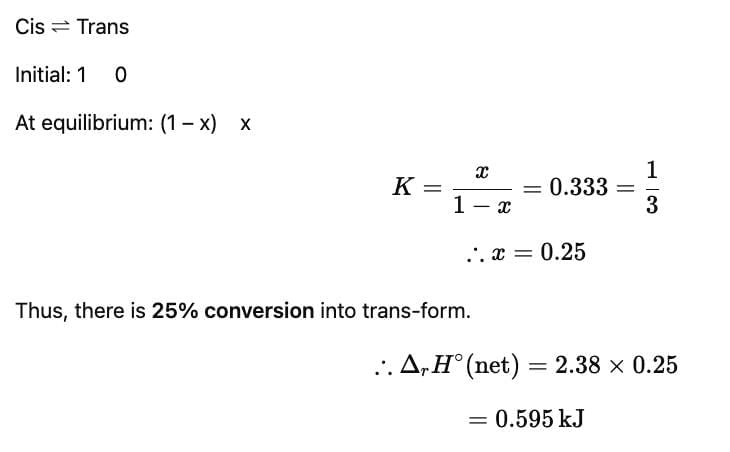
For a gaseous phase reaction
When equilibrium is set up, K = 0.33
Energy involved (in kJ) is
One mole of a non-ideal gas undergoes a change of state (2.0 atm, 3.0 L, 95 K) → (4.0 atm, 5.0 L, 245 K) with a change in internal energy, ΔrE° = 30.0 L atm. The change in enthalpy (ΔrH°) of the process in L-atm is
[IIT JEE 2002]
Direction (Q. No. 10) This sectionis based on statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the code given below.
Q.
Statement I : Based on the following thermodynamic data
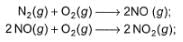
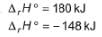
NO2 is more stable than NO.
Statement II : NO (g) is an endothermic compound while, NO2(g) is an exothermic compound.
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-12) This section contains 2 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Given,
Q. Thus, standard heat of formation of
Direction (Q. Nos. 13-15) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given ptions (a),(b),(c),(d).
Based on the following thermodynamic data,
Q. Which oxidising agent will generate the greatest amount of energy per mole of H2(g)?
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 - 18) This section contains 3 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q. How much heat (in kcal) is required to convert 36 g of diamond into graphite?
Based on the following reactions,
Q. Heat of formation of NO2 (in kcal) is ........