Test: Accounting & Financial Management of Banking - 2 - Bank Exams MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Accounting & Financial Management of Banking - 2
A company reports a decrease in cash flow from operating activities and increase in cash flow from investing activities. What can be inferred about the company's fund flow?
Salary for the month of March has been incurred during the month but will be paid in April.
What type of adjustment entry is this?
What type of adjustment entry is this?
Which of the following statement/s is/are correct regarding units of production method?
I. This method is a usage based method.
II. This is a method assumes a higher depreciation charge and a greater tax benefit in the early years of an asset's life
III. The depreciation amount is not based on passage of time but actual use of the asset.
I. This method is a usage based method.
II. This is a method assumes a higher depreciation charge and a greater tax benefit in the early years of an asset's life
III. The depreciation amount is not based on passage of time but actual use of the asset.
According to the Companies Act, What is the interest rate chargeable under Table F for calls in arrears and calls in advance?
Which of the following statements are correct regarding the Password Protection ?
I. Users should ensure that nobody is watching when they are entering password into the system.
II. Users who have been authorised to use the smart cards or private keys should safeguard them carefully as compromising the same could have wide ramifications.
III. Users should change their password regularly.
Which of the following statements is correct
I. The Financial statements of Banking Companies need to be signed by the manager or the principal officer of the company and all the directors when there are fewer than 3 directors in the banking company.
II. The financial statements and auditors' reports of the bank need to be submitted to RBI within 3 months from the end of the period to which it refers.
Consider the following statements and choose the correct answer.
Statement I: A computerized accounting system is that accounting information system that helps in processing the financial transactions events.
Statement II: A computerized accounting system is not as per GAAP( generally accepted accounting principles)
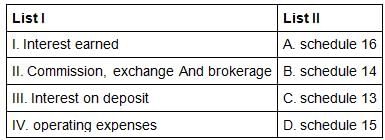
Match the following List I with List II regarding the items in the profit and loss account of the banking company with its schedule.
ABC ltd had advanced a loan amounting to Rs 4,00,000. Invested Rs 5,000,00 in shares. And purchased machinery for Rs 8,00,000. It receives a dividend of Rs 40,000 on investment on shares. The company sold an old machine of the book value of Rs 87,000. And at a loss of Rs 10,000. Compute cash flows from investing activities.
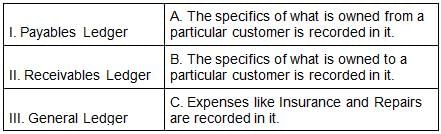
There are three types of ledgers in the accounting system. Match the following with the appropriate option.
Which of the following is not a feature of cost accounting
A furniture manufacturer has received an order to supply 150 identical wooden chairs. The company estimates the material cost at ₹125,000, labor cost at ₹60,000, and manufacturing overheads at ₹25,000. The fixed/non-manufacturing overheads are allocated at 15% of the material cost. What will be the cost of one chair, applying the batch costing system?
From the information given below, calculate the total amount of depreciation charged after two years under Straight Line Method.
Machine I - Original Cost - 45,000, Scrap Value - 5,000 , Number of Years - 10
Machine II - Original Cost - 25,000 , Scrap Value - 2,500 , Number of Years - 15
Following are the differences between GAAP and IFRS. Choose the correct differences.
I. GAAP is a framework based on principles based approach while IFRS is based on legal authority
II. GAAP is more detailed and perspective while IFRS is more high level and flexible
III. GAAP requires more disclosure while IFRS require fewer disclosure
IV. GAAP is more focused on the historical cost of the asset while IFRS allow for more flexible in the valuation of asset
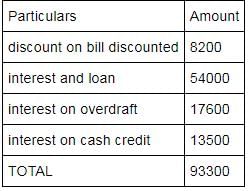
From the following information calculate interest earned under schedule 13
Interest on deposit 12000
Commission (Cr) 12000
Interest and loan 54000
Discount on bill discounted 8200
Interest on overdraft 17600
Interest on cash credit 13500
Sundry Charges (Dr) 10000
A company's actual sales volume for the year was 20,000 units Sales cost per unit is Rs50. The company had prepared a flexible budget based on 25,000 units. The flexible budget showed a variable cost of Rs 40 per unit. The fixed cost was Rs 2,00,000 . The actual variable cost was Rs 7,80,000 and actual fixed cost was Rs 2,30,000. What will be the total flexible budgeted profit?
Which of the following statement/s is/are correct regarding Break-Even Analysis?
I. In narrow sense it is concerned with computing the break-even point
II. In broad sense this technique is used to determine the possible profit/loss at any given level of production or sales.
Identify which of the following is the correct statement given below towards functions performed by the back office ?
Statement I : Its functions include settlements, clearances, record maintenance, regulatory compliance, accounting, and IT services.
Statement II : Undertaking safe custody of valuables, important documents, and securities by providing safe deposit vaults or lockers.
12% Debentures were issued by AAA ltd.
Face value = Rs 10, Payable as under Application Rs 2, Allotment Rs 8
Mohit, a debenture holder failed to pay the allotment money, AAA ltd forfeited the debentures and recorded the same as in the case of shares. What amount should be debited to 12% Debentures during forfeiture?
Which of the following provisions regarding the clubbing of income of minors is true?
I. Clubbing provisions are not applicable in respect of the income of a minor married daughter.
II. The income of the minor will be included in the income of that parent, whose total income, excluding the minor's income, is lower.
What will be the balance as per pass book?
Balance as per Cash Book(Dr.) = 7200
Out of cheques worth Rs.4,000 issued, Rs.2,800 is not presented for payment
Direct deposit by a customer in the bank account - Rs. 3500
Out of cheques worth Rs.4000 sent for bank collection, cheques of Rs.2100 not credited by bank.
Debit side of the Cash book overcast by 200.
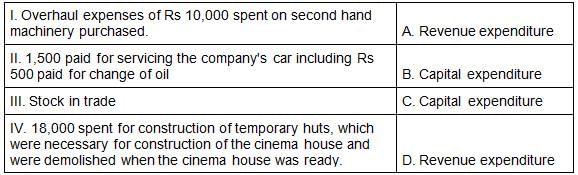
Match the following in reference to the examples of different kind of expenditures.
Which among the following restricts the access to user data by hackers?
Identify which of the following the correct statement is given below.
- Statement I: Accounting principles are static.
- Statement II: Incomes receivable must be added in revenues and incomes received in advance must be deducted from revenues.
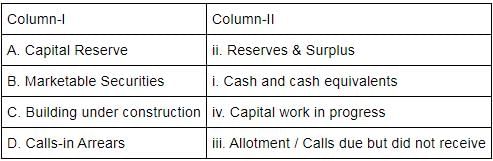
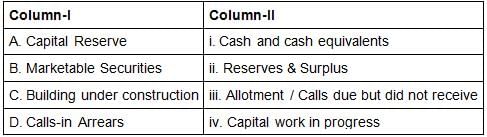
Match the columns with reference to share capital of a company:
Which of the following is the basic difference between financial accounting and cost accounting?
I. Financial accounting aims at rendering information all over while cost accounting safeguarding the interests of the business.
II. Financial accounting reveals profits and losses of the business as a whole while cost accounting shows, by analysis and localisation, the unit costs.
Which of the following statement/s is/are incorrect regarding hedging approach of working Capital Management strategy
I. Under this approach the permanent working capital requirement should be financed by long term funds
II. According to this approach the expected life of an asset is matched with the period of source of finance with which the asset is financed
III. This approach is known as matching approach and self liquidating approach
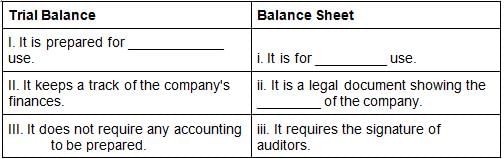
Fill in the blanks about the differences between a trial balance and a balance sheet?
Which of the following statement/s is/are correct regarding marginal costing?
I. Under marginal costing, total costs are segregated into the fixed cost and the variable costs.
II. Only the average variable cost of a unit is considered as its value.
III. Marginal costing involves both cost recording and cost analysis
Which of the following classes is to be shown under the head Share Capital ?
I. Shares in the company held by each shareholder holding more than 5 per cent shares specifying the number of shares held
II. The rights, preferences and restrictions attaching to each class of shares not including restrictions on the distribution of dividends and the repayment of capital
III. The number of shares issued, subscribed and fully paid, and subscribed but not fully paid