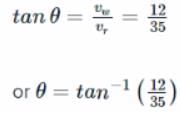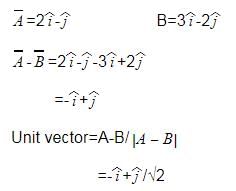Test: Addition Subtraction and Multiplication of Vectors (May 13) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Addition Subtraction and Multiplication of Vectors (May 13)
Which of the following is not a property of a null vector?
Given a + b + c + d = 0, which of the following statements is incorrect?
Two vectors A and B inclined at an angle θ have a resultant R which makes an angle α with A. If the directions of A and B are interchanged, the resultant will have the same
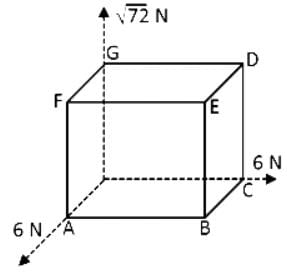
Three forces of magnitude 6 N, 6 N and √72 N act as a corner of a cube along three sides as shown in fig. Resultant of these forces is
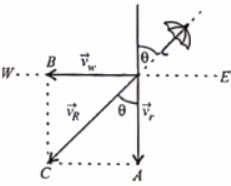
Rain is falling vertically with a speed of 35ms−1. Winds starts blowing after sometime with a speed of 12ms−1 in east to west direction. At what angle with the vertical should a boy waiting at a bus stop hold his umbrella to protect himself from rain?
A cyclist moves along a circular path of radius 70m. If he completes one round in 11s, calculate total length of path.
Find the odd one out:
An object thrown from an aeroplane is an example for
The vector product of parallel vectors is always:
Given,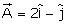 and
and 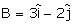 . The unit vector of
. The unit vector of 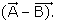 is
is



 as shown in the figure. To protect himself from the rain the boy should hold his umbrella in the direction of resultant velocity
as shown in the figure. To protect himself from the rain the boy should hold his umbrella in the direction of resultant velocity 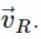 If θ is the angle which resultant velocity
If θ is the angle which resultant velocity 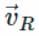 makes with the vertical, then
makes with the vertical, then