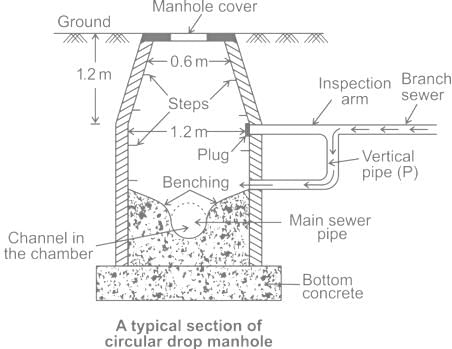
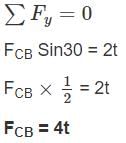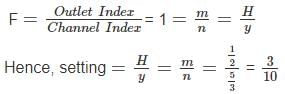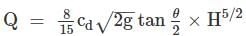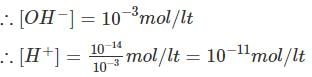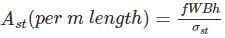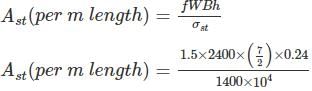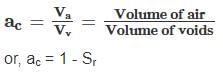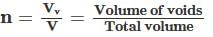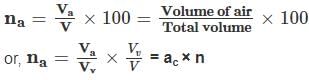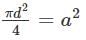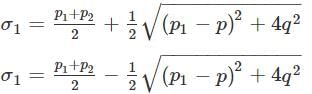JKSSB JE Civil Mock Test - 1 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JKSSB JE Civil Mock Test - 1
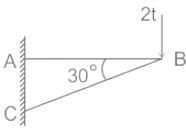
If reduced bearing of a line is N87°W , its whole circle bearing will be:
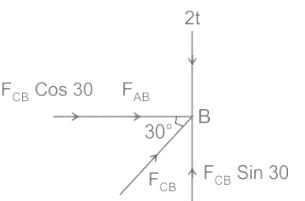
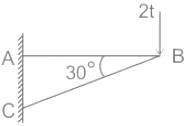
The load shared by the member BC of the structure shown in figure below is :

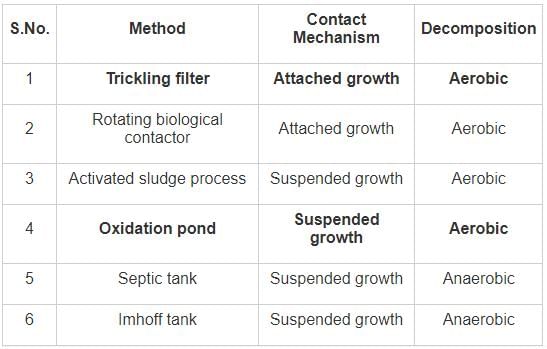
Which one of the following types of samples is relatively employed for the design of waste water treatment plants?
Check rail should normally be provided where the radius is ________ m or less in BG.
The ratio of the water stored in the root zone during irrigation, to the water needed in the root zone prior to irrigation is called:
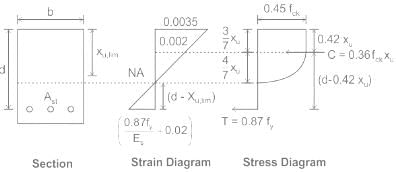
In limit state design of concrete for flexure, the area of stress block is taken as
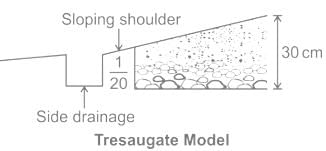
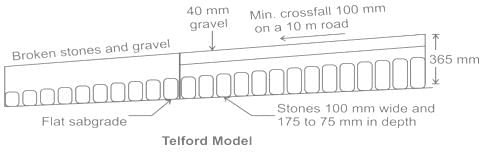
The importance of subgrade drainage and compaction was recognized and so the subgrade was compacted and was prepared with a cross slope of 1 in 36. In which type of Road Construction, the above statement came into picture?
In quality management system, the set of activities which builds confidence of both customers and managers and suggests that all quality requirements are being met is called as
What are the recommended setting options of an adjustable proportional module worked with an open flume orifice type outlet?
In horizontal curves of Railway Tracks, Negative Super elevation means-
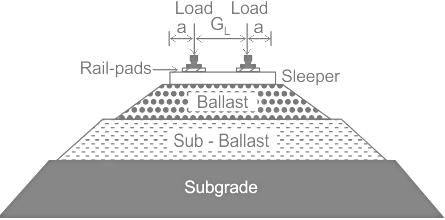
Ballast is used in Railway section to serve as ________.
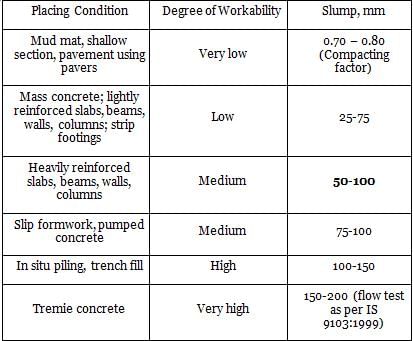
What is the slump of pumped concrete used in heavily reinforced section if the degree of workability is medium as per IS 456-2000 ?
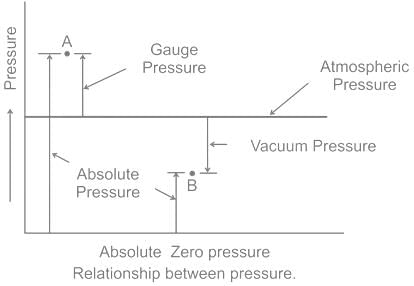
Which of equation represents the correct relation between absolute pressure Pabs, atmospheric pressure Patm, the gauge pressure Pg, vacuum pressure Pvac?
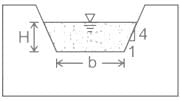
A Cippoletti notch is a trapezoidal notch having inclination of sloping sides as
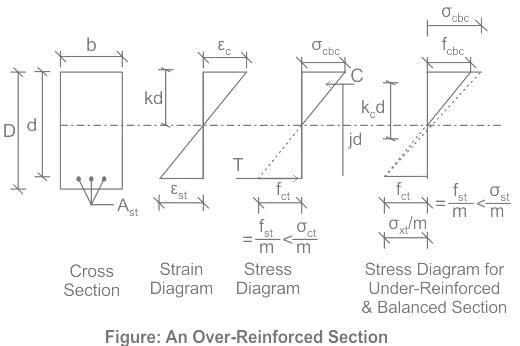
Select the correct statement with respect to an over-reinforced cement concrete section under the working stress method.
The concentration of OH- ion in a water supply is measured as 17 mg / L at 25° C. What is the pH of the water sample?
What is the area of steel required per meter length of longitudinal joint in a rigid pavement of thickness 24 cm with two lanes of total width of 7 m?
Allowable working stress in steel in tension = 1400 kg/cm2
Unit weight of concrete = 2400 kg/m3
Coefficient of friction = 1.5
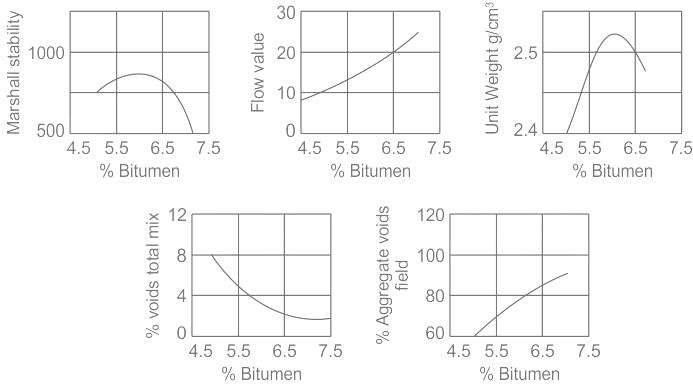
A typical Marshall test graph is shown in the given figure. The variable on the x-axis is % binder content by weight of total mix. The variable on the y-axis for the given graph will be
The relationship between air content of soil (ac) and its degree of saturation (Sr) is expressed as
Two beams, one of circular cross-section and the other of square cross-section, have equal area of cross-section, when this beam are subjected to bending?
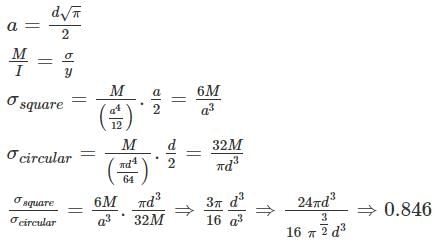
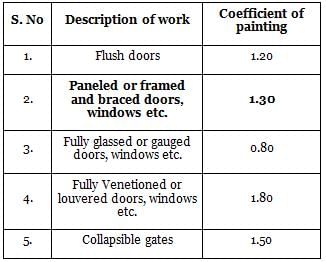
Painting coefficient for measuring the paneled or framed and braced doors , measured flat including chowkats is
If p1 and p2 are the bi-axial normal stresses and q is shear stress on a plane in a strained body then what is condition that both the principal stresses will be of the same sign?
According to BIS method of measurement, the order of the sequence is