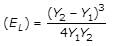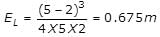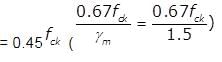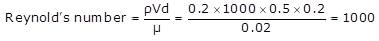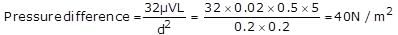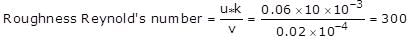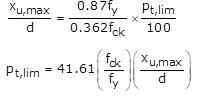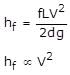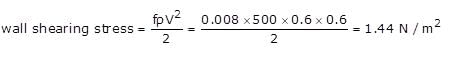JKSSB JE Civil Mock Test - 2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JKSSB JE Civil Mock Test - 2
Fill in the blank given below.
________ means original cost of construction of property whereas _______ means present value of property which may be higher or lower than former.
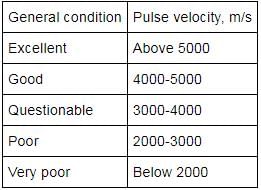
A concrete has a pulse velocity reading as 5500 m/s. The concrete can be classified as,
A sluice gate discharges water into a horizontal rectangular channel with some velocity. Depth of flow before and after the jump are 2m and 5m respectively. Energy loss will be,
The slope at which the sewer is laid should be designed for,
For a rectangular channel of width 'b' and depth of flow 'd', section will be most economical when,
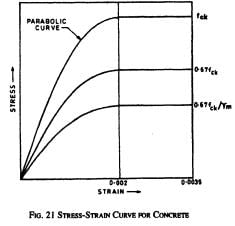
If fck is the characteristic compressive strength of concrete, then the maximum design compressive strength of concrete is,
Quantities for earthwork, damp proof course and plastering respectively are measured in,
What will be the pressure difference in a 5m length of a circular pipe of diameter 200 mm, through which a fluid having viscosity of 0.2 poise and relative density as 0.2, is flowing with velocity of 0.5 m/s?
A fluid having kinematic viscosity of 0.02 stokes is carried by a pipeline. If shear velocity and the average height of irregularities projecting from the surface of the boundary of pipe is 0.06 m/s and 10 mm respectively, roughness Reynold's number will be,
A single room building is 6 m x 5 m. Total centre length of walls which are 30 cm thick is,
If the back bearing of a line is 95o, what will be its fore bearing?
If coefficient of linear expansion is 12x10-6/oC for a steel bar subjected to a temperature raise by 18oC, what will be the temperature strain in it?
As per Indian railways standards in which of the following test a rail specimen should withstand the blow without fracture?
The expression for limiting percentage tensile steel is,
Which of the following should be the minimum depth of ballast BG track?
Which of the following sleepers are used most in Indian railways?
In turbulent flow, if V is the velocity of flow, loss of head is directly proportional to,
What will be annual depreciation, assuming that a property loses its value by the same amount every year?
Which of the following connects the highway with commercial establishments like fuel stations, service stations etc.?
Which among the following is not a mandatory/regulatory sign?
Which of the following is the effect on design shear strength of concrete in the presence of uniaxial compression?
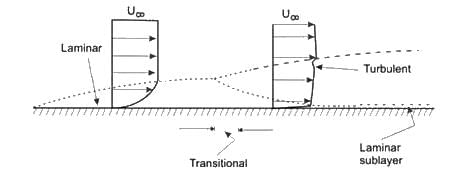
In a boundary layer flow, laminar sub layer can be defined as,
A transverse rigid deformation of pavements that occurs at areas subject to severe acceleration, is known as,
For design by working stress method, what is the permissible stress for Fe 500 grade in flexural tension (in N/mm2)?
Initially the cost of a component is Rs.500000. The salvage value at the end of its useful life of 15 years is 380000. What will be the book value at the end of second year of its useful life, by straight line method?
If for a turbulent flow,
Friction factor = 0.008
Relative density of fluid = 0.5
Mean velocity of flow = 0.6 m/s
What will be the value of wall shearing stress?
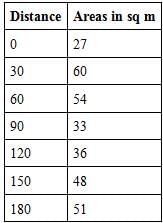
What will be the volume of earthwork in an embankment for which cross-sectional areas are given below at 30 m interval (use prismoidal rule)?