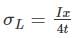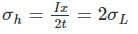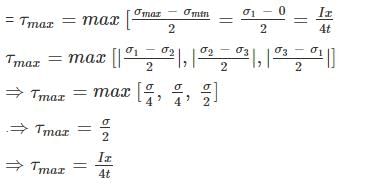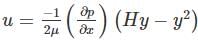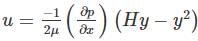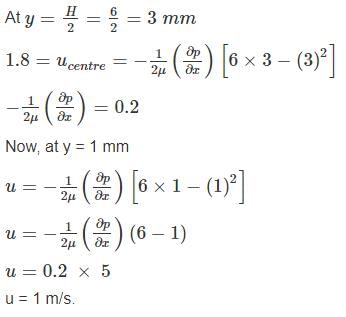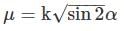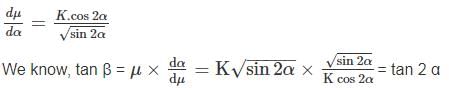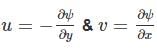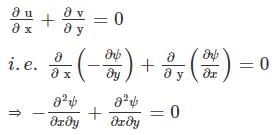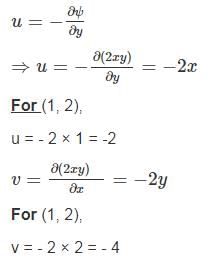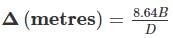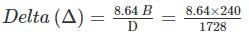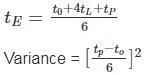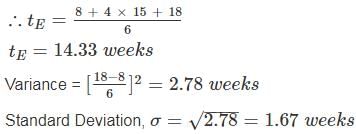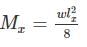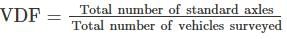JKSSB JE Civil Mock Test - 4 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JKSSB JE Civil Mock Test - 4
When Froude’s number is equal to unity, the flow in an open channel is called
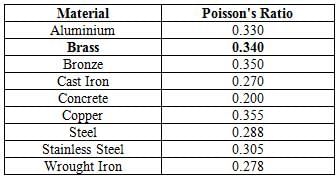
Consider a thin-walled cylindrical vessel having diameter 'x'. What would be the value of shear stress given that it is constrained to internal pressure 'I'? (where t is thickness)
What will be the optimum depth of ballast cushion required for a BG railway track below the sleepers with sleeper density of (M + 5) and bottom width of 22.22 cm?
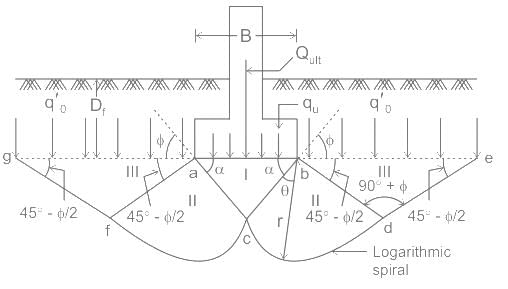
In Terazaghi's theory of bearing capacity of shallow foundation, which of the following zones is assumed to act as if it were part of the footing
The recommended alum dosage for coagulation is in the range of?
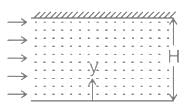
In a laminar flow between two parallel plates with a separation distance of 6 mm, the centre line Velocity is 1.8 m/s. The velocity at a distance of 1 mm from the boundary is:
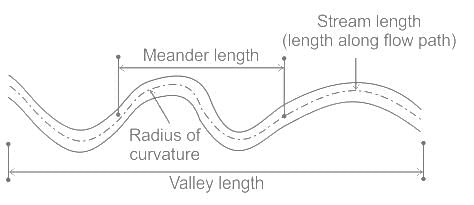
Formation of successive bends of reverse order may lead to the formation of a complete S curve called
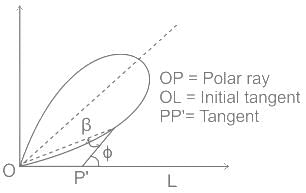
In a lemniscate curve, the angle between the tangent at the end of the polar ray and the tangent at the commencement of the curve (i.e. straight) is
If stream function ψ = 2xy, then the velocity at a point (1, 2) is equal to ________.
If the sewer is to be designed for the non-scouring velocity of 5 m/sec, which among the following material would you recommend?
A light house is visible just above the horizon at a certain station at the sea level. The distance between the station and the light house is 50km. The height of light house is
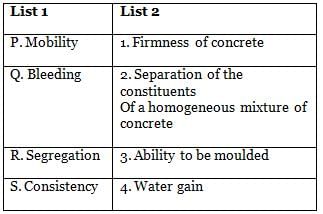
Match the items under List I (Terms associated with placing of concrete) with those under List 2 (Definition of the phenomena). Use codes in lists for matching.
Find the delta for a crop when its duty is 1728 hectares/cumec on the field, the base period for the crop is 240 days.
The Garret diagram is applicable only for channel sections having side slopes of -
The optimistic, most likely and pessimistic time estimates of activity are 8, 15 and 18 weeks respectively. The Probable range of completion time of the activity will be
Arrange the order of permanent adjustments of a theodolite
I. plate level test
II. cross-hair ring test
III. bubble tube adjustment test
IV. spire test
V. collimation in azimuth test
VI. vertical are test
The sag in the dissolved oxygen curve results because of DO is a function of
Which one of the following is a gap developed in the canal bank due to erosion of some portion of the bank?
Which method of contouring is most suitable for hilly terrains?
Which of the following square slab will behave as one-way slab ?
Vehicle damage factor (VDF) as given by I.R.C., is used in
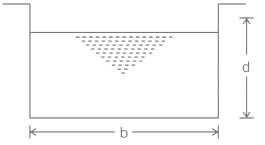
Which of the following represents the correct conditions for maximum discharge through a rectangular section?(Symbols and notations carry their usual meaning)
Which roller is most suitable for the compaction of a gravelly sand mixture with 25% fines?
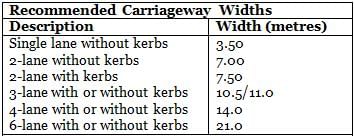
The minimum width recommended for kerbed urban road, so as to give allowance for stalled vehicle is:
In Construction Management, the Critical Path Network helps an engineer
Assumptions made in Euler's theory is/are -
(i) The column is initially straight
(ii) The cross-section is uniform throughout
(iii) The line of thrust coincides exactly with the axis of the column
(iv) The material is homogeneous but not isotropic
(v) The shortening of the column due to axial compression is negligible